Economy of Russia and Economic Crisis
After the breakup of the USSR, Russia's first slight recovery, showing signs of open-market influence, occurred in 1997. That year, however, the Asian financial crisis culminated in the August depreciation of the ruble. This was followed by a debt default by the government in 1998, and a sharp deterioration in living standards for most of the population. Consequently, 1998 was marked by recession and an intense capital flight.
Nevertheless, the economy started recovering in 1999. The recovery was greatly assisted by the weak ruble, which made imports expensive and boosted local production. Then it entered a phase of rapid economic expansion, the GDP growing by an average of 6.7% annually in 1999-2005 on the back of higher petroleum prices, a weaker ruble, and increasing service production and industrial output.
Russia remains heavily dependent on exports of commodities (товары), particularly oil, natural gas, metals, and timber, which account for about 80% of exports, leaving the country vulnerable to swings in world prices. In recent years, however, the economy has also been driven by growing internal consumer demand that has increased by over 12% annually in 2000-2005, showing the strengthening of its own internal market.
There has been a significant inflow of capital in recent years from many European investors attracted by cheaper land, labor and higher growth rates than in the rest of Europe. Amazingly high levels of education and societal involvement achieved by the majority of the population, including women and minorities, secular attitudes, mobile class structure, better integration of various minorities in the mainstream culture set Russia far apart from the majority of the so-called developing countries and even some developed nations.
The world economic crisis is manifesting itself primarily (в первую очередь) in the area of finance (destabilisation of stock markets, bank losses, growing inflation, and rising interest rates). Following the commercial crisis and the fall in demand on the American market, the crisis spreads to the “new industrial countries”, where production starts coming to a halt (остановка). The contraction (сокращение, decline) in sales and in world industrial output leads to new collapses on the world’s stock (ценные бумаги) markets and problems from inflation to stagflation (стагфляция). Oil prices are falling (plumping) down, the number of unemployed is rising, and a massive decline in consumption takes place.
For the present, the impact of the crisis on the economy of Russia remains insignificant, affecting primarily the financial sphere. The economy of the Russian Federation is continuing to grow, but the country’s consumer market is under pressure from inflation. This is preparing the way for national commercial and mortgage crises. The advent (приход) of the global crisis in Russia will be delayed, probably occurring later than in the “new industrializing countries” and in the European Community. The decline of world oil prices will lead to a crisis in Russia’s national economy, to a collapse on the share (акции) market, to a fall in industrial production and an increase in unemployment, to a strengthening of inflation, and to sharply reduced consumption. The global crisis will be especially severe (жесткий) for Russia due to the orientation of the country’s economy to raw materials exports. The emergence of the country from the crisis will be associated with major structural changes in the economy, with social unrest, and with a decline in the role played by the raw materials corporations.
Похожие работы
... , no organisation including the IMF would have been looking forward to further negotiations with such countries and provided them with credits. But the worst thing is that the economic crisis entailed the political crisis. Because, as one of the most famous writers, philosophers and politicians of the Renaissance Niccolт Machiavelli said, "the only way to reach prosperity of the country is to ...
... end of an age of raw exports conducted in their most primitive form, however, the Russian metal industry is given an opportunity to participate in the international division of labor on equal basis and to reach a qualitatively new level of production. The share of chemicals made 9.6 percent. Mineral fertilizers still remain a key export item in the industry. Export volumes of mineral fertilizers ...
... the same time, for eign reserves held by the CBR were so low that the government could no longer defend the currency by buying rubles. Three components fueled the expectations of Russia’s impending devaluation and default. First, the Asian crisis made investors more conscious of the possibility of a Russian default. Second, public relations errors, such as the publicized statement to government ...
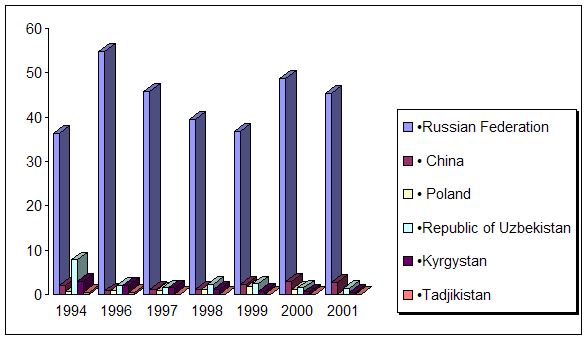
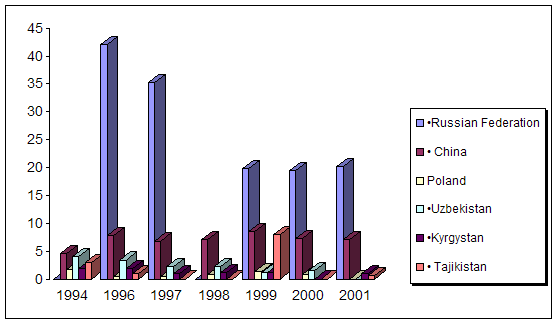
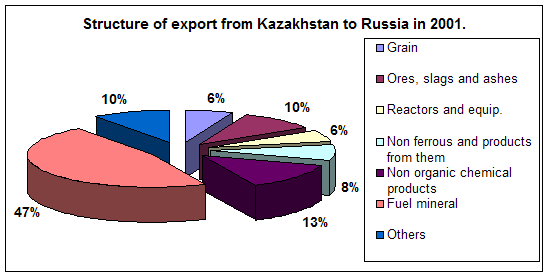
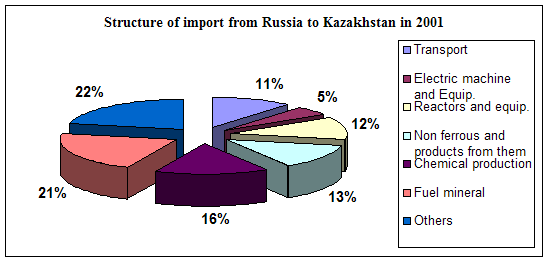
... course of republic. A complex of the reasons conditions and factors having not tactical, but basic essence and long-time character stipulates it. Today common balance of mutual relation between Kazakhstan and Russia has positive character, as consider each other as the strategic partners and it establishes the important premise for their mutual cooperating in the field of policy, economy, ...

0 комментариев