Навигация
Контактная информация
5. Контактная информация
Координатор конкурса: Климик Геннадий Иванович, председатель комитета по информационной политике и работе со СМИ.
телефон: 517-558, 465 (внутр.), электронная почта: klimik@tomsk.gov.ru
Приложение
к Положению о проведении
областного творческого конкурса
журналистов на соискание грантов
Губернатора Томской области
АНКЕТА
участника областного творческого конкурса журналистов
на соискание грантов Губернатора Томской области
| Ф.И.О. участника | |
| Дата рождения | |
| Образование | |
| Стаж работы в СМИ | |
| Наименование средства массовой информации | |
| Юридический адрес средства массовой информации | |
| Фактический адрес, тел./факс, |
Руководитель СМИ
«___»___________2010 г.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
В заключение дипломной работы можно подвести итоги исследования, определить их значение для решения актуальных теоретических и практических задач. В рамках работы, с целью проанализировать информационное пространство Томской области, было проведено социологическое исследование медиа-пространства Томской области. Учитывая результаты социологического исследования, были выработаны рекомендации для работы по оптимизации ПР-деятельности Департамента по информационной политике и работе с общественностью, и оптимизации основных направлений совершенствования информационной политики Администрации Томской области.
Совершенствование информационной политики Администрации Томской области является особо актуальной задачей, решение которой выступает важным условием ведения политики Администрации в целом.
В данной дипломной работе были рассмотрены такие понятия как информационная политика, средства массовой информации, информационное пространство, государство, ПР-служба, медиа-карта. Данные понятия являются основой для изучения темы государственной информационной политики. Так же были изучены теоретические аспекты государственной информационной политики, включающие сущность и структуру информационной политики органов власти, особенности работы государственных служб по связям с общественностью со СМИ, отношения государства с медиаструктурами.
В аналитической части ВКР была дана общая характеристика Департамента по информационной политике и работе с общественностью, ее структура и виды деятельности, целевые аудитории, информационно-коммуникационные каналы, а также направления PR-деятельности Департамента. Были охарактеризованы основные направления информационной политики Администрации Томской области.
В соответствии с поставленной целью дипломной работы - разработка проектных рекомендации по направлениям совершенствования информационной политики Администрации Томской области, был проведен теоретический и аналитический анализ материалов, посвященных проблеме формирования и совершенствования информационной политики органов государственной власти. В качестве проекта была разработана Концепция информационной политики Администрации Томской области. Концепция определяет цели, задачи государственной информационной политики Администрации Томской области, результаты воздействия информационной политики на социально-экономическое, политическое и культурное развитие Томской области. Концепция должна создать основу для подготовки перспективных и календарных планов мероприятий по реализации информационной политики Администрации Томской области, разработки нормативных документов, целевых программ и проектов в сфере, связанной с созданием, преобразованием и потреблением информации. Данная Концепция может стать основополагающей для ведения информационной политики Администрации Томской области и рассмотрена руководством Департамента по информационной политике и работе с общественностью на внедрение.
В работе представлен еще один проект, направленный на совершенствование информационной политики Администрации Томской области. Разработано Положение о проведении Областного творческого конкурса для журналистов на соискание грантов Губернатора Томской области, преследующее цель обеспечения конкуренции на рынке печатных и электронных средств массовой информации в части всестороннего и объективного информационного обеспечения деятельности Администрации Томской области, установления эффективных взаимоотношений между властью и журналистским сообществом области, стимулирования мастерства журналистов.
Реализация предложенных основных идей, и практических мероприятий, для совершенствования информационной политики Администрации Томской области должна способствовать достижению следующих результатов:
1. Создание системы регулярного информирования населения органами государственной власти о политической и социально-экономической жизни через средства массовой информации и другие формы распространения информации.
2. Создание основы для подготовки перспективных и календарных планов мероприятий по реализации информационной политики Администрации Томской области, разработки нормативных документов, целевых программ и проектов в сфере, связанной с созданием, преобразованием и потреблением информации.
3. Своевременная коррекция информационной политики Администрации и ее положительного имиджа;
4. Формирование единого информационного пространства на территории Томской области
5. Установление отношений между органами государственной власти и Средствами Массовой Информации Томской области. Выделение грантовой поддержки со стороны властей на развитие районных СМИ.
6. В сфере связей с общественностью – обеспечение максимально высокой степени прозрачности и открытости деятельности органов государственной власти, создание системы эффективной «обратной» связи с населением. Совершенствование форм, методов и PR-технологий информационно-аналитической деятельности Администрации.
Практические рекомендации, представленные в работе могут быть полезны для совершенствования информационной политики органов государственной власти других регионов.
СПИСОК ИСПОЛЬЗОВАННЫХ ИСТОЧНИКОВ
1. Капитонов Э.А. Управление общественными отношениями: уч. Пособие/ Э.А. Капитонов, Г.П. Зинченко, А.Э. Капитонов. – 2 изд. – М.: Издательско-торговая корпорация «Дашков и К», Ростов н/Д: Академцентр, 2009. – 386с.
2. Политические коммуникации: уч. пособие для студентов вузов/ Петрунин Ю.Ю. и др. – под.ред. А.И. Соловьева. – М: Аспект Пресс, 2004. – 332с.
3. Лукиева Е.Б. Теория и практика связей с общественностью: Учеб. пособие. – Томск: Изд - во ТПУ, 2006. - 146 с.
4. Ольшанский Д. В. Политический PR. - СПб.: Питер, 2003. - 544 с.
5. Почепцов Г. Г. Паблик рилейшнз для профессионалов. - М.: Рефл-бук, Киев: Ваклер, 2000. - 624 с.
6. Информационная политика. Учебник / Под общ. ред. В. Д. Попова. М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2003.
7. Информационная политика. Учебник / Под общ. ред. В. Д. Попова. М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2003.
8. Шевченко А.В. Государственная служба и СМИ: правовое регулирование отношений: Учеб. пособие. - М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2007.
9. Попов В.Д. Тайны информационной политики: социальный психоанализ информационных процессов. М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2003.
10. Коновченко С.В., Киселев А.Г. Информационная политика в России. Монография. – М.: РАГС, 2004. – 528с. –
11. Коновченко С.В. Общество-СМИ- власть. – Ростов-на-Дону: СКАГС, 2001.
12. Алешина И. В. Паблик рилейшнз для менеджеров. - М.: ИКФ, 2003. - 480 с.
13. Концепция государственной информационной политики Российской Федерации, 1998г.
