Навигация
Planning of actions for a labour safety
5.2 Planning of actions for a labour safety
In connection with inclusion of questions of a labour safety of workers of branch in the Concept of development of public health services and a medical science in the Russian Federation, considering the numerous offers arriving from controls, establishments of public health services and the trade-union organisations, on the basis of the Recommendations confirmed by the decision of Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation from 29.12.96? 74, Ministry of Health of Russia has prepared the project of the Program which has been considered and approved at session of Board of Ministry of Health of Russia 23.12.97. The program consists of 4 sections: 1) Legal and standard maintenance of protection works. 2) organizational and technical maintenance of a labour safety. 3) training of workers on a labour safety, a supply with information in the field of a labour safety. 4) scientific maintenance of a labour safety. The Program purpose? Working out of prime measures under the prevention of an industrial traumatism and the professional ache diseases, elimination of the negative moments in the organisation of this work. Program section 1 provides work on revision operating and working out of new rules and typical instructions on a labour safety and safe operation of branches, offices, laboratories, the equipment of establishments of public health services and Gossanepidnadzor. Financing of these works is supposed to be carried out at the expense of means of the Federal budget. Section 2 provides working out of programs of improvement of conditions and protection work at level of controls and establishments of public health services of subjects of the Russian Federation (there where such programs are not developed yet). In section 3 creation of system of improvement of professional skill concerning a labour safety for heads, experts, attendants, working out differentiated (according to volume of performed work) training programs on a labour safety is provided. Training of heads will be carried out on the basis of the Russian medical academy последипломного formations and on places, the medical institutions having the permission to the right of training concerning a labour safety. The basic actions of section 4 are researches of working conditions and preparation of scientifically well-founded offers on a work and rest mode, and also on granting of privileges and indemnification workers of the branch, working in especially harmful and dangerous working conditions. These actions it is planned to carry out forces of a branch science. It is supposed to provide financing at the expense of means of Federal fund of obligatory medical insurance. Planning of actions for a labour safety consists in working out of instructions on a labour safety, actually planning of actions, the control over carrying out of these actions and observance of instructions, and also to investigation of accidents and the illnesses connected with dangerous factors at realisation of professional work. Instructions on a labour safety can be developed for workers of separate trades, and for separate kinds of works. Instructions are developed for workers on the basis of typical instructions, safety requirements stated in operational and repair documents of the equipment, used on the given enterprise, and also in the technological documentation of this enterprise taking into account conditions of production. Instructions by trades and on separate kinds of works are developed for workers according to the list which is made by a protection service of work of the enterprise with participation of heads of divisions.
The conclusion
So, the innovative project considered in the present degree research consists in the organisation of manufacture and sale of the diagnostic device? The biotest?, for a finding points, carrying out the express train of diagnostics of a condition of a human body by results of measurements of parametres of biologically active points, testings of preparations and therapy according to R.Follja's technique. The Scope? The diagnostic device of the doctor of the therapist, the homeopathist, the anaesthesiologist, etc. Novelty of the project (innovation, an innovation) consists what release of the product, analogue not having to in Russia, abroad is supposed? The device very cheap and reliable. Besides questions theoretical (economic and legal) the bases of innovative activity, questions of management the personnel in the scientific organisations and safety issues of ability to live, the central part of the present degree work was:? Working out of own model of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project;? The comparative description of two techniques (traditional and offered) estimations of efficiency of the innovative project;? Carrying out of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project of manufacture of the device? The biotest? By both techniques;? Comparison of results of an estimation of efficiency of the project by both techniques. We will short formulate conclusions on these positions. Existing (standard, classical) the technique of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project