Íàâèãàöèÿ
Areas in which the Bank leads and there is no direct IMF involvement include the social sectors, infrastructure and environment
3. Areas in which the Bank leads and there is no direct IMF involvement include the social sectors, infrastructure and environment.
· In the social sectors the Bank conducts annual updates of Georgia’s Poverty Assessment based on household data collected on a quarterly basis. The Bank’s focus has been to improve the budget execution of expenditures for health, education and poverty benefits and to raise the efficiency in the use of scarce public resources. Through the Social Investment Fund Credits IDA is focusing in particular on areas with high poverty levels to provide basic infrastructure to the poorest communities. A recently approved Self-reliance Fund Grant will help authorities address the complex issues related to internally displaced people. IDA is also supporting a dialogue with the Government on social protection reform that may lead to an IDA-supported project.
· In education the Education Adaptable Program Credit aims at improving the learning outcomes of primary and secondary students, through curriculum reform, development of an examination system, training of teachers, provision of learning materials, and development of capacity to make better use of Georgia’s physical, financial and human resources. While the investment needs of school buildings are substantially higher than is currently affordable for Georgia, the Social Investment Fund projects continue to assist in financing urgent repairs to school facilities in many communities.
· In health IDA Credits to support the Government in improving the health care financing system, exploring risk-pooling options, introducing a new system of primary health care and improving the focus of services funded through public funds on the poor and on priority public health interventions. In addition hospital restructuring has been supported by SAC 3 and the Structural Reform Support Credit.
· In infrastructure support is being provided through the Municipal Development and Decentralization Credit and the Social Investment Fund Credit. These projects are providing financing at the community level for critical infrastructure needs, primarily for school and health facilities heating and repair, small hydropower schemes to provide electricity, drinking water and sanitation rehabilitation, as well as transportation infrastructure rehabilitation.
· In rural development IDA credits have supported the development of private sector farming and agro-processing improvements, agricultural credit, irrigation and drainage, and agriculture research and extension. IDA has also been supporting the creation of local institutions such as rural credit unions and water users associations through its Credits.
Areas in which the World Bank leads and its analysis serves as input into the IMF program
4. The Bank has been leading the dialogue on structural reforms through SAC 3, approved by the Bank’s Board of Executive Directors in June, 1999, and closed in October, 2002. Despite considerable delays, the core conditions of SAC 3 were met, but their impact was reduced by poor governance. Institution building and technical assistance has been supported through the Structural Reform Support Credit, also approved by the Bank’s Board of Executive Directors on June 29, 1999. The Bank also leads in the areas of:
· Private sector development. SAC 3 supported improvements in the environment for private sector development, focusing on: (i) simpler licensing regulations; (ii) more transparent government procurement; (iii) reduced cost of entry for businesses; and (iv) privatization of state-owned commercial assets. IDA has also been supporting private sector participation in other areas such as energy, telecommunications, urban services and agriculture. The IMF has worked with the authorities to initiate audits of the 2002 accounts of three major state owned enterprises.
· Energy. The energy system is in poor condition, with unreliable supply, massive non-payment and mounting debts. IDA has been working with other donors, including the IMF, to encourage more private management and ownership, and to implement a series of short-term action plans to improve the overall functioning of the sector. The IMF has also been focusing on improved payments for electricity.
· Public Sector Management. The Bank is supporting the development of a civil service reform program, while the Fund is providing technical assistance in support of tax and customs administration reform.