14. Г.В. Лысенко Взаимодействие власти и СМИ: стратегия и технологии ее реализации (региональный аспект) // Социологические исследования, № 4, Апрель 2008, C. 73-77
15. Попов В.Д. Информациология и информационная политика. — М., 2003]
16. В. А. Ядов. «Социологическое исследование; методология, программа, методы» / В. А. Ядов. — Самара : Самарский университет, 1995. — 331 с.
17. Н.А. Колодий. «Социология массовой коммуникации часть 2» : учебное пособие / Н.А. Колодий. – Томск: ТПУ. – 116 с.
18. Связь с общественностью в политике и государственном управлении. / Под общ. ред. В.С. Комаровского. - М. : РАГС, 2001.- 520 с.
19. Чумиков А.Н. Связь с общественностью: учеб.пособие. - М.Дело,2000 г.
20. Социальная информациология. Словарь./ Сост. Л.И.Мухамедова. Под общ.ред. В.Д.Попова. -М.: РАГС,2006.
21. Нисневич Ю. А. Информация и власть. М., 2000.
22. Анникова В. А. Информационная политика в системе властных отношений: региональный аспект. Кемерово, 2000.
23. Попов В.Д. Государственная информационная политика: состояние и проблемы формирования, М., 2002
24. Манойло А.В. Государственная информационная политика в особых условиях: Монография. — М.: МИФИ, 2003
25. Дзялошинский И.М. СМИ, власть и гражданское общество в регионе. — М..2002. - 43 с.
26. Пашенцев Е.Н. ПР: от бизнеса до политики – м.: 2000
27. Почепцов ГГ. Информационные войны. Киев. 2000
28. Мирошниченко А.А. ПР в общественно-политической сфере – М.: 1998
29. Королева В. Из жизни властей: четвертая надеется на первую // Советник – 2009. - № 3, с.22-25
30. Русаков А.Ю. Связи с общественностью в органах государственной власти
31. Сибирцева Ж.Е. Особенности PR деятельности в государственном учреждении// Актуальные проблемы гуманитарных наук. Труды IV международной научно-практической конференции, с. 337-340
32. Попов В.Д. Социальная информациология и журналистика: Учебное пособие. - М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2007. - 336 с. –
33. Стратегия развития информационного общества в Российской Федерации. № Пр-212 // Российская газета. 2008, 11 февраля.
34. Синяева И.М. Сфера PR в маркетинге: уч. Пособие/ И.М. Синяева, В.М. Маслова, В.В. Синяев – М.: ЮНИТА-ДАНА, 2007.-383с.
35. Отчет о работе Департамента по информационной политике и работе с общественностью Администрации Томской области за 2008, 2009г.
36. Политические коммуникации: уч. Пособие для студентов вузов – М.: Аспект Пресс, 2004. – 332с. –
37. Чумиков А.Н., Бочаров М.П. Связи с общественностью: теория и практика: уч. Пособие – 4е издание. – М.:Дело, 2007. -552с. –
38. Мандель Б.Р. PR: методы работы со средствами массовой информации: Учеб.пособие. — М.: Вузовский учебник, 2009. — 205 с.
39. Бюрократия и власть в новой России: позиция населения и оценки экспертов / Аналитический доклад / Институт социологии РАН. М., 2005.
40. Руководящие принципы политики совершенствования информации, являющейся общественным достоянием, создаваемой государственными органами, подготовлены Полом Ф. Улиром. Париж, 2004
41. Концепция ФПЦ «Развитие телерадиовещания в Российской Федерации на 2009–2015 годы». URL: http:www.cnews.ru
42. Федеральная целевая программа «Электронная Россия на 2002–2010 годы». Правительство РФ. М., 2001
43. Законодательство Российской Федерации о средствах массовой информации. М., 1996.
44. www.tomsk.gov.ru – официальный сайт администрации Томской области
45. www.kress.tomsk.ru – официальный сайт губернатора Томской области
46. www.novotomsk.ru - информационно-аналитический портал Администрации Томской области
47. The free encyclopedia [Electronic resource]: http://www.wikipedia.org
48. Free management library [Electronic resource]: http://managementhelp.org/blogs/crisis-management/2010/04/09/trial-by-media-dos-and-donts
49. http://www.mediarelationsblog.com/
50. Nonprofit Newswire [Electronic resource]: http://nonprofitnewswire.com
51. Make Me Media Savvy: The Art of Working with the Press [Electronic resource]: http://makememediasavvy.com
Приложение_А
(обязательное)
Peculiarities of government PR Agencies’ work with Mass Media
(заголовок раздела)
Part__1___
(номер раздела)
Студент ___11150 _______________ Е.В. Нисина
(номер группы) (подпись)
_______________
(дата)
Консультант кафедры КТЛ
доцент, к.ф.н. ______________ Т.В.Конюхова
(должность, ученая степень, звание) (подпись)
_______________
(дата)
Консультант-лингвист __ АЯБК___
(аббревиатура кафедры)
старший преподаватель_ ____________ Ю.В.Фалькович
(должность, ученая степень, звание) (подпись)
_____________
(дата)
Tomsk 2010
Peculiarities of governmental PR agencies interaction with Mass Media is urgent topic under study in terms of information policy research. The main problem of interaction between authorities and mass media is difference in aims of informing society. It is extremely important for the state that the information on public institution activity had a positive orientation taking into consideration problem of political stability maintenance in a society. The journalist, publishing exposing materials, often works on his own image. As a rule, for the journalist negative information which, undoubtedly, attracts much more attention from read will be the most interesting and sensational. Government services employees of public relations face necessity of this dilemma solution in their daily work.
Governmental PR agencies create information occasions where mass media are used, that help agencies provide a society with news, form «the public agenda». Mass media regularly use press releases, material prepared by governmental PR agencies.
There are a lot of ways to attract attention of the press. All mass media are ready to place mere information materials even if they treat them differently because of distinctions in the editorial policy and habits of their basic audience. The press always welcomes any news material if only this material was authentic and issued in time.
The press also publishes articles, correspondence and comments which give the background information to news, or articles and essays on the topic of the day or the general character. There are ample opportunities of cooperation of governmental PR agencies with journalists.
There is special division in the governmental PR agencies that is engaged in the given direction of activity. As a rule, it is called the PR Department (or Mass Communications Department) that deals with mass-media or the PR agency. For the PR agency mass media are both audience and tool that requires specific treatment.
A good, solid media team includes three important roles: a media coordinator, a writer, and a spokesperson. Each is critical to the others, and each is also vital independently to the process of effective media management. Roles may overlap, and often can be handled by the same person, but each position must be covered. [47]
The Media Coordinator
The media coordinator must be someone who is personable, can succinctly articulate the issues, and is willing to spend a great deal of time on the telephone. This person makes sure press releases go out on time, keeps media lists updated, makes press calls, and works actively behind the scenes during events.