includes: 1. Calculation of factor of the pure resulted cost (NPV); 2. Calculation of an index of profitability of investments (PI); 3. Calculation of internal rate of return or norm of profitability of the investment (IRR); 4. Decision-making on project realisation. The Offered model of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project will include: 1. An estimation of competitive advantages of the goods (service) offered by the considered project; 2. Estimation of a market capacity of sale on which the considered project, including as the basic indicator the sales volume forecast is focused; 3. Calculation of the capacity necessary for realisation of the project, and its comparison to a predicted sales volume; 4. Calculation of the project of volume of investments necessary for realisation; 5. Calculation? Break-even points?, i.e. critical for a recoupment of the project of volume of output; 6. Summarising calculation of the basic indicators of the project, such as profit (total and pure); profitability of production; profitability of funds; the full cost price; labour input; the predicted price for production; a critical sales volume and release; efficiency of capital investments; a time of recovery of outlay; a stock of financial durability; 7. Decision-making on realisation (or to a deviation) the project. How it has been noted in degree work, the standard model is less labour-consuming in the application? In it, undoubtedly, there is an advantage of standard model before offered model. However, the basic difference between standard and offered models what the offered model gives more information on the concrete project? And in it the big advantage of offered model before the standard. For example, the standard model of an estimation of efficiency of the project cannot answer on a question, in what volume it is necessary to make production that the project was profitable? The standard model uses this indicator, but does not count it whereas the offered model at first counts it, and then uses. So, both those and other models can tell that, for example, as a result of three years of realisation the project will be profitable whereas the offered technique can tell that the project will pay off in 7 months. The offered model also has one essential lack? All basic indicators pay off on the basis of the sales volume forecast. But it is the forecast, obviously, can be only approximate. Hence, all basic indicators of offered model will be approximate. We will describe results of application of these models to an estimation of efficiency of the concrete innovative project. 1. On the importance for an estimation of efficiency of the project in two considered models are comparable factor of the pure resulted cost (NPV) from standard model and an indicator of net profit plus size of initial investments. That is in standard model an indicator
Whereas in offered model a similar indicator 2209 + 14011 = 16220 c.u., where 2209 c.u.? Profit at the disposal of the organisation (a difference between net profit and returned investments). A difference in the sum here that the offered model in calculations uses the predicted size of a sales volume. It is the forecast becomes on the basis of linear approximation which, as it is known, yields approximate results. It is necessary to notice, what the divergence of values of these factors makes all .
The literature list
1. Авдеев В.В. Управление персоналом: технология формирования команды. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2002. – 431 c.
2. Аккредитация и лицензирование медицинских учреждений: сборник материалов. – Новосибирск: Управление здравоохранения мэрии г. Новосибирска, 2001, Т.2. – 408 с.
3. Анализ финансово-хозяйственой деятельности предприятия / Н. П. Любушин, В. Б. Лещева, В. Г. Дьякова.; Под ред. Н. П. Любушина. – М.: ЮНИТИ, 2004. – 219 с.
1. Ансофф И. Стратегическое управление. - М.: Экономика,1999. – 318 с.
2. Артамонов Б.В. Стратегический менеджмент. - М.: ЮНИТИ, 2002 – 213. с.
3. Артеменко В. Г., Беллендир М. В. Финансовый анализ. – М.: Издательство «ДИС», 2003. – 327 с.
4. Арустамов Э.А., Пахомкин А.Н., Платонов А.П., Рыкова И.В. Организация предпринимательства. – М.: Издательско-книготорговый центр «Маркетинг», МУПК, 2004. – 279 с.
5. Берл Г. Киршнер П. Мгновенный бизнес-план: двенадцать быстрых шагов к успеху. – М: Дело, 2003. – 289 с.
6. Бернстайн Л.А. Анализ финансовой отчетности. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2004. – 118 с.
7. Бизнес-план. Методические материалы // Под. ред. профессора П.Л. Маниловского. – М: Финансы и статистика, 2002. – 518 с.
8. Бизнес-план. Методические указания. // Под редакцией Н.А. Колесниковой – М: Финансы и статистика, 2003. – 319 с.
9. Бизнес-план. Рабочая книга – СПб: ЭИС, 2002. – 489 с.
10. Бринк И.Ю., Савельева Н.А. Бизнес-план предприятия. Теория и практика. – Ростов н / Д: Феникс, 2003. – 513 с.
11. Буров В.Н. Стратегическое управление фирмами. – М.: Инфра-М, 2002. – 285 с.
12. Буров В.П., Морошкин О.К. Бизнес-план. Методика составления реальный пример. – М: ЦИПКК, 2003. – 218 с.
13. Бухалков М.И. Внутрифирменное планирование. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2000. – 318 с.
14. Виханский О.С. Стратегический менеджмент. – М.: Издательство МГУ, 2003. – 159 с.