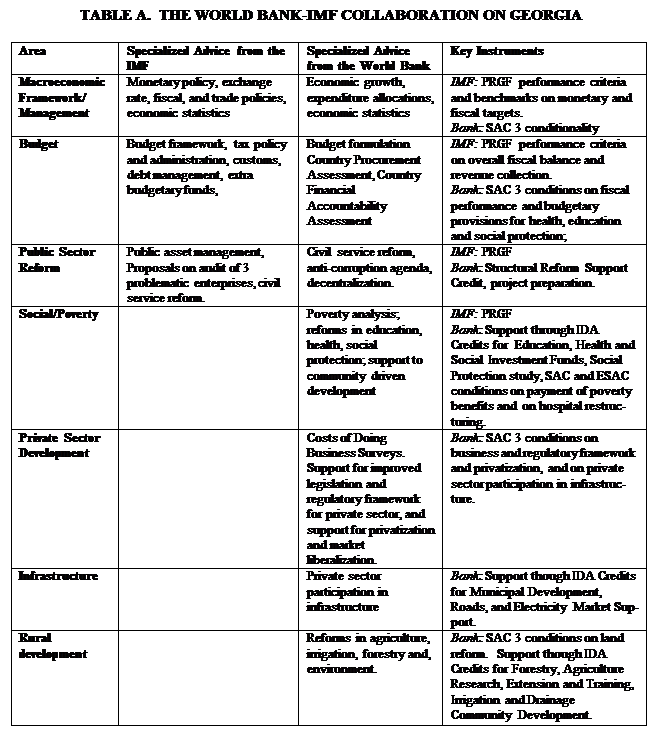
Areas of shared responsibility of the World Bank and IMF
5. The Bank and the Fund have been working jointly in the following main areas (supported by the Bank’s SAC 3 and Structural Reform Support Credit, several investment operations and the Fund’s PRGF):
· Poverty Reduction Strategy. Both institutions have been working closely with the Government to provide support to the development of the PRSP, through seminars and workshops, direct staff input, and a multi-donor Trust Fund to support the work of the PRSP secretariat..
· Budget Planning and Execution. The annual process-based Public Expenditure Reviews will provide the underpinnings for systemic changes in expenditure management, with the immediate aim being improved budget formulation in 2004. The IMF is focusing on Treasury reform within the Ministry of Finance.
· Financial Sector Reforms. The joint Financial Sector Assessment Program has supported: (i) strengthened banking and non-banking supervision; (ii) introduction of international accounting standards; (iii) and consolidation of banks through higher capital requirement ratios; and (iv) anti money-laundering legislation. The IMF has focused in particular on banking supervision.
· Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA). Given Georgia’s heavy external debt burden, the Bank and the Fund conduct joint Debt Sustainability Analysis on a regular basis.
Areas in which the IMF leads and its analysis serves as input into the World Bank program
· Fiscal Framework. The IMF’s focus on prudent fiscal policy has served as an important framework for IDA’s work on public expenditure management.
Areas in which the IMF leads and there is no direct World Bank involvement
· Monetary Framework. The IMF closely collaborates with the NBG in the design and implementation of a monetary program that aims at remonetization of the economy, while keeping inflation low and the exchange rate of the Lari stable
· Economic Statistics. IMF technical assistance has been conducive to improvements in national accounts, price, monetary and government financial statistics.
5.1.5 The World Bank Country Assistance Strategy for Georgia
| Activities (as identified in the EDPRP) | Responsible Agencies | Focus of Bank Actions | Expected Results FY04-06 | Bank Group Program | Part-ners | WB Performance Indicators for End FY06 |
| Improvement of Governance | ||||||
| · Development of a comprehensive, long-term concept and action plan of executive government reforms, and of a program to improve structure and number of employees in organizations under budgetary financing | State Chancellery, Ministry of Justice, Ministry of Finance relevant executive government bodies | Assistance to the State Chancellery in carrying out a functional analysis of the central government agencies and assessment of budgetary employment, remuneration, and training policy; on the basis of the above studies, develop recommendations | Widely owned program to improve functioning of government administration and agencies; remuneration and retrenchment policy for core civil service introduced, and plans for civil service training developed | Public Sector Management Project | DFID, USAID, UNDP | Initiation of reform and restructuring of civil service |
| · Inventory of normative acts defining the competence of government agencies to avoid duplication of local government functions | State Chancellery of Georgia, Ministry of Justice | Review of the existing legal framework | Initiation of legislative change and amendments | Public Sector Management Project; Public Expenditure Reviews | DFID EU USAID UNDP | Duplications and overlap among the central state agencies reduced, mandates more clearly defined |
| · Distinction of municipal property from central government and private property | State Chancellery, Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade, Agency of State Property Management, Ministry of Justice, Ministry of Finance | Advice on financing mechanism for transfer of road and transport properties and legal mechanisms for owning and managing very low volume farm access roads | Revised functional/administration classification of roads; sound allocation formula for dividing Road Fund revenues between road owners | Secondary Roads Project; Trade and Transport Facilitation Project; Rural Infrastructure Study | Kuwait Fund for Economic Development | New road classification; new procedures for managing the road fund, including allocation of funds between road owners |
| Macroeconomic Stability | ||||||
| · Preparation of indicative plans of development for the economy for 2004 and 2005 | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade | Improvement of linkage between policy, resource constraints and budgets | Develop a more realistic medium-term budget framework | Public Expenditure Reviews, PRSC in High Case | IMF DFID | Budget execution closer to planned |
| · Initiate the process to convert a portion of government debt liabilities into long-term debt instruments | National Bank | Assistance to the MoF develop long-term debt instruments, e.g. government bond market | MoF starts to use medium to long-term government bonds to replace the rolling of short-term debt instruments | Financial Sector Advisory Program | IMF | 1-10 year government bond market in place |