The media coordinator should become as well-known behind the camera as the organization's spokesperson is in front of it. One person handling press calls can cultivate important relationships with assignment desk personnel, news producers, and camera people. These people are key to getting the coverage of events you need, and the kind of coverage you want.
The Spokesperson
While the spokesperson must be someone who is articulate, he should also be more than that. He should be a good listener, have camera presence, be well-informed about your issue, be able to think quickly on his/her feet, have credibility, be able to develop a good rapport with a reporter, and be intuitive enough to know when a reporter is not friendly.
The Writer
Finally, the writer creates the undergirding for all your press events. Clear, concise, effective writing is essential. Because someone is articulate does not mean he/she can write. Have a good editor available to "tighten up" news releases. Everything that is written and released must reflect accurately the position of your organization. Make sure more than one set of eyes from the media team reviews what goes out.
Governmental PR agencies often use the following forms of media: [48]
• Preparing and distributing of press releases containing information about new events, structural changes in government and administration; about public presentations in the media by administration management.
• Meeting with reporters. This is one of the forms of press-service external and internal life. Meetings are held regularly in the daily activities.
• Organization of “round tables” - one of the forms of joint discussion of ideas, issues and situations relevant to the general public;
• Press conference. It may be necessary to find out the outstanding issues with the public and attracting its attention to solving any problem. In this case, use a press conference, inviting representatives of the media.
• Briefings. The briefing is a meeting of leaders of administration briefly with reporters, inviting representatives of other government bodies. This is the same press conference, but without comment. Briefings are usually arranged in cases of emergencies, public scandals, to give an explanation of what occurred, its causes, to prevent possible.
• Organize regular presentations of management staff in the media. Typically, in the governmental PR agencies from Russian and foreign media have been a number of requests for interviews. Of course, it is impossible to meet all of them, but you must try to make sure that not a single request, not a single proposal has been left out;
• Information exchange. One of the main tasks of the governmental PR agency is to turn the media into the ally. [30, p.55]
Governmental PR agency bases its work with the media conversationally on cooperation and mutual responsibility. Agreement can be documented or be informal, verbal agreements, but, nevertheless, be respected in any case.
One of the principles of work with the media is the flexibility and adaptability to the situation. As governmental PR agencies tend to be widely known, you need a media plan and a comprehensive program of PR-support.
Forming relationships with the media, the service should develop a common policy of these relations. On the one hand, it must determine the rules of providing information for the media, on the other hand - the rules of collection and analysis of information already released by the media for the public. Specialists of the department are constantly monitoring communications in print, radio and television stations, daily press reviews are preparing to lead the administration, assess the results of feedback with target audiences, answer questions, complaints and statements, perform a disproof.
Media in terms of their typological features and capabilities of reaching target audiences
Information space of society is characterized by mass communication, including the mass media, publishing, film, multimedia communications, the Internet.
Journalism is a community of professional multidisciplinary activity of collection, processing and regular dissemination of relevant political, economic and social information through print, radio and television.
Since the public has been interested in reliable information, journalists tend by any means to obtain it, that ultimately leads to misunderstandings, conflicts with the authorities and legislative bodies. Journalists tend to strive to achieve pluralism, development of democratic principles, forms and methods of work with the audience.
Journalists always have responsibility to the readers, listeners and viewers, as well as to society as a whole for the content of messages for informing the audience about the current issues of interest to society. Implementation of citizens rights to information is the primary responsibility of journalists. It is not allowed to use media as the detriment of the moral interests and rights (personality, interests of the state, society, promoting war, violence, ethnic and religious intolerance, manipulation of public opinion).
Mass media is the independent industry, aimed at shaping public opinion, using organizational and technical systems that ensure the quick transfer and mass reproduction of words, imagery and music information. [49]
Mass media are one of the most characteristic features of modern civilization. People are united into one global community with the help of mass media. People can learn about what is happening in the world very fast using mass media. The mass media include newspapers, magazines, radio and television.
Mass media denotes a section of the media specifically designed to reach a large audience. The term was coined in the 1920s with the advent of nationwide radio networks, mass-circulation newspapers and magazines. However, some forms of mass media such as books and manuscripts had already been in use for centuries.
Mass media includes Internet media (like blogs, message boards, podcasts, and video sharing) because individuals now have a means to exposure that is comparable in scale to that previously restricted to a select group of mass media producers. The communications audience has been viewed by some commentators as forming a mass society with special characteristics, notably atomization or lack of social connections, which render it especially susceptible to the influence of modern mass-media techniques such as advertising and propaganda.
Mass media can be used for various purposes: [49]
· Advocacy, both for business and social concerns. This can include advertising, marketing, propaganda, public relations, and political communication.
· Entertainment, traditionally through performances of acting, music, and sports, along with light reading; since the late 20th century also through video and computer games.
· Public service announcements.
The major institutions of media industry information included press, radio and television. The media of Russia refers to print, broadcast and online media in Russia. [34, p.82] A selection of different medias is wide and diverse. According to the Russian Ministry of Press, the country has almost 37 thousand media outlets, including over 22 thousand newspapers and 12 thousand magazines. In audiovisual media, there are over three thousand television channels and two thousand radio channels registed. According to Freedom House, the Russian government owns two of the 14 national newspapers, 60 percent of newspapers, and in whole or in part, all six national television stations.
The press
Russia has very wide range of newspapers, over 400 daily, for every field. However, the consumption of serious newspapers is declining. A newspaper is a publication containing news and information and advertising, usually printed on low-cost paper called newsprint. Newspaper is a publication issued periodically, usually daily or weekly, to present information about current events. The newspaper articles give much more information about events. That is the main advantage of newspapers.
Newspapers cover more stories than any other news media does. They also cover stories in great detail. However, the newspapers present information later then radio or TV. The great advantage of newspapers over radio and TV is that they can report stories in depth. Readers can skip items that don’t interest them. Newspapers also can print certain material that appeals to only a small percentage of readers.
Newspapers differ according to: • frequency - daily, weekly, monthly, there are also morning and evening. Daily newspapers provide operational news material information, whereas weekly and monthly magazines and newspapers provide the material for analytical assessments; • scale - central, national (federal), regional, national, local, regional, municipal, district, departmental; • special purpose-oriented - sectoral, departmental, corporate, professional
A magazine is a periodical publication containing a variety of articles, generally financed by advertising and/or purchase by readers. Magazines are typically published weekly, biweekly, monthly, bimonthly or quarterly, with a date on the cover that is in advance of the date it is actually published. Magazines fall into two broad categories: consumer magazines and business magazines.