15. Герчикова И.Н. Менеджмент.– М.: Банки и биржи, ЮНИТИ, 2001.– 456 с.
16. Глущенко В.Д. Предпринимательская деятельность ЛПУ: основные направления // Главный врач, 2001, №4. – С. 12-19.
17. Дегтяренко В.Н. Оценка эффективности инвестиционных проектов. – М.: Инфра-М, 2002. – 165 с.
18. Деловое планирование: Методы. Организация. Современная практика. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 1999. – 315 с.
19. Ефремов В.С. Стратегическое планирование в бизнес-системах. – М.: Финпресс, 2001. – 240 с.
20. Ильин А.И. Планирование на предприятии. В 2-х частях. Часть 1. – Минск: ООО «Новое знание», 2001. – 321 с.
21. Ильин А.И. Планирование на предприятии. В 2-х частях. Часть 2. – Минск: ООО «Новое знание», 2001. – 341 с.
22. Информационно-справочная система «Новосибирская область». – Новосибирск: Инжгеодезия, 2003. – 1 компактдиск.
23. Кадыров Н.Ф. Экономическая служба лечебно-профилактических учреждений. – М.: ГАРАНТЪ, 2000. – 800 с.
24. Карлоф Б. Деловая стратегия. – М.: Экономика, 1999.- 146 с.
25. Ковалев В.В.. Финансовый анализ: методы и процедуры. Финансы и статистика. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2002. – 572 с.
26. Котлер Ф. Основы маркетинга. – М.: Прогресс, 2002. – 517 с.
27. Кучеренко В.З. Основы медицинского маркетинга. – М.: ММА им. И.М. Сеченова, 2000. – 121 с.
28. Лебедев А.А. Использование маркетинговой философии в деятельности медицинских учреждений государственной системы здравоохранения в условиях рыночной экономики // Экономика здравоохранения, 1999. №7. – С. 31-37.
29. Лебедев А.А. Рыночная экономика и медицина. – Самара: Дом печати, 2001. – 201 с.
30. Лившиц К.А. Аналитическая функция маркетинга // Мир медицины, 1998. №7. – С. 13-14.
31. Липсиц И.В. Бизнес-план – основы успеха: Практическое пособие. – М: Машиностроение, 2003. – 321 с.
32. Малахова Н.Г. Маркетинг медицинских услуг. – М.: МЦФЭР, 2001. – 184 с.
33. Маркова В.Д., Кузнецова С.А. Стратегический менеджмент. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2002. – 288 с.
34. Медынский В.Г., Скамай Л.Г. Инновационное предпринимательство. – М.: «Инфра-М», 2002. – 445 с.
35. Методические указания по оценки эффективности инвестиционных проектов и их отбору для финансирования. – М.: Официальное издание, 2004. – 278 с.
36. Основы экономического анализа хозяйствующего субъекта. // Под ред. А.Н. Богатко – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2003. – 287 с.
37. Оценка бизнеса. Сборник статей. / Под общ. Ред. А.Г.Грязновой. М.А. Федотовой. – М.: Инфра-М, 2002. – 312 с.
38. Сборник бизнес-планов с комментариями и рекомендациями. Изд. 2. Под ред. В.М. Попова. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2002. – 386 с.
39. Скопылатов И.А., Ефремов О.Ю. Управление персоналом. – СПб.: Изд-во Смольного ун-та, 2000. – 512 с.
40. Справочник финансиста предприятия. 3-е изд., доп. и перераб. ИНФРА-М, 2001. – 326 с.
41. Старобинский Э.Е. Как управлять персоналом. – М.: ЗАО «Бизнес – школа «Интел – синтез», 1999. – 368 с.
42. Стародубов В.И. Инвестиционные проекты в области медицины // Экономика здравоохранения, 2001. №10. – С. 23-27.
43. Стратегическое планирование и управление. // Под ред. Иванова П.Д. – СПб.: Питер Ком, 2001. – 348 с.
44. Травин В.В., Дятлов В.А. Основы кадрового менеджмента. – М.: Дело, 2001. – 336 с.
45. Томпсон А.А., Стрикленд А. Дж. Стратегический менеджмент: Искусство разработки и реализации стратегии. // Пер. с англ. Под ред. Л.Г. Зайцевой, М.И. Соколовой. – М.: Банки и биржи, ЮНИТИ, 2000. – 576 с.