| · Improvement of the management of international reserves of the NBG | National Bank | Advise to National Bank on management of reserves | Increased import coverage | Financial Sector Advisory Program | IMF | Gross foreign reserves to reach over 2 months of imports |
| · Completion of tax and customs administration reform | Ministry of Finance, State Tax and Customs Departments | Development of a business-friendly tax environment | Increased collection of excise taxes and improved VAT administration | Public Expenditure Reviews, Business Environment Study, PRSC in High Case | IMF USAID EU | Collection of excise taxes to reach over 2 percent of GDP |
| · Implementation of treasury reform, centralization of treasury service; development and introduction of commitment accounting and control system; development and introduction of expenditure control system | Ministry of Finance | Assistance to the MOF to improve its cash and debt management capacity and skills | Consolidation of effective control system, and adoption of a single treasury account | CPAR Updates, Public Expenditure Reviews, PRSC in High Case | IMF | Improved cash management and debt management capacity |
| · Improve government procurement system and expand scope of its coverage | State Procurement Department, Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade | Establishment of a transparent state procurement system; decentralization of State procurement functions to line agencies | Greater efficiency and competition within the system; reduced delays and corruption in procurement process | CPAR, Public Expenditure Reviews, PRSC, project lending (e.g. Secondary Roads and Trade and Transport Facilitation) | Recommendations of Country Portfolio Assessment Report implemented | |
| · Gradual increase of the share of targeted programs in the state budget | Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade | Develop program-based budgeting | Improve consistency between medium-term indicative plan and the budget | Public Expenditure Reviews, Public Sector Management Credit, PRSC in High Case | DFID | Public Expenditure Reviews assessment of better targeting of programs in the budget |
| · Inventory of budgetary arrears | Ministry of Finance | Establish accurate estimates of past government liabilities | Better information on, and reduction in, arrears | CFAA Updates, Public Expenditure Reviews | IMF | Reduced arrears |
| · Increase the number of participants in treasury bill market and improve bidding mechanisms to increase maturity and reduce the discount rate through market | Ministry of Finance, National Bank, National Commission of Securities | More competitive and efficient T-bill market | Short term: more participants for competitive bidding, and for non-competitive quota; medium term: cash management, coordination between MOF & NBG on T-bills/open market operations; long term: independent debt management office | Financial Sector Advisory Program, PRSC in High Case | USAID FIRST | Lower T-bill yield |
| · Develop legislation promoting the activities of investment funds in order to introduce best corporate management practice in enterprises and develop stock market | Ministry of Finance, National Commission of Securities | Help build legal environment for investment funds; provide information/advice | Establishment of legal environment for investment funds | Financial Sector Advisory Program | Regulation of investment funds in place; NCS has capacity to supervise those funds | |
| · Prepare and adopt bill “on Personification and Registration of Insurance Contributions to Social Insurance System” required for regularizing first (distributive) pillar of pension system and development of pensioners’ personified registration system | Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Protection | Support to Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Protection on legal reforms and their implementation | Law adopted successfully | Social Protection Reform Project | Regularization of 1st pillar of pension system; better links between pensions and contributions | |
| · For private pension funds, adopt statutory normative acts in accordance with the laws “on Non-Government Pension Funds” and “on Securities Market” | National Securities Commission, Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Protection | Support to National Securities Commission and Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Protection on legal reforms and their implementation | Normative acts developed and adopted | Social Protection Reform Project | Improved regulatory environment in the area of private pensions | |
| · Prepare amendments to the Tax Code and investment rules of pension assets to promote the development of non-banking financial sector, including nongovernmental voluntary insurance system | Ministry of Finance, State Service of Insurance Supervision, National Commission of Securities | Support to relevant agencies on amendments to tax code and investment rules | Improved functioning of non-banking financial sector, including insurance companies/private pension funds | Social Protection Reform Project | Greater and more effective role for non-banking financial sector, including insurance companies and private pension funds |