Radio
Radio has a complex of unique properties that make it publicly available. People listen to radio, doing other work while constantly receive comprehensive information about all events, it is - and news, and entertainment, and theater, and the market. Clarity, simplicity, and at the same time, the emotion of the living word allows the radio to enjoy continued appreciation of the audience.
Radio is generally the first of news media to report a local story or a news service bulletin. Most stations present regular news bulletins every half-hour or hour. The national radio broadcast major news events. However, most radio news bulletins do not report the news in detail. Radio also provide weather forecasts and traffic information.
Unlike newspapers and magazines radio comes to our house, living in a human voice, able to transmit news, state prices and market conditions in the markets of the world, the problems of commerce and business in the country. Radio allows you to preserve information on magnetic tape in order to be able to return to the true facts liking the program. Radio is able to transmit information simultaneously from the field events. With the development of telecommunications radio not only did not lose the audience, but also increased its due to the rapid use of information and popularity of many programs that are loyal audience of listeners.
Radio broadcast formats of materials are determined by largely technical factors, among which there are the following elements: [34] I. Type of broadcasting (radio):
a) Broadcasting network;
b) the range of long-wave broadcasting, and) the range of medium of broadcasting;
c) range VHF broadcasting;
d) the range of FM-broadcasting; II. Type of radio receiver :
a) normal unsteady;
b) stationary single-program
c) stationary multiprogram;
d) Automobile.
Due to the absence of the spectacular images it provides the opportunity for every radio listener analytically interpret and weigh each thought pronounced that concerns the world community anywhere on the planet.
State radio in Russia:
· Radio Russia - national network
· Echo of Moscow
· Radio Mayak - state-run national network
· Voice of Russia - state-run external service, broadcasts in English and other languages
Television
Television is the main source of news for many households around the world. TV does what none of the other media can: it brings the sight and sounds of some important news events by means of filmed, taped or live reports. Like regular radio news bulletins, daily TV news programmes provide only brief accounts of relatively new stories. But the visual aspect of TV news story can often help viewers understand the story. In addition to daily news reports, television covers special news events. Coverage of such an event may replace many hours of regular TV shows.
Television and the people - is one of the most intimate and close communication in society. On the one hand, television divides society - forgotten meetings, theaters, cinemas, on the other - it brings together around pressing issues of national interests. Television creates the background of our everyday life, leisure, business activity throughout our lives. The images, voices, music, included in our flat-screen, do not give a closed, expanding our horizons, forming \ tastes are changing habits and stimulate to the evaluation of emerging and traditional qualities of products and services.
Television attracts the discussion of social problems, fosters attitudes, ethics, forms a vital position of each member of society and creates a rapid feedback from the audience of millions. All television and radio company, operating in Russia, can be divided into four groups: government, intergovernmental, public and private. All television in the Russian Federation, independently of their type and ownership enjoy equal rights and bear equal responsibility in accordance with the law.
Russian television is state-owned, directly or by companies with close ties with the Russian government. Television for most Russians is the main source of news. • Russia - a national network
• 1 Channel - national network
• NTV - national network
• TV Center - belongs to the Government of Moscow
• Ren TV - Moscow's commercial station with strong regional network
• In Russia today - government funding, the international English language news channel, via satellite
Modern TV can be classified by the following features. 1. By method of translation:
• on-air broadcasting
• Satellite
• Cable
2. By type of activity:
• broadcasting companies, which broadcast of program.
• software-producing company in the form of producer companies;
• Distributors, who furthered TV-product with the requirements of the supplier and user requests.
3. By reaching the audience: all-Russian, regional, local.
4. The form of ownership
• state channels
• Commercial,
• mixed with the presence of foreign capital.
5. By source of funding:
• State-financed channels;
• Pay TV channels, which operate solely through subscription fees viewers;
• Public television stations, existing as a result of contributions of funds of public organizations, voluntary donations from businesses and individuals;
• commercial channels, which operate under very return, primarily through advertising;
• lease channels as a result of lease airtime from political parties, public organizations, individuals, production house.
Internet
The Internet (also known simply as "the Net" or less precisely as "the Web") is a more interactive medium of mass media, and can be briefly described as "a network of networks". Specifically, it is the worldwide, publicly accessible network of interconnected computer networks that transmit data by packet switching using the standard Internet Protocol (IP). It consists of millions of smaller domestic, academic, business, and governmental networks, which together carry various information and services, such as electronic mail, online chat, file transfer, and the interlinked Web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web.
The invention of the Internet has also allowed breaking news stories to reach around the globe within minutes. This rapid growth of instantaneous, decentralized communication is often deemed likely to change mass media and its relationship to society.
The internet is quickly becoming the center of mass media. Everything is becoming accessible via the internet. Instead of picking up a newspaper, or watching the 10 o'clock news, people will log onto the internet to get the news they want, when they want it. Many workers listen to the radio through the internet while sitting at their desk.
Mass media plays a crucial role in forming and reflecting public opinion, connecting the world to individuals and reproducing the self-image of society. The media has a strong social and cultural impact upon society. It is through the persuasiveness of media such as television, radio and print media that messages reach their target audiences. Television broadcasting has a large amount of control over the content society watches and the times in which it is viewed. This is a distinguishing feature of traditional media which New media have challenged by altering the participation habits of the public. The internet creates a space for more diverse political opinions, social and cultural viewpoints and a heightened level of consumer participation.
Trying to briefly formulate the main directions of PR-specialist with various types of media, we define them as follows - the highest PR-effect is achieved in the case when working with: [50]
- Print media, our focus on the identification and logical aspects,
- Radio - to sound,
- TV - on the visual imagery.
The importance of mass media and journalism has greatly increased in recent years. In democratic countries, people depend on the news media for the fair and truthful reporting of current events. Freedom of the press encourages the exchange of ideas among citizens. In government-controlled countries, however, the news media serve as an instrument of the state. Media forms public opinion now. A lot of politicians strive to possess mass media. Media carries great possibilities for society, but they are not only good ones. Nobody should forget, that media- is the fourth power. [50]
Basic principles of interaction with media
Media relations involves working with various media for the purpose of informing the public of an organization's mission, policies and practices in a positive, consistent and credible manner. The goal of media relations is to maximize positive coverage in the mass media without paying for it directly through advertising.
Many people use the terms public relations and media relations interchangeably; however, doing so is incorrect. Media relations refer to the relationship that a company or organization develops with journalists, while public relations extend that relationship beyond the media to the general public.
Dealing with the media presents unique challenges in that the news media cannot be controlled — they have ultimate control over whether stories pitched to them are of interest to their audiences. Because of this, ongoing relationships between an organization and the news media is vital. One way to ensure a positive working relationship with media personnel is to become deeply familiar with their "beats" and areas of interests.
