Навигация
Comparison of standard and offered models of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project
2.3 Comparison of standard and offered models of an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project
Two models applied to an estimation of efficiency of the innovative project were above described. A problem of this point? To give their comparative description. These models in two basic directions will be compared: by results and under the maintenance. Concerning comparison by results. Certainly, both these models bring the purpose the answer to an attention to the question, whether it is necessary to put up money in the considered innovative project or not; but these two models differently answer this question. In what here similarities and distinctions? It also is a problem of the comparative description of models by results. Comparison of models under the maintenance assumes transfer qualitative and the quantitative parametres used in both models, and also a conformity establishment between these two sets of parametres. Also it will be necessary to draw the general conclusion under the analysis of two models: what are? Pluses? And? Minuses? Applications of everyone them them what of them it is necessary to prefer at the analysis of the considered project, etc. Let's remind that the standard model assumes: 1) calculation of factor of the pure resulted cost (NPV); 2) calculation of an index of profitability of investments (PI); 3) calculation of internal rate of return or norm of profitability of the investment (IRR); 4) decision-making of realisation of the project. The offered model assumes 1) an estimation of competitive advantages of the goods (service), offered by the considered project; 2) an estimation of a market capacity of sale on which the considered project, including as the basic indicator the sales volume forecast is focused; 3) calculation of the capacity necessary for realisation of the project, and its comparison to a predicted sales volume; 4) calculation of the project of volume of investments necessary for realisation; 5) calculation? Break-even points?, i.e. critical for a recoupment of the project of volume of output; 6) summarising calculation of the basic indicators of the project, such as profit (total and pure); Profitability of production; profitability of funds; the full cost price; labour input; the predicted price for production; a critical sales volume and release; efficiency of capital investments; a time of recovery of outlay; a stock of financial durability; 7) decision-making on realisation (or to a deviation) the project. As it is possible to see, in sense of the purpose of application both these models have the purpose to answer a question, to accept to realisation or to reject the considered innovative project. On a way of the answer to this main point of model differ. Distinction consists what the standard model basically uses relative factors, and offered model? The absolute. To show this difference it is possible on a simple example: the standard model will tell that it is necessary to put money, as each enclosed rouble will bring 20 copecks of the income (i.e. Let's enclose 1 rouble, we will receive 1 rouble of 20 copecks), whereas the offered model of an estimation of efficiency will tell what to put up money in the innovative project costs, as the enclosed 1000 roubles will return as 1200 roubles. It is obvious, what this distinction not essential since at use of that and their other model it is possible to add with corresponding indicators? Standard model absolute, offered? The relative. The standard model uses relative indicators owing to tradition; the offered model uses absolute indicators from convenience reasons? At application of offered model it is possible to draw a conclusion of such grade that for realisation of the innovative project it is necessary to involve 14011 c.u. that through 7 months to receive 19873 c.u. Under the maintenance of indicators two considered models basically coincide. We will prove it. The standard model does not give possibility to execute an estimation of competitive advantages of the goods (service) offered by the considered project. However the standard model should contain this indicator as intermediate result? If the project is not directed on manufacture of a competitive product the project will be unprofitable and inefficient. A similar situation with a market capacity indicator? This indicator is not necessary for application of standard model, however, it does not mean that the offered model wins at standard, having this indicator. Capacity calculation is designated as an obligatory indicator at application of offered model. This indicator is not present as a part of standard model, however for calculations of factors of standard model anyhow it is necessary to know the capacity requested by the project. For this reason for application of standard model more low we will use this factor, but counted within the limits of application of offered model. Calculation of necessary volume of investments is necessary for application of both models: in offered model it is taken out as a separate indicator, in the standard? Is present at quality of parametre (intermediate result) at calculation of all indicators of standard model. Means, at application of standard model we will address partly to results of application of offered model. The break-even point pays off at application of offered model, but anything similar is not present in standard model. It is caused by what a break-even point? An indicator absolute whereas the standard model uses relative indicators. As to such characteristics of the project, such as profit (total and pure), profitability of production, profitability of the funds, the full cost price, the labour input, the predicted price for production, a critical sales volume and release, a time of recovery of outlay, a stock of financial durability? All of them are present at offered model, and at standard model there are only relative indicators, namely: efficiency of capital investments and analogue of an indicator of profitability of production. If the purposes of application of models coincide, some indicators and intermediate results are crossed, in what a difference between them and what for it is necessary to use two models? First of all, the numerical characteristics given by models, not should differ strongly from each other as we consider their application to the same project: If the standard model gives any numerical indicator its accuracy will be difficult for improving owing to that the standard model has already proved. We will draw conclusions by results of considerations of techniques of an estimation of efficiency of innovative projects. How it was possible to notice, the standard model is less labour-consuming in the application? In it, undoubtedly, there is an advantage of standard model before offered model. However, the basic difference between standard and offered models what the offered model gives more information on the concrete project? And in it the big advantage of offered model before the standard. For example, the standard model of an estimation of efficiency of the project cannot answer on a question, in what volume it is necessary to make production that the project was profitable? The standard model uses this indicator, but does not count it whereas the offered model at first counts it, and then uses. So, both those and other models can tell that, for example, as a result of three years of realisation the project will be profitable whereas the offered technique can tell that the project will pay off in 7 months. The offered model also has one essential lack? All basic indicators pay off on the basis of the sales volume forecast. But it is the forecast, obviously, can be only approximate. Hence, all basic indicators of offered model will be approximate. In the following chapter the comparative analysis of application of standard and offered model on an example of the concrete innovative project will be given.
Похожие работы
... . The advertising idea is defined. Advertising strategy is however insufficiently clearly stated. We will take advantage of the given reserve for increase of efficiency of an advertising campaign of Open Company "Натали", i. e. we will develop advertising strategy. 3.3 Use of methods of optimization in advertising activity One of optimisation methods in advertising activity is use of ...
