Навигация
Basis of the ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility
1.2. Basis of the ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility
The basis of occurrence of the ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility of the subject of the international law is the fulfilment by him(it) of an international offence.
The international offence is an action or inactivity of the subject of the international law infringing norms of the international law and the international obligations, íàíîñÿùèå to other subject either group of the subjects of the international law or all international community as a whole damage of material or non-material character (for example, sertificates(acts) of aggression, illegal restriction of the sovereignty, encroachment on territorial integrity and political independence, infringement of the obligations under the agreements and other.) 1. For want of it the responsibility arises, as a rule, only for want of availability ïðè÷èííîé of communication(connection) between illegal behaviour of the subject and caused damage.
Thus, components of an international offence attracting behind self the ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility, are: action or inactivity of the subjects infringing norms of the international law; âìåíÿåìîñòü of an offence of the subject of the international law; causing of damage or âðåäà to other subject or group of the subjects of the international law.
Any references of the state to the national laws and rules in the justification of the behaviour which has resulted(brought) in infringement of norms the international laws and drawing of damage or âðåäà, are inadmissible. The references to ignorance of norms of the international law or on wrong their interpretation and application also are inadmissible. Practically all international offences are made consciously, purposely, is guilty. It is impossible to justify aggression of USA against Ãðåíàäû (October, 1983) and Libya (March, 1986), íàëåòû of aircraft ÞÀÐ on cities Çàìáèè and Çèìáàáâå (May, 1986), destruction by Israeli aircraft of iraq centre of nuclear researches (June, 1981), exhibiting by American mercenaries of mines in waters and ports of Nicaragua and other similar actions by the references to necessity « protection of life » or «interests». Especially, they cannot be issued for the sertificates(acts) of «self-defense» 1.
The illegal actions or inactivity presenting(causing) to occurrence of the ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility the subjects of the international law can be made by state bodies (without dependence from their rule(situation) in system of public authorities and management), officials of the state acting on his(its) assignment(order) or from his(its) name, and also special bodies of the states allocated imperous authorities and acting from his(its) name. For example, responsibility for grab by the Israeli military ships of a greek vessel (the summer 1984) should bear government of Israel. The responsibility of the state can come(step) behind acceptance of the law or other normative sertificate(act) contradicting to norms of the international agreement, which participant it is by, or, on the contrary, for íåïðèÿòèå of the law, which it was obliged to accept according to the international obligations and which would prevent ïðîèñøåäøåå illegal event or action.
The responsibility of the state arises because of inactivity of government bodies in cases, when the duly interference of authorities could prevent wrongful actions. USSR in USA for want of connivance of the American official persons is known, for example, numerous cases of violence and even the armed attacks on diplomatic representations. In such cases the state was born by(with) ё ò the responsibility for criminal actions of the persons from among the citizens both foreigners and their organizations both for the foreigners and for actions (and inactivity) bodies, which have not prevented illegal actions, though could and should it make.
The responsibility of the state «Х» can arise and as a result undertaken on it(him) (or from it(him)) territory of illegal actions of the foreign state or his(its) bodies against the third state or group of the states. For want of it if these actions of the foreign state are made with is driven also of consent of the state «Х», it is the accomplice of illegal actions of the foreign state. However, if such actions are made without the knowledge of the state «Х», it bore ё ò the responsibility only in case his(its) bodies have not displayed « necessary vigilance » and these illegal actions of the foreign state did not stop. Is differently solved the problem concerning the states granting the territory for creation of foreign military bases or accommodation of the weapon: their ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility for all possible(probable) dangerous consequences comes(steps) by virtue of the most legal fact - sanction to creation of military base or accommodations of the weapon.
The ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility of the state can arise and for want of increase of authorities by state bodies or officials of the state, therefore can be has put ё í damage to the foreign state or his(its) natural or legal persons. In particular(personally), the state should compensate damage for want of interference in the high sea in case of failure of an oil tanker under condition of, if the measures undertaken by him(it), will exceed those, which were reasonably necessary for prevention, reduction or removal(elimination) ñåðü ё heat and real danger of pollution of coast нефтью1.
For actions of state bodies, military parts and divisions during war, when as a result of these actions the norms of the Geneva conventions about protection of victims of war of a 1949 and other international conventions, ðåãëàìåíòèðóþùèõ of a means and methods of management of struggle are infringed, the responsibility was born by(with) ё ò the state, which posesses these bodies, military parts and divisions. The state should accept legislative, administrative and other measures by, that the laws and customs of war, çàêðåïë ё ííûå in the acting conventions and agreements, were punctually executed by all state bodies, military connections and military men.