Working with the media on the behalf of an organization allows to raise awareness of the entity to be raised as well as the ability to create an impact with a chosen audience. It allows access to both large and small target audiences and helps build public support and mobilizing public opinion for an organization. This is all done through a wide range of media and can be used to encourage two-way communication.
Key elements of strategy-based media relations [47]· The media strategy is documented and implemented according to principles agreed to by public affairs and senior management.
· A media policy is drawn up with responsibilities, profiles and positioning.
· Media activity is planned to reach target audiences in direct support of your organizational mission and goals.
· Media contact is broadly divided into proactive and reactive activities.
· Issuance of press releases, position statements and key announcements through both offline and online methods to prompt media coverage.
The media work in the new legal environment since 1991, the first serious step in this direction was the Federal Law "On Mass Media" [48], on 27 December 1991 № 2124-1, entered into force on 8 February 1992 they legislate common principles of freedom of the media, the new organization and the media. At the same time, the Law defined the basic principles of interaction with the media. Among them there are the following: [34, p.72]
• Objectivity: a journalist should cover the facts exactly as they occur in reality - without any fraud, drama, without interference in the personal lives of citizens. Do not make public reports of serious incidents in society as long as there is no given careful and prudent assessment of seriousness of the situation;
• Integrity: punishable by getting information by illegal means in the form of blackmail, any suggestions and requests, which could affect the participants in the events;
• Ethics: media should refuse to grant broadcast assumptions, rumors, their own guesses for the exact facts.
• Pluralism: the audience has the right to obtain information about all that, one way or another, affects social life. And the journalist's own view should not insult the present and possible, be neutral. In this case the journalist is not obliged to be responsible for the information obtained from official government or public sources. When you publish the facts, he should give clear reference to source materials.
In the process of organizing the activities PR should remember the basic rules of interaction with the media: [51]
• the design information for the media should be in addition to corporate objectives to comply with the public interest. Cleared message must be accurate, understandable, have important facts of interest and news value to media and other contact groups;
• the mechanism of interaction with the press should be done on a regular basis in the partnership mode, tact, truthfulness and respect;
• need time to respond to media requests and to provide comprehensive information services, observing the two necessary conditions: accuracy and speed. If there are misunderstandings between the PR-specialists and journalists, they should be eliminated in the shortest time at the expense of the actual materials, documents, explanations and clarifications on the highest level;
• Planning to prepare the information, its release to the press, PR-specialists to organize the work of assessment feedback to the recommendations of the management to improve marketing activities;
• PR-specialist should make every effort to prepare presentations leader, his press interviews on radio, in the PR-campaign, using interviews, briefings, presentations, etc.;
• PR-department should always be open and available for establishing contacts with the media in any form. On a regular basis should be monitored in the field of tracking, analysis and evaluation of press releases, radio and television.
• Be smart. Be professional. Learn from others. Media Invitation to the friendly people come to your organization, to give workshops on interviews, and other topics. To understand the media you are trying to influence and make sure they understand you.
The tasks of media professionals
Today in the newly formed society of media workers the following tasks must be performed: [49]
• coverage in the press, on radio and television major events taking place in society from the standpoint of the neutral critics, without favoring one viewpoint over another in order to win the trust of the masses as a vital guarantor of the functioning of the institutions of media;
• the media should initiate them pulses of positive change in society. In the first place to establish business contacts with representatives of PR, business, government and legislative bodies
Solving these problems, the media do a great job in the field of informatization of society, the formation of the national economy, the coordination of multiple movements, aesthetic orientation in society, protection of citizens, their interests, respect for the rule of law in the country.
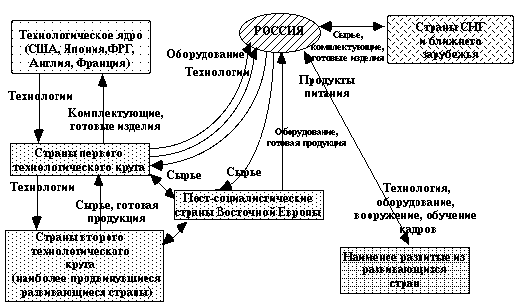
Control system information space [37, с.288]
Media in practice is controlled element and directly dependent on those who finance them. In our country, a large proportion of the information space media is controlled by the state under the doctrine of information security state channels TV - the first TV channel "Russia", "Culture". Control system information field of mass media in Russia is presented in pic. 3.2. [34, p.383]
The first level of control the media is controlled by a politicized capital and is owned by the state. It is this level of opinion-Russians in the field of political propaganda in the light of public facilities. At this level, a great role do news agency ITAR-TASS, RIA Novosti, RosBusinessConsulting; Channels TV «Russia", "Culture", "Sport", "Euronews", "Radio Ros ¬ is this", "Mayak" ; print media "Rossiyskaya Gazeta", "Parliamentary Press, Media of the Government of Moscow. Typically, this level serves as the state control to state security, the authority of the Russian economy, the achievement of national projects.
The second level of print and electronic media controls society-wide interregional coverage by news agencies – “Interfax”, “Prime-TASS”; TV “STS”, “TNT”, “Ren-TV”, “TV-3”, “DTV –Viasat”, “Home”; radio station “Mayak-24”, “Russian radio”, “Echo of Moscow”, the frequency channels of FM-range; printed media “Kommersant”, “Expert”, “Komsomolskaya Pravda”.
At the interregional level the role of commercial media significantly increases, smoothly integrating into the overall media-political system, but the impetus is not only national interests, but also achievement of commercial success.
It is known that in regions of the country an increased interest in local radio, television and print media is always observed. Thus it is difficult to overestimate the importance of the third level of information space management.
| 1 Federal level | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Information agency | Print press | Media of the Government Moscow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Media holdings | Radio | TV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Interregional level | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| News Agencies | Commercial publication | printed media | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radio | TV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| 3. Regional level | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| News Agencies | Regional Printing presses | Local TV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radio | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| 4. 4. Internet |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Website | Personal Website | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign holdings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. Polymedia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Business Feed RBC | Mobile network MegaFon | Interactive Family TV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pic. 3.2. Control system information space
As part of the global project "Public Expertise" Russian Union of Journalists at the regional level identified seven parameters of the relationship of local media and the state, they are:
• information openness of government;
• The level of freedom of information production;
• The level of freedom of information;
• Media richness of the region;
• development of media and advertising markets;
• The level of media conflict in the region and the nature of conflict;
• The level and nature of media community selforganization.
The fourth level of information space management through a powerful World Wide Web of the Internet, representing the global business environment with multiple communication channels, represents a huge opportunity for PR-specialists.
The fifth level management information space is Polymedia. As an example, the television station RBC, combining a variety of channels broadcast media. System business channel (agency RosBusinessConsulting) has a live broadcast, broadcasting on the Internet, as well as on mobile phones and smartphones "MegaFon".