46. Управление проектами / Под общ. Ред. В. Д. Шапиро. – СПб.: Два-Три, 1996. – 412 с.
47. Уткин Э. А., Кочетков А. И. Управление персоналом в малом и среднем бизнесе. – М.: Аналис, 2000 – 206 с.
48. Фатхутдинов Р.А. Инновационный менеджмент. – Спб.: «Питер», 2003. – 400 с.
49. Ховард К., Коротков Э. Принципы менеджмента. Управление в системе цивилизованного предпринимательства. Учебное пособие. – М.: ИНФРА – М, 2002. – 224 с.
50. Шеин В.Н и др. Корпоративный менеджмент. Опыт России и США. – М.: Новости, 2003. – 208 с.
51. Шекшня С.В. Управление персоналом современной организации. – М.: «Бизнес-школа «Интел-синтез», 2001. – 300 с.
52. Экономика предприятия. / Под ред. И.О. Волкова. – М.: Инфра – М, 2002. – 416 с.
53. Экономика предприятия. / Под ред. В.М. Семенова. – М.: Центр экономики и маркетинга, 2001. – 328 с.
54. Экономическая стратегия фирмы. // Под ред. А.П. Градова. – СПб.: Специальная литература, 2002. – 415 с.
55. Экономический анализ и планирование деятельности медицинских учреждений: Трудовые показатели. Производственная деятельность. Финансовое состояние. Составление смет. – М.: Международный центр финансово-экономического развития, 2002. – 198 с.
56. Экономико-правовые основы организации оказания платных медицинских услуг. – М.: ГРАНТЪ, 2000. – 436 с.
57. Яковлев В.К. Правовые основы охраны труда. Комментарии. // Материалы для подготовки и проведения аккредитации и лицензирования медицинских учреждений (Утверждены Верховным Советов Российской Федерации от 06.08.93 №5600-1 (в ред. Федерального закона от 18.07.95 №109-AP)) – Новосибирск: Управление здравоохранения мэрии г. Новосибирска, 2001, Т.3.
58. Якушев К.Р. Новосибирск в цифрах: сборник статистических материалов. – Новосибирск, Издательство ГПНТБ, 2004. – 116 с.
59. www.unitc.ru/lawprint.php
60. www.unitc.ru/law.php?id=2&fs=40
61. www.invur.ru/index.php?page=docs&cat=oficial&scat=zakon&doc=zak_tymen
Похожие работы
... . The advertising idea is defined. Advertising strategy is however insufficiently clearly stated. We will take advantage of the given reserve for increase of efficiency of an advertising campaign of Open Company "Натали", i. e. we will develop advertising strategy. 3.3 Use of methods of optimization in advertising activity One of optimisation methods in advertising activity is use of ...
... her behavior, beliefs, or perceptions. The manner in which a particular individual classifies cognitions in order to impose order has been termed cognitive style. 7. Tests and Measurements Many fields of psychology use tests and measurement devices. The best-known psychological tool is intelligence testing. Since the early 1900s psychologists have been measuring intelligence—or, more accurately ...
