Навигация
Regulation of External Economic Activities
2. Regulation of External Economic Activities
In 1995 certain changes were introduced to the mechanism of the state regulation of the foreign trade. In the first half of 1995 the state regulation of oil exports was substantially amended: quotas and licenses in oil exports were abolished alongside with preferences (with exclusion of supply pursuant to intergovernmental agreements) while export duties on oil and oil products were significantly reduced; certain oil products were excluded from the list of strategically important commodities. Producers' access to channels allowing transportation of oil to other countries (pipelines and terminals in sea ports) became a natural restraint on exports.
The list of strategically important raw commodities was shortened and the institution of special exporters was abolished altogether. The system of contracts' registration became the main instrument of control over exports. Individual preferences granted to participants of external economic activities were abolished, excluding those issued in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation.
The law "On State Regulation of Foreign Trade" adopted in July came into force in October. The law stipulated what authority in this area shall be with the President, the Government and the Ministry of Foreign Economic Relations. The exclusiveness of the MFER's position was emphasized by the fact that only it was vested with the right to license import and export transactions subject to quantitative restrictions or to approval procedures.
As pursuant to the law, the Russian Government shall submit a program of foreign trade development together with a draft of the Federal budget for the Parliament's approval. Alongside with other provisions this program shall embrace customs tariff rates planned for the year in question as well as the band of their possible fluctuation, thus making the foreign trade more predictable. The Government has the right to introduce export and import quantitative restrictions on national security grounds, to comply with international agreements or to protect the domestic market, however, these measures shall be announced not less than 3 months prior to their actual introduction. The law envisages a possibility to introduce state monopoly for trade in certain products. In this case a special procedure of licensing import and export operations exclusively to state-owned enterprises shall be applied.
As the above mentioned law was effectuated, the Commission of the RF Government on Safeguard Measures in Foreign Trade became fully legitimate and in December it received "Procedures of Investigation Prior to Application of Safeguard Measures" approved by the MFER (Russ.abbr. MVES). A possibility to apply safeguard measures against competitive imported products complies with usual practices applicable in the world trade. In this area Russia is late in working out and application of such measures, especially taking into account that Russian exports are often and in most cases unjustifiably subject to discrimination on foreign markets. So, the RF import regime loses its exceptional liberalism which has been characteristic of it until recently.
Tariff regulation. From September through December export duties levels were gradually lowered until their complete abolition since January 1, 1996, with an exception of a small group of goods including oil, natural gas and some other raw commodities.
In June and in October, 1996 import duty rates were changed. On the whole, changes were made in direction of an increase in tariffs. Earlier goods taxable at 1 percent have constituted a rather significant part of the list, at present this rate is only applicable to certain goods within Group 10 of the External Economic Activity commodity nomenclature (grain) and 1701 (cane sugar, beet firm sugar and sucrose). A 10 percent tariff is now applied to medicines which earlier have been exempt from duties while fish and fish products are subject to a double rise of duties (from 5 to 10 percent) and duties on vegetables were tripled (from 5 to 15 percent). For foodstuffs earlier exempted from duties new tariffs made 5 percent on bananas and citrus fruits, 10 percent on tee and coffee, 15 percent on fresh cucumbers, however, rates of import duties in Russia still remain considerably lower than in the EU countries (16 percent against 21 percent). There were effectuated provisions stipulating a 30 percent duty on goods such as luxuries, tobacco products, alcoholic beverages and weapons.
Tax regulation. As before, close attention was paid to products subject to excise taxation. In July and in December, 1996 a price difference between excise stamps and special stamps designated for imported tobacco and alcohol products were adjusted. There were created equal conditions for importers of these products both from countries within and outside of the former Soviet Union (ECU 0.1 per unit of an alcohol beverage and ECU 0.01 per unit of a tobacco product). In December the rate of excise tax on tobacco products was increased from ECU 1.2 to ECU 2 per 1000 pieces.
In June the list of products subject to a preferential 10 percent value added tax was shortened; it was again examined in detail in November and some new products were added to it. In December works and services, both produced domestically and purchased, being exported to countries outside the CIS alongside with services concerning the transit of foreign cargo through Russian territory were exempted from the value added tax.
Preferences in External Economic Activities. In October, 1996 the Government abolished previously applicable preferential taxation of alcoholic beverages imported from abroad by certain legal entities which were exempt from customs duties (for instance, the National Fund of Sports and the All-Russian Society of Invalids). Since December, pursuant to the Presidential Decree "On Customs Preferences" of November 30, 1995, it is inadmissible for Federal agencies to adopt decisions which would provide prolongation of preferences in terms of customs duty exempts and receipts of additional compensations.