Policy in the media ("The concept of government information policy of Russia") [13]
Russia's transition to a new type of economic development, civil society and rule of law, political pluralism, generate huge public demand for information. The necessity to address this need determines the special role of media in society. Thus such peculiarities as mass media, replicated, the periodicity, the use of revolving information resources appear. Media is an effective channel to inform the public about the activities of the authorities and informing the authorities and society about the life of society and its reaction to the action of the authorities. These features make the media the most important social institution and a necessary object of government information policy. Modern mass media do not only reflect world events, but are also largely engaged in the analysis of information, its pre-filtration and targeted selection. These media have a powerful influence on people's minds.
The main directions of the Government Information Policy, implementing the path-oriented to an open democratic development of Russian society and state should be:
• Non-submission media-serving interests of business and government and strengthen the capacity of their influence on the media (direct pressure, the supply of media incomplete, unclear, distorted or false information, deliberate misinformation, the deliberate understatement, fused structures of government, business, media, etc.) ;
• regulating the level of concentration and monopolization of the media (the obstacle reducing of independent sources of information, media concentration in the hands of economic elites, lack of rights of journalists, etc.);
• protecting the interests of regional markets media and promoting the local media;
• improving national legislation in terms of guarantees of freedom of expression and information, free flow of media, preventing the spread of violence and intolerance through the media, to safeguard media pluralism and access to official information.
The main objective of the Government Information Policy in relation to the media is to develop the legal, economic and institutional measures to ensure that in the media balance the interests of the individual, society and state. It is necessary to solve complex issues of state support for public media and develop a position in relation to non-state media.
In this case, the media really can serve as a mechanism for organizing the relations between population and social institutions of society, expressing the interests of government, business, cultural development, to be an instrument of dialogue between them. This can help overcome rigid attitude much of the population to mass media, distrust of messages that do not meet a personal or social expectations. Institutional, legal, economic and technological conditions must be created under which the media will effectively serve as the objective of informing the population, social institutions and the state. From this perspective, all the existing and future laws, other regulations and certain legal rules relating to media should be considered,.
The problem of informing the public about the activities of government bodies is also important. There is need in ensuring accessibility to the general public objective information on the progress of economic reforms, solving social problems, legal acts and regulations governing public and private lives of citizens.
Do not forget that media is not only an object of information policy, but also an active actor of it. This tool is has even grater social influence on the mass consciousness, an instrument for shaping public opinion. Ideas on regulatory system of electronic and print media must be carefully accommodated with current and newly adopted legislation in this area.
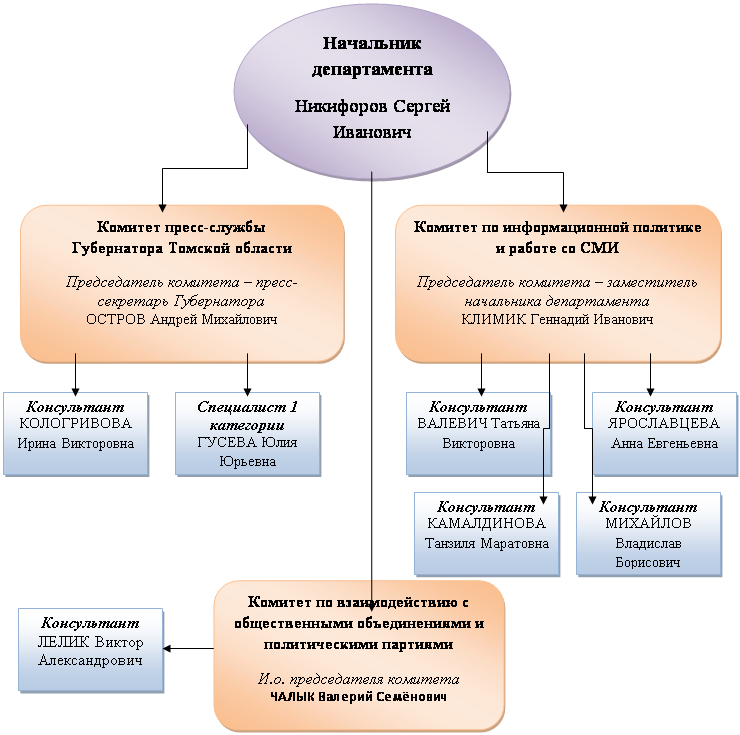
ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ Б
Организационная структура Департамента по информационной политике и работе с общественностью
ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ В
Медиа-карта Томской области
| № | Районы | Телевидение | Радио | Газеты | Интернет |
| 1. | Александровский (Райцентр – с.Александровское) Население: 9,8тыс. человек | Инфо Стрежевой СТВ Тел. 5-27-87 Главный редактор: Шабунина Наталья Валентиновна e-mail: stv@stv-tv.ru сайт: www.stv-tv.ru | · «Северянка» Общественно-политическая, социально-экономическая газета Редактор: Парфенова Ирина Владимировна Тел: +7(38255) 2-58-52 e-mail: severjnka@rambler.ru; severynka70@mail.ru | Сайт Александровского р-на: www.als.tomskinvest.ru Сайт с. Александровское www.alsp.tomskinvest.ru | |
| 2. | Асиновский (Райцентр – г.Асино) Население: 38,7 тыс. человек | Асиновская студия телевещания АСТВ-Рен ТВ (26 ДМВ-канал, ООО «Асино ТВ») Тел. (38-241) 2-12-79, 2-26-23 Главный редактор: Люхтенвальд Ирина Владимировна E-mail: asinotv@rambler.ru | Радио «Сибирская волна» (УКВ 69,50) Сайт: www.radiosv.tomsk.ru Главный редактор: Выдрин Виктор Викторович Тел. (38-241) 23878 | · «Диссонанс» общественно-политическая, социально-экономическая газета Гл. редактор: Клюев Виктор Васильевич Тел: (8-38-241) 2-46-47, 21236, (8-241) 2-55-39 E-mail: dissonans2003@bk.ru · "Образ Жизни" Гл. редактор: Нестерова Вера Александровна Тел.: (241) 2-15-19, 2-27-01 E-mail: obzregion@mail.ru Сайт: www.obraz.asino.ru | Сайт Асиновского р-на: www.asino.ru Сайт г. Асино www.gorod.asino.ru www.asino.tomsk.ru городской чат: www.asinocity.tomsk.ru развлекательный портал города: www.viasat.tom.ru |
