Навигация
30 September 1961
aim-to promote economic cooperation
and development
members-(24) Australia, Austria,
Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany,
Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg,
Netherlands, NZ, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden,
Switzerland, Turkey, UK, US special members-(2) EC, Yugoslavia
Group of 10 (G-10)
note-also known as the Paris Club
established-NA October 1962
aim-wealthiest members of the IMF who provide most of the money to be loaned and act as the informal steering committee; name persists in spite of the
addition of Switzerland on NA April 1984
members-(11) Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan,
Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, US
Franc Zone (FZ)
established-NA
aim-to form a monetary union among countries whose currencies are
linked to the French franc
members-(15) Benin, Burkina, Cameroon,
Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Cote
d'Ivoire, Equatorial Guinea, France, Gabon, Mali,
Niger, Senegal, Togo; note-France includes
metropolitan France, the four overseas departments
of France (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique,
Reunion), the two territorial collectivities of
France (Mayotte, Saint Pierre and Miquelon), and the
three overseas territories of France (French
Polynesia, New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna)
International Energy Agency (IEA)
established-15 November 1974
aim-established by the OECD to promote
cooperation on energy matters, especially emergency
oil sharing and relations between oil consumers and
oil producers
members-(21) Australia, Austria,
Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Ireland,
Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, NZ, Norway,
Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, UK, US
Group of 8 (G-8)
established-NA October 1975
aim-the developed countries (DCs) that participated in the
Conference on International Economic Cooperation (CIEC), held in several
sessions between NA December 1975 and 3 June 1977
members-(8) Australia, Canada, EC (as one member), Japan, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland,
US
Australia Group
established-1984
aim-to consult on and coordinate export controls related to chemical and biological weapons
members-(25) Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland,
France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg,
Netherlands, NZ, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, US
observer-(1) Singapore
Group of 5 (G-5)
established-22 September 1985
aim-the five major non-Communist economic powers
members-(5) France, Germany, Japan,UK, US
Group of 7 (G-7)
note-membership is the same as the Big Seven
established-22 September 1985
aim-the seven major non-Communist economic powers
members-(7) Group of 5 (France, Germany, Japan, UK, US) plus
Canada and Italy
Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)
established-April 1987
aim-to arrest missile proliferation by controlling the export of key missile technologies and
equipment
members-(24) Australia, Austria,
Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece,
Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, NZ, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK, US
North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC)-an extension of NATO
established-8 November 1991
effective-20 December 1991
aim-to form a forum to discuss cooperation
concerning mutual political and security issues
members-(38) Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan,
Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Czech
Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Georgia,
Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland,
Italy, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Moldova,
Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia,
Slovakia, Spain, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine,
UK, US, Uzbekistan, Yugoslavia
Liberation Organization Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS)
established-5 March 1992
aim-to promote cooperation among the Baltic Sea states in
the areas of aid to new democratic institutions, economic
development, humanitarian aid, energy and the environment,
cultural and education, and transportation and communication
members-(10) Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia,
Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden
observers-(2) Belarus, Ukraine
ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ, ВКЛЮЧАЮЩИЕ ГОСУДАРСТВА РАЗЛИЧНЫХ СКС, НО СВЯЗАННЫЕ С ТЕРРИТОРИЕЙ И НАСЕЛЕНИЕМ ЗАПАДНОЙ СКС, А ТАКЖЕ ЕЕ ГРАНИЦАМИ С ИНЫМИ СОЦИО-КУЛЬТУРНЫМИ ОБРАЗВАНИЯМИ
United Nations Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP)
established-4 March 1964
aim-established by the UN Security Council to serve as a
peacekeeping force beween Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots in Cyprus
members-(7) Austria,Canada, Denmark, Finland, Ireland, Sweden, UK
RUSSIAN SCS's ORGANIZATIONS
ВНУТРЕННИЕ ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ РОССИЙСКОЙ СКС
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
established-8 December 1991
effective-21 December 1991
aim-to coordinate intercommonwealth relations and to provide a mechanism for the orderly dissolution of the USSR
members-(10) Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan
МЕЖДУНАРОДНЫЕ ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ РОССИЙСКОЙ СКС, СВЯЗАННЫЕ С КОНТРОЛЕМ И СОЦИО-КУЛЬТУРНОЙ ПЕРЕРАБОТКОЙ СТРАТЕГИЧЕСКИ ВАЖНЫХ ТЕРРИТОРИЙ
Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CEMA)
also known as CMEA or Comecon,
was established 25 January 1949
to promote the
development of socialist economies and was abolished
Похожие работы
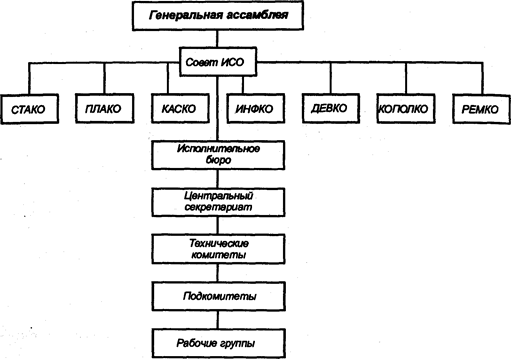
... на всех языках. Для этого было решено использовать греческое слово isos – равный, вот почему на всех языках мира Международная организация по стандартизации имеет краткое название ISO (ИСО). Сфера деятельности ИСО касается стандартизации во всех областях, кроме электротехники и электроники, относящихся к компетенции Международная электротехнической комиссии (МЭК). Некоторые виды работ выполняются ...
... оказание конкретной поддержки партнерам МОТ, в том числе при проведении национальных симпозиумов и создании компьютерных информационных сетей, содействие социальному диалогу и применению норм. IV. Главные цели и задачи МОТ В своей деятельности Международная организация труда руководствуется четырьмя стратегическими целями: · продвижение и проведение в жизнь основополагающих принципов ...
... определенной право- и дееспособностью, чем создают новый субъект права, осуществляющий правотворческие, правоприменительные и правоохранительные функции в сфере международного сотрудничества. Однако это не означает, что правовой статус международной организации идентичен статусу государства, основному субъекту международного права. Отличие правоспособности организаций - меньший и преимущественно ...
... организации, а также претворение в жизнь разработанных международным сообществом в последние годы концепций. 2. Принципы деятельности и основные институты права международных организаций, их юридическая природа, компетенция и функции. Международная межправительственная организация - это добровольное объединение суверенных государств или международных организаций, созданное на ...
0 комментариев