| Structural Reforms | ||||||
| · Assess magnitude and share smuggled goods and those manufactured in informal sector of the economy by various commodity groups | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade; State Department of Statistics | Support for initiatives to reduce smuggling and the shadow economy | Reduction in smuggling and in the shadow economy | Trade Facilitation Project; Private Sector Development Project; Public Sector Reform Project; PRSC in High Case | USAID | Increase in tax revenues, including increase in revenues from petroleum products and cigarettes to over 2.5% of GDP |
| · Develop proposals to encourage investment | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade; Ministry of Finance; Ministry of Justice | Intensified dialogue with Government on reform of the banking system as a means of improving the investment climate | Increase in banks’ capitalization; better corporate governance principles and internal control systems; expansion of banking networks; real time banking settlement; anti-money-laundering legislation; deposit insurance introduced | Private Sector Development Project; Financial Sector Advisory Program; Business Environment Study | USAID IMF FIRST | Minimum capital raised to ?3.5m; improved confidence in banking system; better access to finance; anti money laundering regulations in compliance with FATF requirements |
| · Implement export promotion measures | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade; Ministry of Finance | Support for removal of institutional (governance) obstacles to fulfilling Georgia’s Export Potential | Progress in implementing recommendations of Trade Study/Workshop | Trade and Transport Facilitation Project; Private Sector Development Project; Business Environment Study; Rural Development Project | USAID | Improved perception of environment for exporters in business surveys |
| Human Capital Development | ||||||
| Improvement of Health | ||||||
| · Revise government commitments in healthcare sector to ensure full financing | Ministry of Labor, Healthcare and Social Protection; Ministry of finance | Assist government to define health financing strategy focusing on improvements in mobilization, allocation and management of public and private resources, help build government capacity in evidence based policy-making, planning, monitoring and evaluation, as well as regulation | Definition of basic benefit package, financing methodology and co-payments, as well as recurrent costs; improved resource mobilization and allocation, including introduction of incentive-compatible provider payment systems | Health Sector Note, JSDF Grant on community health insurance | JSDF SIDA DFID WHO | Definition of basic benefit package, financing methodology, co-payments, and recurrent costs; better resource mobilization and allocation, including introduction of incentive-compatible provider payment systems |
| Improvement of Education | ||||||
| · Develop programs for basic education | Ministry of Education, Ministry of Culture | Improving quality of education and access of the poor | Stakeholders actively engaged in improving education quality and outcomes | Education Project | SOROS | 97 percent enrollment in basic education for the poorest quintile; 60% of consolidated education expenditures continue to be allocated to primary/secondary education |
| Improvement of Social Risks Management | ||||||
| · Definition of nature and periodicity of government commitments in the social sector to ensure full financing | Ministry of Labor, Healthcare and Social Protection; State Social Security Fund; Ministry of Finance | Timely execution of Government obligations in the social sectors; fiscal affordability and sustainability | No-arrears in social transfers, increased poverty alleviation impact | Public Expenditure Reviews, PRSC in High Case | No new arrears; poverty incidence decreased by 6 percentage points | |
| · Enforce package of draft bills on compulsory social insurance | Ministry of Labor, Healthcare and Social Protection, State Social Security Fund | Support to implementation of social insurance system | Better performance of the pension system | Social Protection Reform Project | No pension arrears; financing of social insurance/assistance benefits separated | |
| · Phased increase of pensions | Ministry of Labor, Healthcare and Social Protection, State Social Security Fund | Dialogue on pension policies | Increase in pensions | Public Expenditure Reviews; Social Protection Reform Project | Average real pension increased by 20%; extreme poverty among elderly reduced | |
| · Fiscal sustainability of pension system based on compulsory social insurance | Ministry of Labor, Healthcare and Social Protection, State Social Security Fund | Dialogue on pension policies | Satisfactory performance of the pension system | Public Expenditure Reviews; Social Protection Reform Project | Improved fiscal sustainability of pension system | |
| Development of Priority Branches of the Economy | ||||||
| Energy and Infrastructure | ||||||