| 3. | Бакчарский (райцентр – с. Бакчар) Население: 15, 6 тыс.человек | · "Бакчарская жизнь" Редактор: Карчагина Елена Юрьевна Тел.: (38249) 2-15-62, 2-23-13 E-mail: redbakchar@rambler.ru | Сайт Бакчарского р-на: www.bakchar.tomsk.ru | ||
| 4. | Верхнекетский (райцентр – Белый Яр) Население: 18 151 чел. | · Верхнекетский районный телерадиокомитет Редактор: Маскинова Людмила Николаевна Тел.: (258) 2-13-32, 2-21-93 E-mail: zs@belyar.tomsknet.ru | · "Заря Севера" Тел.: (258) 2-13-32, 2-16-35, (258) 2-66-35 E-mail: zs@belyar.tomsknet.ru Гл. редактор: Маскинова Людмила Николаевна | Сайт Верхнекетского р-на: www.vkt.tomsk.ru www.saiga.tomskinvest.ru | |
| 5. | Зырянский (райцентр – село Зырянское) Население: 14.934 человек | · Доброе утро, Зырянское” 73.01 мГц Тел.: (38-243) 2-16-86 Редактор: Солоненко Ольга Францевна | · "Сельская правда" Общественно-политическая газета Тел.: 8 (243) 212-12, 2-15-84 E-mail: selskaya_pravda@mail.ru Гл. редактор: Епифанцева Татьяна Владимировна | Сайт Зырянского р-на: www.zir.tomsknet.ru | |
| 6. | Каргасокский (райцентр – с. Каргасок) Население: 24 тыс. человек | Каргасокская студия телевидения (КСТВ) Директор Татаренко Татьяна Юрьевна Тел. : (38253) 2-17-06, 2-19-20, e-mail: kstv1961@mail.ru | · «Северная правда» Тел.: (253) 2-13-53, (253) 2-29-87, 2-19-42, 2-15-72, 2-14-56 E-mail: gazeta@kargasok.tomsknet.ru Редактор: Тарновский Михаил Юрьевич | Сайт Каргасокского р-на: www.kargasok.ru Неофициальный сайт Каргаска www.sokik.ru Администрация Каргасокского сельского поселения www.sp.kargasok.ru Администрация Новосюганского сельского поселения www.novvas.tomsk.ru Сайт управление образования, опеки и попечительства Каргасокского р-на: www.kargasok.tom.ru | |
| 7. | Кожевниковский (райцентр – с.Кожевниково) Население: 22, 222 человек | · "Знамя труда" Общественно-политическая газета Тел.: (244) 2-17-12, (244) 2-17-13, 2-14-23, 2-19-28 E-mail: kogred@mail.ru Гл. редактор: Колмакова Римма Геннадьевна | Сайт Кожевниковского р-на: www.kog.tomskinvest.ru Администрация Староювалинского поселения www.seladm.narod.ru | ||
| 8. | Колпашевский (райцентр – г.Колпашево) Население: 44816 человек | Студия телевидения Колпашева "ТВК" Директор: Вихров Сергей Александрович Тел.: (838 254) 40333, (254) 5-16-32, (38254) 5-24-77, E-mail: tvk@ok.ru | · "СОВЕТСКИЙ СЕВЕР" Общественно-политическая газета Колпашевского района Редактор - Луговской Александр Николаевич. Телефоны: (254) 5-37-04, 5-36-31, 5-37-62, 5-29-86. E-mail: sovsev@kolpashevo.tomsknet.ru
· "КОЛПАШЕВСКАЯ" Информационная общественно-политическая газета Редактор: Вихров Сергей Алексанрович Тел.: (254) 41-777, 40-333 E-mail: gk@70.ru | Сайт Колпашевского р-на: www.kolpadm.tom.ru Сайт г. Колпашево www.kolpashewo.ru Неофициальный сайт г.Колпашево www.kolpashevo.net | |
| 9. | Кривошеинский (райцентр - с.Кривошеино) Население: 15,7 человек | · "Районные вести" Общественно-политическая газета Тел: (251) 2-13-64, 2-14-75. E-mail: krvvesti@mail.ru Редактор: Шиянов Иван Алексеевич | Сайт Кривошеинского р-на: www.kradm.tomsk.ru Администрация Кривошеинского сельского поселения www.krivsp.tomsk.ru | ||
| 10. | Молчановский (райцентр – с.Молчаново) Население: 14,4 тыс. чел. | · «Знамя» Гл. редактор: Кучереносов Николай Васильевич Тел.: (256) 2-14-81, (256) 2-13-04, 2-14-82 E-mail: znamja@mail.tomsknet.ru · "Молчановские вести" Общественно - политическая газета | Сайт молчановского р-на: www.molchanovo.tomskinvest.ru Блог Молчановского р-на www.molchanovo.tomsk.ru Администрация молчановского сельского поселения: www.msp.tomskinvest.ru Администрация Наргинского сельского поселения www.nsp.tomskinvest.ru Администрация суйгинского сельского поселения www.ssp.tomskinvest.ru Администрация Тунгусовского сельского поселения www.tsp.tomskinvest.ru | ||
| 11. | Парабельский (райцентр – с.Парабель) Население: 13,5 тыс. чел | Телестудия Парабель Тел.: (38252) 5-23-62, e-mail: parabtv@yandex.ru, an_chud@hotmail.com
| · "Нарымский вестник" Тел.: (252) 2-16-08, (252) 2-18-56, 2-19-91, 2-11-97, 2-17-41 Редактор: Гордиевский Михаил Александрович E-mail: navest@parabel.tomsknet.ru | Сайт Парабельского р-на: www.parabel.tomsk.ru Администрация Новосельского сельского поселения www.novoselcevo.tomsk.ru | |
| 12. | Первомайский (райцентр - с.Первомайское) Население: 20304 человек | Первомайское телевидение Директор: Басаргина Марина Васильевна Тел.: (245) 2-10-74 | · «Заветы Ильича» Главный редактор: Нахтигалова Валентина Петровна Тел.: (245) 2-16-34, (245) 2-15-46 E-mail: pzi@pervomay.tomsknet.ru | Сайт Первомайского р-на: www.pmr.tomsk.ru | |
| 13. | Тегульдетский (райцентр – с.Тегульдет) Население: 8,1 тыс. человек | · "Таежный меридиан" Редактор: Сугатова Татьяна Петровна Тел.: (246) 2-14-68, 2-18-85, 2-19-81 E-mail: tmeridian@mail.ru | Сайт Тегульдетского р-на: www.teguldet.tomsk.ru | ||
| 14. | Томский (Административный центр – г.Томск) Население:84 тыс. человек | · "Томское предместье" Общественно-политическая газета Редактор: Лаврова Любовь Николаевна Тел.: (382-2) 44-22-91, 44-13-23. E-mail: predmestie@sibmail.com Сайт: www.predmestie.tomsk.ru · «Известия Томского района» Издается Томским региональным общественным фондом «Фондом развития Томского района» совместно с Местным отделением Томского района Всероссийской политической Партии «ЕДИНАЯ РОССИЯ». Редактор: Ефимов Сергей Николаевич Тел.: (3822) 40-92-82, 21-95-01 E-mail: izvestiyaatr@yandex.ru · «Сельский перекресток» Редактор: Лобыня В.Н. Тел.: (3822) 915-319 E-mail: zorkpos@narod.ru | Сайт Томского р-на: www.tr.tomskinvest.ru Воронинское сельское поселение www.voronino.tomskinvest.ru Заречное сельское поселение www.zarechnyi70.narod.ru Зональненское сельское поселение www.zonalnoe.tomskinvest.ru Зоркальцевское сельское поселение www.zorkpos.narod.ru Итатское сельское поселение www.itatka.tomskinvest.ru Калтайское сельское поселение | ||