In August, 1996 the control mechanism over incoming export proceeds denominated in foreign exchange was adjusted. All proceeds in foreign currencies shall be entered into accounts with authorized banks--that became a requirement of the customs regime. Customs service now enjoys the right to control all capital flows and apply relevant sanctions if necessary.
In September, 1996 the control over exports and imports of military-purposed products, works and services, subject to licensing, was tightened.
In December the set of instruments of the state control mechanism over imports was supplemented. The system of foreign exchange control over imports introduced on January 1, 1996, is basing on the same principles as the export control existing since 1994 and envisages the same chain of relations: an importer--an authorized bank--customs. The key document fundamental for the whole control system is a registration certificate for import transactions.
Похожие работы
... power of the financial capital. The determinatives are the educational level and volume of the knowledge accumulated by a society. Chapter II. The international trade at the present stage of development 2.1 Concept and laws of development of the international trade Basis of economic relations in the world economy is international trade. International trade is sphere of the international ...
... The conclusion In the given work some moments which open rights and duties of participants of commodity circulation are resulted. But, it is possible to draw a conclusion that, in Russia and in foreign countries, the law protects the interests of consumers. In conclusion I highlight some important positions and compare Russian and European legislation related to consumers rights. The ...
... course of republic. A complex of the reasons conditions and factors having not tactical, but basic essence and long-time character stipulates it. Today common balance of mutual relation between Kazakhstan and Russia has positive character, as consider each other as the strategic partners and it establishes the important premise for their mutual cooperating in the field of policy, economy, ...
... as a nation and was not dissolved by foreign invaders. The problems in Russia are immese, but Russia will be able to cope with all its problems and will rise again as a great power on the world stage. Russia’s population, the crux of Russian reform, of 148 million is shrinking annually by 0.7 percent. Ethnic Russians form 82 percent of the entire population. Other groups include Tartars (4 ...
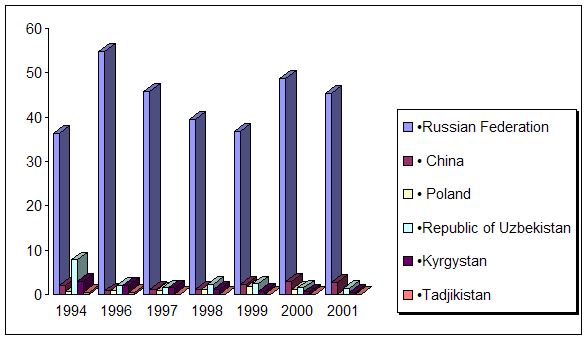
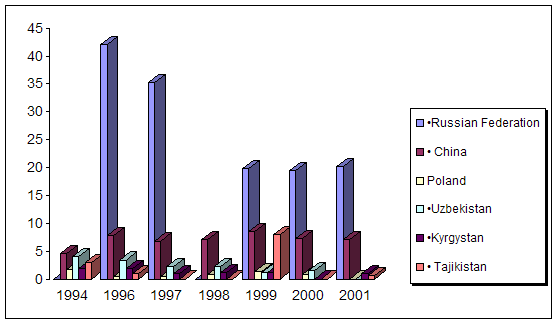
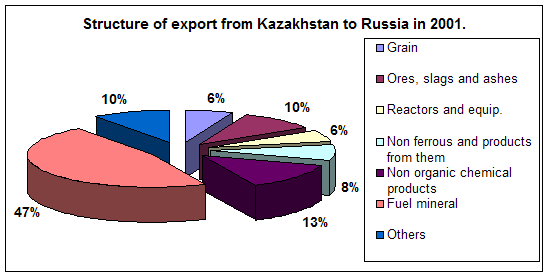
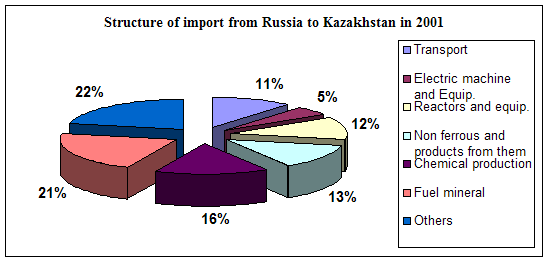
0 комментариев