| · Reorganize electricity wholesale market to resume the functions of financial and technical operator | Ministry of Fuel and Energy | Support for direct contracts between generators and large end consumers, subject to transparent terms and implementation | Direct contracts between generators and large end consumers | EMSP | EBRD KfW USAID | Electricity market successfully reorganized |
| · Amend tariff policy in line with model of wholesale market and consider liberalization of prices | Ministry of Fuel and Energy; Energy Regulatory Commission; Ministry of Economy | Tariff policy; adequate appropriations to energy in state budgets | Lower commercial losses; state budgets fully cover energy costs; higher collections by state energy companies in distribution, transmission; improved financial viability | EMSP | EBRD IMF KfW USAID | Cash payment collections at the wholesale electricity market above 65%; dissemination to public of detailed sector performance indicators |
| · Approve strategy to manage energy sector debts | Ministry of Fuel and Energy, Ministry of Finance | Establishment of a professional Debt Restructuring Agency for the power sector | Legacy debt no longer a threat to the financial viability of the power sector | EMSP | EBRD IMF KfW USAID | Debt Restructuring Agency led by international experts in full operation; legacy debt issue resolved |
| · Transfer energy sector companies, including National Distribution Company, under management contract in accordance with existing strategy | Ministry of Fuel and Energy | Georgian Unified Distribution Company (GUDC) under long-term management contract | GUDC under long-term management contract | EMSP | EBRD KfW USAID | GUDC under long-term management contract; other management contracts fully operational |
| · Improve transport regulatory administration | Ministry of Transport and Communication | MOTC restructuring | Improved functioning of restructured MOTC | Secondary Roads Project; Transport Facilitation Project | SDRG restructured and road financing arranged to provide stable source for road funding to maintain and improve roads | |
| · Technical monitoring of emergency conditions, restore status of premises and constructions of strategic importance and special complexity of the energy, transportation, communication and construction infrastructure as well as those damaged from earthquakes | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade, Ministry of Fuel-Energy, Ministry of Transportation and Communication, State Department of Highways | Development of road data bank for SDRG to take prompt, cost-effective action in emergencies | The data bank is used to prioritize annual road program | Secondary Roads Project; Transport Facilitation Project | Road data bank in use and SDRG expanded to cover local rural roads | |
| · Improve implementation of road construction plan, identify strategic projects and sources of financing | State Department of Highways | Road construction plan, equipping SDRG with tools to develop and manage the plan | 5 year rolling plan a standard procedure in SDRG | Secondary Roads Project; Transport Facilitation Project | EU, Kuwait Development Fund | Performance indicators to be developed in Secondary Roads project |
| · Form information network covering the entire country | State Department of Information | Improving rural access to telecommunications services | Better and more affordable access by the rural population to telecommunications | Rural Telecommunications Project | Higher proportion of the rural population having affordable access to telecommunications | |
| Tourism | ||||||
| · Prepare special program to attract additional funding from international donor organizations to develop tourism | State Department of Tourism and Resorts | Development of community-based tourism | Realistic development strategy for tourism -- especially community-based tourism -- that promotes broad-based local development, reduces administrative barriers to tourism, and supports preservation | Community-based tourism | Realistic development strategy for community-based tourism, including reduced administrative barriers and more focus on preservation | |
| Agriculture and Food | ||||||
| · Establish water consumer associations in rural areas | Ministry of Agriculture, Melioration System Management Department | Support to establishing new, and strengthening existing, water users associations to manage irrigation facilities | More and better functioning water user associations | Irrigation and Drainage Rehabilitation Project | EU TACIS | Legal framework for WUAs established; number of water user associations registered increased |
| · Develop unified geographic computer system of land cadastre and registration | Ministry of Agriculture and Food, State Department of Land Management | Support to strengthening capacity of State Department of Land Management to carry out land registration based on cadastre survey | Increased capacity of State Department of Land Management | Agriculture Development Project | IFAD, USAID KfW | Eleven land registration centers established; satellite imagery used for titling in mountainous regions |