| 15. | Чаинский (райцентр – с.Подгорное) Население: 12889 человек | · Чаинское радио Тел.:(38-257) 2-17-07; e-mail: gazchay@mail.ru Редактор Красноперова Лариса Ананьевна | · «Земля Чаинская» Гл. редактор: Пушкарева Юлия Сергеевна Тел.: (257) 2-11-36, 2-11-00, (257) 2-12-24 E-mail: chainskland@chainsk.tomsk.ru | Сайт Чаинского р-на: www.chainsk.tom.ru | |
| 16. | Шегарский (райцентр – с.Мельниково) Население: 9979 человек | Шегарское Телевидение Редактор: Ермолаева Олеся Александровна Тел.: (247) 2-18-03, 2-16-75, 2-25-55, 2-18-04 E-mail: gazeta2003@bk.ru | · «Шегарский вестник» Редактор: Ермолаева Олеся Александровна Тел.: (247) 2-18-03, 2-16-75, 2-25-55, 2-18-04 E-mail: gazeta2003@bk.ru | Сайт Шегарского р-на: www.sheg.tomskinvest.ru Анастасьевское сельское поселение www.anastas.tomskinvest.ru Побединское сельское поселение www.pobeda.tomskinvest.ru Северное сельское поселение www.severnoe.tomsk.ru Шегарское сельское поселение www.shegsp.tomskinvest.ru |
ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ Г «Бланк анкеты»
(для социологического исследования медиа-пространства Томской области)
Добрый день!
Департамент по информационной политике и работе с общественностью Администрации Томской области проводит исследование медиа-пространства Томской области. Целью данного исследования является изучение средств массовой информации, действующих в нашей области. Нас интересует, какие областные СМИ пользуются популярностью и доверием у населения. Что смотрят, читают и слушают жители Вашего района. Для составления объективной картины медиа-пространства Томской области, обращаемся к Вам, как к эксперту. Просим Вас ответить на несколько вопросов. В тех вопросах, где варианты отсутствуют, просим Вас разборчиво и подробно написать Ваш ответ. Заранее благодарим за сотрудничество!
Анкета разбита на 3 блока по видам СМИ (телевидение, радио, газеты). Отвечайте, пожалуйста, на тот блок вопросов, в котором можете дать объективную и профессиональную экспертную оценку.
v ТЕЛЕВИДЕНИЕ
1. Какие ТВ-каналы смотрят жители Вашего района?
(Отметьте знаком «+» присутствие ТВ-каналов в вашем районе, знаком «-» отсутствие ТВ-каналов в вашем районе. На месте пропусков впишите свой вариант, если имеется)
| Федеральные | +/- | Областные | +/- | Местные (районные) | +/- |
| ОРТ (Первый канал) | ТВ2 | ||||
| Россия 1 | ГТРК Томск (Россия) | ||||
| Петербург(Пятыйканал) | |||||
| НТВ | |||||
| Эфир - РЕН ТВ | |||||
| Культура | |||||
| СТС - открытое ТВ | |||||
| Спорт | |||||
| NTSC - ТНТ | |||||
| ТВ3 | |||||
| Студия Антен - Звезда | |||||
| ТВ-Центр | |||||
| 37телеканал(НВ Томск) | |||||
| Муз ТВ |
2. Расставьте оценки по шкале от 1 до 5 по мере популярности телеканалов в Вашем районе
1 – не популярно вообще
2 – почти не популярно
3 – средней популярности
4 – достаточно популярно
5 – очень популярно
(На месте пропусков впишите свой вариант, если имеется)
| Федеральные | Оценка от 1 - 5 | Областные | Оценка от 1 - 5 | Местные (районные) | Оценка от 1 - 5 |
| ОРТ(Первый канал) | ТВ2 | ||||
| Россия 1 | ГТРК Томск (Россия) | ||||
| Петербург (Пятый канал) | |||||
| НТВ | |||||
| Эфир - РЕН ТВ | |||||
| Культура | |||||
| СТС - открытое ТВ | |||||
| Спорт | |||||
| NTSC - ТНТ | |||||
| ТВ3 | |||||
| Студия Антен - Звезда | |||||
| ТВ-Центр | |||||
| 37 телеканал (НВ Томск) | |||||
| Муз ТВ |
Похожие работы
... размещения заказов на выполнение научных работ. Используя международный опыт организации финансирования НИОКР, высокий потенциал регионов страны (Новосибирская, Томская области) как исторически сложившиеся научные центры России, государство должно стимулировать развитие новых структур работающих в данном направлении (венчурных фирм и фондов, научно-финансовых групп), создавая необходимую ...
... 12 470 рублей, в 2008 году не менее 14 090 рублей; · проведение работы по расширению круга участников областного Соглашения. Как было сказано выше, одной из задач промышленной политики Томской области является создание безопасных условий труда. В соответствии с постановлением Министерства труда и социального развития Российской Федерации от 24.04.2002 г. № 28 «О создании системы сертификации ...
... Продолжают увеличивать объемы производства овощеводческие хозяйства: ЗАО «Овощевод», ООО «Агротеховощ», ЗАО «Томь». · Объём продукции сельского хозяйства. Выпуск продукции сельского хозяйства в Томской области всеми сельхозпроизводителями (сельскохозяйственные организации, хозяйства населения, крестьянские (фермерские) хозяйства и индивидуальные предприниматели) в январе-сентябре 2009 ...
... Основные тенденции развития финансового сектора В условиях сложившейся экономической ситуации, постепенного выхода из кризиса, можно пронаблюдать несколько основных тенденций развития финансового сектора экономики Томской области. Первая связана с временным усилением роли госбанков и дочерних банков с участием иностранного капитала. Российские вкладчики напуганы отбором банковских учреждений в ...
0 комментариев