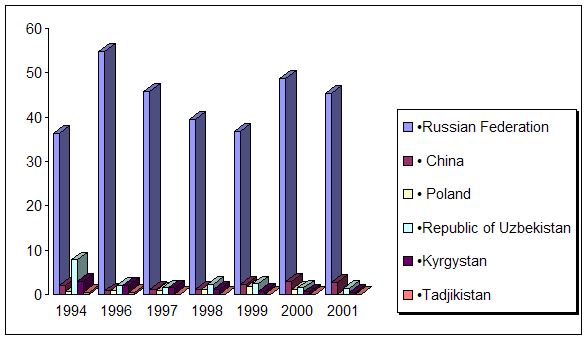
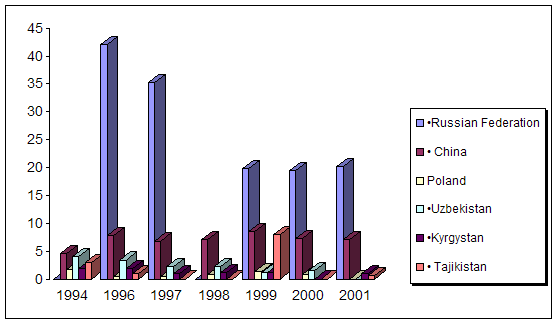
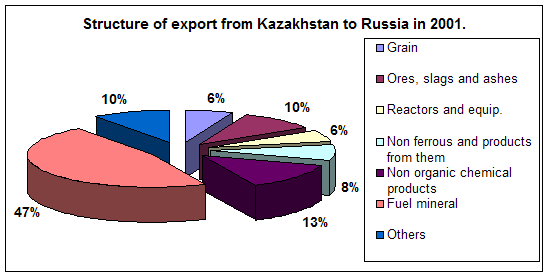
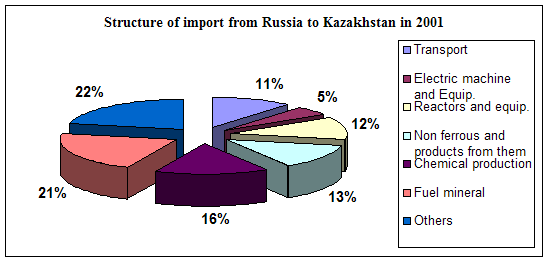
... course of republic. A complex of the reasons conditions and factors having not tactical, but basic essence and long-time character stipulates it. Today common balance of mutual relation between Kazakhstan and Russia has positive character, as consider each other as the strategic partners and it establishes the important premise for their mutual cooperating in the field of policy, economy, ...
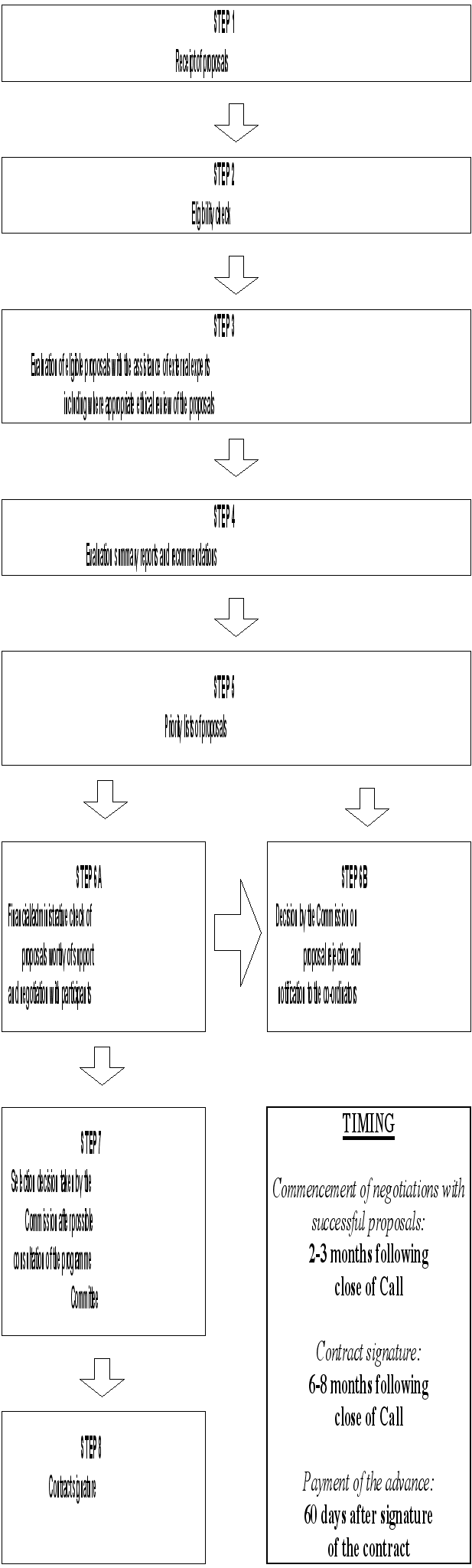
... a request for interested parties (Expression of Interest /Needs) to suggest ideas for activities that could be included. II.5.2 Implementation Modalities (“Types of actions") The “Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources” programme is implemented through the following types of actions: 1. Shared-cost actions, excluding “Support for access to research infrastructures”9 2. Concerted ...
0 комментариев