| · Establish private veterinary services | Ministry of Agriculture and Food, Veterinary Department | Dialogue with Government on Veterinary reforms | Law to establish private veterinarians passed | ARET | USAID | Government starts veterinary reform process |
| · Structural reorganization of plants protection services | Ministry of Agriculture and Food, Plant Protection Service | Discussion with MAF on reform of plant protection services | Follow-up to merging of three agencies into a single plant protection agency | ADP | USAID | Reduced illegal trade of agro-chemicals; relevant laws passed |
5.1.6 The World Bank Partners in Georgia
| SECTOR | LEAD NATIONAL AGENCY | PARTNERS |
| Agriculture | Ministry of Agriculture and Food | IFAD, FAO, DFID, UNDP, KFW |
| Culture | Ministry of Culture | EU |
| Education | Ministry of Education | SOROS |
| Energy | Ministry of Fuel and Energy | USAID, KFW, EBRD |
| Financial Sector | Ministry of Finance and Tax Revenues | IMF |
| Forestry | State Department of Forestry | FAO, WWF, CIDA |
| Governance | State Chancellery, Anti-corruption Policy Coordination Council | Netherlands, IMF, DFID, USAID, UNDP, |
| Health | Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs | SIDA, DFID, WHO |
| Judicial | Ministry of Justice | EU, USAID, SOROS, ABA, DOJ |
| Municipal Development and Decentralization | Georgian Municipal Development Fund (MDF) |
|
| Poverty Reduction | Secretariat of Governmental Commission on PREGP (Poverty reduction and Economic Growth Program) | IMF, UNDP, DFID, USAID |
| Private Sector | Ministry of Economy, Industry and Trade | USAID, EBRD, BP |
| Protected Areas | State Department of Protected Territories, Preserves and Hunting Grounds | UNDP |
| Roads | Ministry of Transport, Telecommunications and Post |
|
| Social Infrastructure | Georgian Social Investment Fund (GSIF) | KFW |
| Transport and Communications | Ministry of Transport, Telecommunications and Post |
|
5.2 USAID
USAID assistance in the economic growth area focuses on strengthening agriculture sector, assisting the NBG to improve its supervision, inspection, and enforcement capacity, and furthering land market reform. The Georgian Enterprise Growth Initiative (GEGI) is a major new private sector development activity to be implemented in close coordination with the CAS programs. USAID has been actively involved in the energy and environmental sectors providing TA to regulatory bodies, supporting privatization of the energy sector and improvement of the international investment climate, assisting in elaboration of environmentally sound laws in the energy sector as well as policies in the sector oriented towards energy efficiency, conservation and water management. Through democracy and governance oriented projects USAID supports increased awareness of legal rights, judicial and BAR reform initiatives, strengthening local governments, building professionalism of independent mass media as well as capacity of civil society and NGOs. USAID initiatives in the social sectors include programs in the regions to support income generation and economic self-reliance activities among internally displaced persons, crisis assistance to the most vulnerable, health care partnership programs and reproductive health programs which promote improved maternal and perinatal services, safe motherhood, family planning, health information systems, and STI/HIV awareness and prevention.
5.3 EBRDEBRD main objective in Georgia is to expand private sector development activities in the country. During years 2002 and 2003 it has been engaged in the active political dialogue with the Government to support the substantial reduction of administrative barriers to investments, representation on the board of companies and banks, support of the initiatives of local business associations. EBRD aims at further strengthening of the Georgian banking sector through ongoing support to the regulator, management training, and further consolidation. EBRD’s interventions include financing to business start-ups and existing micro, small and medium-sized enterprises as well as selectively supporting critical investments in infrastructure with specific focus on those projects that promote the commercialization of infrastructure, particularly of the energy sector.
5.4 EUEU’s Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (PCA) provides for cooperation in a wide range of areas including Food Security Program (in amount of ? 25 million for the period 2002-2003), rehabilitation in conflict zones (Engury Power Plan in Abkhazia), macro-financial assistance (establishment of an agricultural credit institutions, reforms in accountancy and audit, assistance to the insurance sector and securities market regulation), support to trade liberalization, customs, and development of transport infrastructure networks, advice on economic legislation and country legislature harmonization with the EU standards, investments in primary health care reconstruction program and development of the Georgian National Health Program and training of medical and administrative personnel as well as provision of the technical assistance for the development of the model of Regional Health financing. TACIS is the main financial instrument supporting the implementation of the PCA.
