Навигация
Grammar explanations as used in the major methods
1.1.4 Grammar explanations as used in the major methods
We shall briefly review the treatment of grammatical explanations by some of the major methods. This is not meant to be an exhaustive study of all available methods; rather it is an attempt to show the variety of ways in which different methods deal with grammar explanations and may help teachers in evaluating available materials.
Grammar translation is associated with formal rule statement. Learning proceeds, deductively, and the rule is generally stated by the teacher, in a textbook, or both. Traditional abstract grammatical terminology is used. Drills include translation into native language.
The direct method is characterized by meaningful practice and exclusion of the mother tongue. This method has had many interpretations, some of which include an analysis of structure, but generally without the use of abstract grammatical terminology.
The audio-lingual method stresses an inductive presentation with extensive pattern practice. Writing is discouraged in the early stages of learning a structure. Here again, there has bee considerable variation in the realization of this approach. In some cases, no grammatical explanation of any kind is offered. In other, the teacher might focus on a particular structure by isolating an example on the board, or through contrast. When grammatical explanation is offered it is usually done at the end of the lesson as a summary of behavior (Politzer, 1965), or in later versions of this method the rule might be stated in the middle of the lesson and followed by additional drills.
Each method is realized in techniques. By a technique we mean an individual way in doing something, in gaining a certain goal in teaching learning process. The method and techniques the teacher should use in teaching children of the primary school is the direct method, and various techniques which can develop pupils` listening comprehension and speaking. Pupils are given various exercises, connected with the situational use of words and sentence patterns.
1.2 Some General Principles of Grammar Teaching
1.2.1 Conscious approach
This means that in sentence patterns teaching points are determined so that pupils can concentrate their attention on some elements of the pattern to be able to use them as orienting points when speaking or writing the target language. For example, I can see a book. I can see many books.
The teacher draws pupils’ attention to the new element in the form of a rule, a very short one. It is usually done in the mother tongue. For example: Помни, что во множественном числе к существительному прибавляется окончание –s [s,z] или –es [IZ]. Or: Помни, что в отрицательных предложениях ставится вспомогательный глагол “do not” (“does not”).The rule helps the learner to understand and to assimilate the structural meaning of the elements. It ensures a conscious approach to learning. This approach provides favourable conditions for the speedy development of correct and more flexible language use. However it does not mean that the teacher should ask pupils to say this or that rule, Rules do not ensure the mastery of the language. They only help to attain the practical goal. If a pupil can recognize and employ correctly the forms that are appropriate, that is sufficient. When the learner can give ample proof of these abilities we may say that he has fulfilled the syllabus requirements.
Conscious learning is also ensured when a grammar item is contrasted with another grammar item which is usually confused. The contrast is brought out through oppositions. For example:

I get up at 7 o’clock.
It’s 7 o’clock. I am getting up.
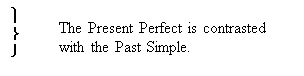
He has come.
He came an hour ago.
|
|
Give me the book (you have promised),
|
|
I like the soup ( you have cooked).
Rule for the teacher:
The teacher should realize difficulties the sentence pattern presents for his pupils. Comparative analysis of the grammar item in English and in Russian or within the English language may be helpful. He should think of the shortest and simplest way for presentation of the new grammar item. The teacher should remember the more he speaks about the language the less time is left to practice. The more the teacher explains the less his pupils understand what he is trying to explain, this leads to the teacher giving more information than is necessary, which does not help the pupils in the usage of this particular grammar item, only hinders them.
Похожие работы
equacy in using games In this paragraph we would like to reflect how modern teachers evaluate the adequacy in using games when teaching English language Famous British teacher and educator Andrew Wright in his books' Language learning is hard work ... Effort is required at every moment and must be maintained over a long period of time. Games help and encourage many learners to sustain their ...
... be learnt in passing but has to be studied and thoroughly practiced before students can produce it confidently and accurately in new contexts. [7:54] 2.1 Ways of presenting articles In the process of teaching English, teachers should pay special attention to countable and uncountable nouns. The distinction between countable and uncountable nouns must be clearly understood because it affects ...
... (for example: If she gets the job she’ll move to London). A list of grammatical items which are regularly focused on in language classes can be found in the contents list of any good learner’s grammar book such as An A-Z of English Grammar and Usage by Leech (Nelson), Practical English Usage by Swan (OUP) or The Heinemann English Grammar by Beaumont and Granger (Heinemann). Language can not only ...
... , even temperately, was a sin. (Dreiser) The verbal noun may be modified by an adjective. He (Tom) took a good scolding about clodding Sid. (Twain ) Chapter 2 Syntax and Semantics of English Verbals 2.2.1 The Functions of the Infinitive in the Sentence The infinitive can be used in different syntactic functions. A single infinitive occurs but seldom: in most cases we find an ...

0 комментариев