... her behavior, beliefs, or perceptions. The manner in which a particular individual classifies cognitions in order to impose order has been termed cognitive style. 7. Tests and Measurements Many fields of psychology use tests and measurement devices. The best-known psychological tool is intelligence testing. Since the early 1900s psychologists have been measuring intelligence—or, more accurately ...
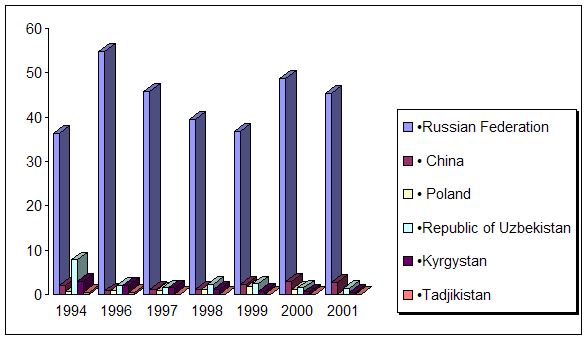
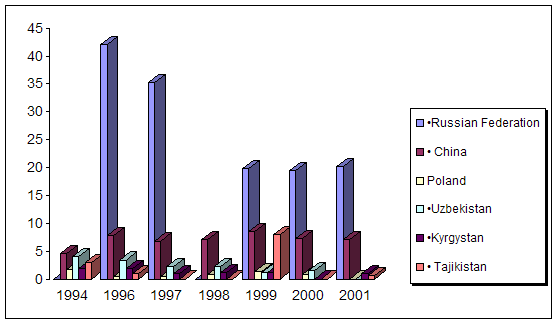
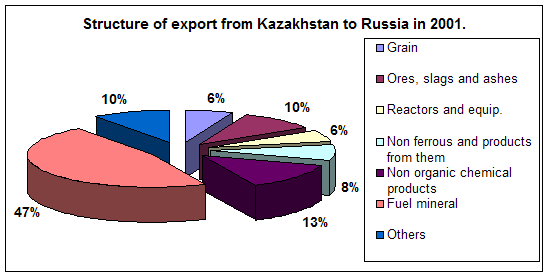
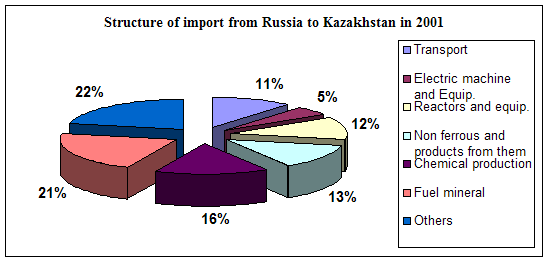
... course of republic. A complex of the reasons conditions and factors having not tactical, but basic essence and long-time character stipulates it. Today common balance of mutual relation between Kazakhstan and Russia has positive character, as consider each other as the strategic partners and it establishes the important premise for their mutual cooperating in the field of policy, economy, ...
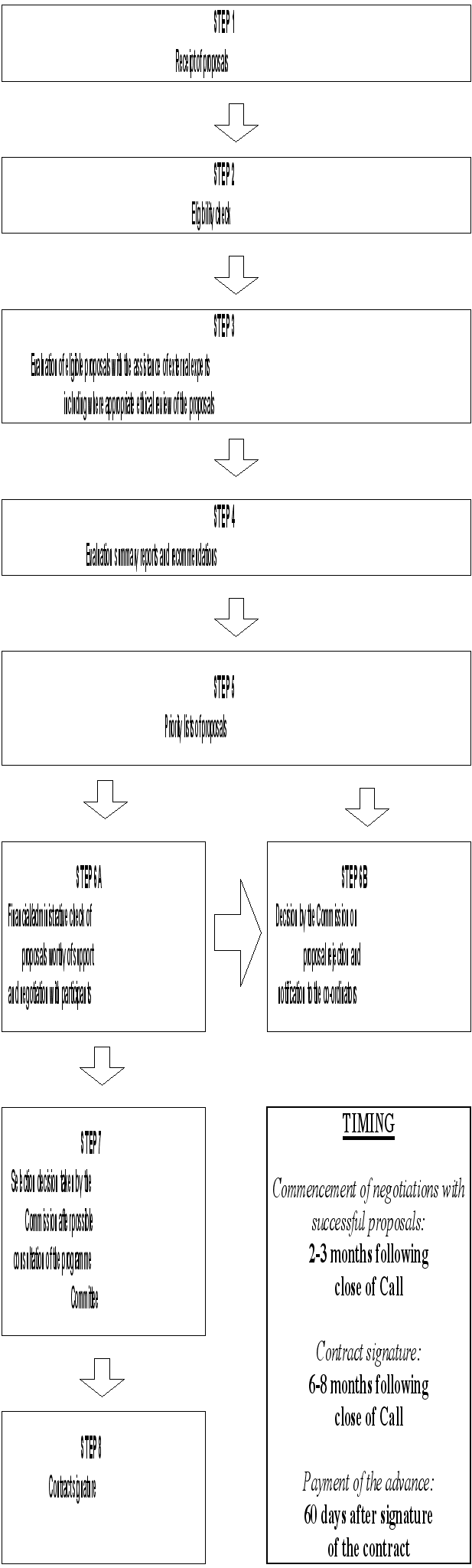
... a request for interested parties (Expression of Interest /Needs) to suggest ideas for activities that could be included. II.5.2 Implementation Modalities (“Types of actions") The “Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources” programme is implemented through the following types of actions: 1. Shared-cost actions, excluding “Support for access to research infrastructures”9 2. Concerted ...
0 комментариев