5.5 GTZGTZ, working on behalf of German Government, provides support in the health sector primarily focusing on structural improvements and training for medical technicians, promotes vocational training sector to improve commercial and agricultural training and upgrading, implements projects to privatize agriculture and build up effective land- and debt-management systems, promotes export and investment, and has been assisting in judicial and legal training as well as practical application of civil law in Georgia. German assistance is also channelled through KfW supporting credit line to agriculture sector enterprises, participating with an equity stake in Procredit Bank, is conducting cadastral works almost all over the country, and contributing to social infrastructure in the districts bordering Borjomi-Kharagauli National Park as well as supporting the Government to rehabilitate schools and health facilities damaged during the recent earthquake.
5.6 CIDABilateral assistance also comes from Canada (CIDA) mostly through the regional projects supporting trade policy capacity, expanding the micro credit programs, promoting NGO capacity development program that supports the principles of good governance, strengthening health reform through the appropriate application of health information technology and information management strategies, and contributing drought victims relief operations.
5.7 DFIDDFID has recently approved a new Primary Health Care (PHC) Development project through which technical assistance will be provided to the Government in the areas of human resource development for the PHC system, health care financing, health management information systems, capacity building for the health policy development. DFID has been supporting the SDS in the multi-sector household and labor market surveys. The ongoing program also has a component aiming at development of good governance and civil society in two regions of Georgia as well as conflict reduction and confidence-building component.
5.8 The Government of the NetherlandsThe Netherlands has provided support for a wide range of activities, focusing on good governance, human rights and peace building, as well as substantial budget support in conjunction with SAC III. Dutch support in the three focus areas will continue, including for . election preparation, prevention of trafficking in human beings, confidence building measures in Abkhazia and support for NGOs involved in poverty alleviation and human rights
5.9 IFADIn the agriculture sector IFAD supports rural development program for mountainous and highland areas and credit-union development and rural credit activities for small farmers, while FAO provides financial support to hazelnut sector rehabilitation project.
5.10 UNDPUNDP in Georgia focuses its program activities in three areas: (a) democratic governance; (b) poverty reduction; and (c) environmental protection, as outlined in the second Country Cooperation Framework for Georgia (2001-2005). In the sphere of Governance, major ongoing initiatives include support to Foreign Investment Advisory Council, strengthening the Anti-corruption Promotion Group, and assistance to the Constitutional Court and Public Defender’s Office. UNDP has been active in capacity building of the Georgian International Oil Corporation and of the National Security Policy Management. UNDP is contributing to land market development through creation of a computerized program of registration. Technical and financial inputs have been provided to strengthen the capacity of Georgian institutions responsible for national statistics, notably the State Department of Statistics. Environmental challenges are being addressed through the projects supporting recovery, conversation and sustainable use of Georgia’s agro-biodiversity, removal of barriers to small hydro power sector development, and capacity building of the Ministry of Environment.
5.11 UNICEFUNICEF priorities in Georgia include: education, integrated childhood development, immunization, fighting HIV/AIDS, and protecting children from violence, exploitation, abuse and discrimination. It has been assisting the Government in national training of health workers and professionals and in providing universal access to basic health services for women and children. UNICEF has been helping the Government in promoting the implementation of the Convention on the Rights of the Child. Support also includes ensuring inclusive education for children with disabilities and providing psychosocial support to children in need of special protection as well as introducing alternative, non-institutional methods of childcare. Child de-institutionalization has been also supported by SIDA through provision of technical assistance during social protection reform project preparation and implementation phases.
[1] Presidential Decree 678 calls for elaboration of a new law on privatization of agricultural land and completion of the national land cadastre by the year 2005. Apparently a draft of such a law is already circulated in the Parliament.
[2] Amended September 3, 1997; September 18, 1997; December 12, 1997; February 5, 1998; May 1, 1998; May 13, 1998; May 29, 1998; June 26, 1998; October 13, 1998; October 30, 1998; December 24, 1998; April 2, 1999; April 16, 1999; June 8, 1999; June 9, 1999; June 25, 1999; July 23, 1999; September 9, 1999; December 9, 1999; December 24, 1999; December 28, 1999; March 24, 2000; June 28, 2000; July 13, 2000; September 27, 2000; September 28, 2000; October 11, 2000; October 13, 2000; November 10, 2000; November 24, 2000; December 5, 2000; December 13, 2000; December 29, 2000; March 16, 2001; April 27, 2001; June 8, 2001.