The ìåæäóíàðîäíî-legal responsibility of the subjects of the international law can come(step) not only by virtue of infringement of norms of the international law or obligations by agreement, but also for harmful consequences of lawful activity. She(it) can come(step) for want of drawing of a material loss by a source of increased danger, use or which application is forbidden by the international law (so-called responsibility for risk).
Sources of increased danger are, for example, court with nuclear power installations(aims) (ßÝÓ) and space objects started in space space. Court with ßÝÓ carry out the activity within the framework of freedom of navigation being a main part of freedom of the high sea, and the space objects can be started according to the Agreement for principles of activity of the states on research and use of space space, including the Moon and other heavenly bodies, 1967.
As in first and in the second cases speech èä ё ò about use of sources of increased danger, the states in the contractual order have agreed to recognize compulsion of reimbursement of the material loss which has arisen not in connection with any international offence, and it is exclusively(extreme) by virtue of the fact of causing of such damage (responsibility without fault).
In the Convention about the international responsibility for damage, reasons ё ííûé by space objects of a 1972 is spoken, that the starting state « was born by(with) ё ò the absolute responsibility for payment of indemnification for damage, reasons ё ííûé by his(its) space object on a surface of the Earth or air vessel in a floor ё those » 1.
Похожие работы
... of that subject of innovative activity on which decision the further destiny of the project [36] depends. So, in chapter 1 of degree work theoretical bases of innovative activity in public health services have been considered, and, the basic terminology is entered, the economic reasons of innovations and legal maintenance of innovative activity are described. From chapter 1 it is possible to draw ...
... . Since 1945, there have been 48 United Nations peacekeeping operations. There are currently 16 under way. Thirty-five peacekeeping operations were created by the Security Council in the years between 1988 — when UN peacekeeping operations were awarded the Nobel Peace Prize — and June 1998: …in Africa In Angola, UN mediation led to the 1994 peace accord and to the installation of a government ...
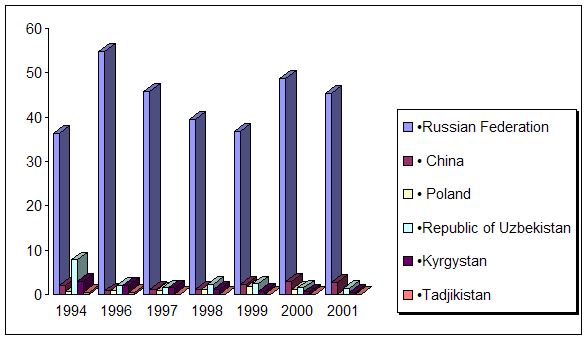
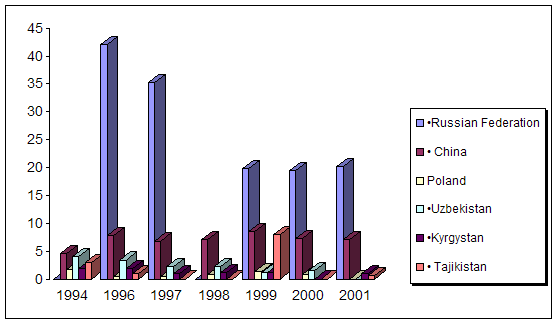
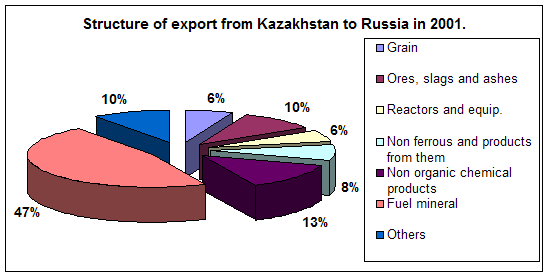
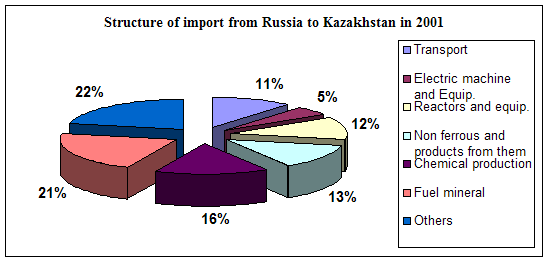
... course of republic. A complex of the reasons conditions and factors having not tactical, but basic essence and long-time character stipulates it. Today common balance of mutual relation between Kazakhstan and Russia has positive character, as consider each other as the strategic partners and it establishes the important premise for their mutual cooperating in the field of policy, economy, ...
... income from sales minus production expenditures of sold goods. This index allows to analyze the effectiveness of production activity of the enterprise; c) profit (loss) from main activity (operational profit or operational loss) – gross profit from sales minus management costs and sales costs. This index reflects the influence of management and sales costs to financial sales result; d) profit ...



0 комментариев