[3] Resident physical persons: who received income that was not taxed at the source of payment in Georgia; who have funds in accounts in foreign banks; or whose expenditures during the tax year exceed 25,000 GEL. As well as, non-resident physical persons with income from a Georgian source that is not taxed at the source of payment.
[4] In hindsight, the VAT threshold should have been much higher when the VAT was adopted.
[5] For example, it would help screen shell companies created for the very purpose to evade tax payments.
[6] FIAS, Georgia: Study of administrative barriers to investment, December 2001.
[7] This also applies to foreign investors, as numerous critical articles on taxation in Georgia published by the American Chamber of Commerce newspaper demonstrate.
[8] O: Observed.
[9] LO: Largely Observed.
[10] MNO: Materially Non-Observed.
[11] NO: Non-Observed.
[12] NA: Not Applicable.
[13] Although a draft law on Investment Funds has been prepared with assistance from USAID (IOSCO, 2001)
[14] C: Compliant.
[15] PC: Partially Compliant.
[16] MNC: Materially Non-Compliant.
[17] NC: Non-Compliant.
[18] NA: Not Applicable.
[21] Because Georgia is a member of the 1961 Hague Convention, on the abolition of legalization requirements of documents issued in foreign countries, only documents originating from countries not signatories to the Hague Convention require legalization by the consular offices.
[22] Article 4.3
[23] No. 2132-11s
Ïîõîæèå ðàáîòû
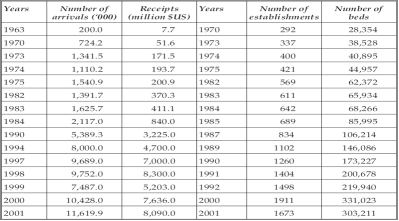
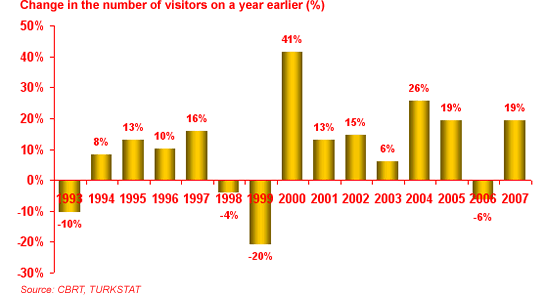
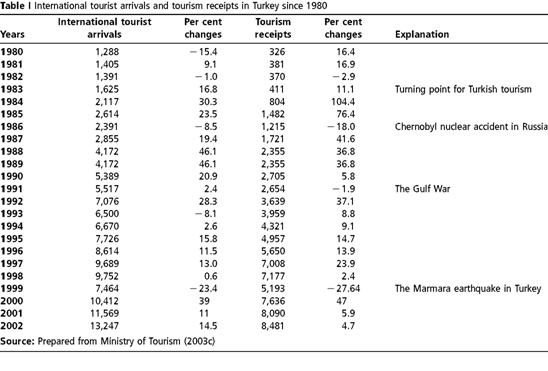
... .” HYPOTHESIS So, let’s examine the first hypothesis Is the number of visitors growing as The Ministry of Culture and Tourism is focused on the development of sustainable tourism? With its objectives: +Examination of sustainable tourism in Turkey +Examination of The Ministry of Culture and Tourism strategy +Examination of tourist growth Turkey (http://www.wikipedia.org ) Turkey is ...
... in 1975 together with Paul Alien, his partner in computer language development. While attending Harvard in 1975, Gates together with Alien developed a version of the BASIC computer programming language for the first personal computer. In the early 1980s. Gates led Microsoft's evolution from the developer of computer programming languages to a large computer software company. This transition ...
... . Only since 1960 has the British Sovereign been featured on English bank notes, giving The Queen a unique distinction above her predecessors. STAMPS There is a close relationship between the British Monarchy and the postal system of the United Kingdom. Present-day postal services have their origins in royal methods of sending documents in previous centuries. Nowadays, the image of The ...
... remain the most optimistic people in the world, but with the century drawing to a close, opinion polls showed that trait in shorter supply than usual. Geography and regional characteristics. The USA stretches from the heavily industrialized, metropolitan Atlantic coast, across the rich farms of the Great Plains, over the Appalachian and the Rocky Mountains to the densely populated West ...




0 êîììåíòàðèåâ