Навигация
Description of the task
5.3.3 Description of the task
Although, learning style according to the foregoing definition is viewed as relatively fixed and non-changeable, Singleton (1989:157) argues that it is possible to help adult learners to explore their own preferences and to shape their learning approach to suit the requirements of a particular learning task. Thus the main goal of observational tasks (see Appendix 3) is to help student teachers to get to grips with pupils’ learning preferences, and thereby to be able to adjust teaching materials and respond to learners’ subjective needs in their future planning, and apply some techniques that can enhance natural learners’ capabilities, habits and develop other skills through training.
Student teachers are recommended to obtain information about learning styles during the third meeting with the group. This time pre-service teachers have to observe language and learning behaviour of students, which is accompanied by emotional and affective state. Linguistic behaviour comprises language production that is organisation of speech, complexity of utterances, pitch of intonation, and speed of production. Observing these variables student teachers can reveal affective styles of their learners. For example, if a learner produces utterances in a low voice without haste and emotions, an observer can assume that this learner refers to introverts and thus s/he requires patience to be listened to. Observing learning behaviour that is the way students approach and process a task, materials they use, manner of solving a problem, their social behaviour student teachers can obtain information about pupils’ cognitive and sensory styles. Trainees should notice whether a pupil uses additional aids such as pencils or fountain pens to highlight some information in the textbook, or whether s/he faces her/his partner during pair-, group work. These situations characterise a visual learner and a FD learner respectively with regard to Violand-Sanchez (1995) and Oxford and Ehrman (1993) research mentioned earlier.
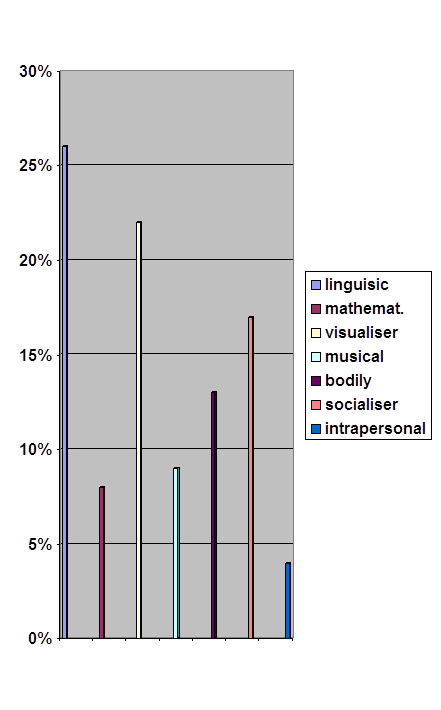
Student teachers are given some examples which describe the language and learning behaviour, and the manner of approaching and processing a task. These examples cover all three groups of learning styles. It is noteworthy to mention that one example might comprise more than one learning style. Thus the characteristic ‘respond in a low voice but accurately’ might describe an introvert and FD learner, whereas ‘speaks fast but with errors’ includes features of an extrovert and FI pupil. But the expression ‘produces long utterances without haste and emotions’ may define an introvert but FI learner. Some examples display sensory preferences only. For example, the behaviour ‘highlight some passages with fountain pen or marker’ reveals a visual leaner, ‘gives the answer to the comprehension question after first listening’ is the feature of an auditory learner. The characteristic ‘volunteers to go to the blackboard’ displays the feature of a kinaesthetic learner but at the same time s/he might be an extrovert as well. Thus all these characteristics make student teachers be aware about the complexity of a child’s personality and give them a hint about affective, cognitive and sensory preferences of learners in accomplishing learning activities.
During the lesson student teachers are recommended to make notices in a chart with four columns: learning activity, name of learners, what and how learners do the activity, comment on the learners’ preferences. Columns are given in the sequence of the typical lesson and observational procedure: the activity is nominated by the teacher by giving instructions, then a learner either volunteers or is nominated by the teacher to fulfil the instruction, after it a student teacher observes the way of doing the activity, and finally s/he comments briefly about student’s manner of doing and infer learner’s preferences.
After the lesson a student teacher should discuss with the teacher and group students according to their learning preferences. This information will be very important for student teacher in their future planning of activities, in grouping of students particularly. They should take into account whether the activity presupposes grouping extrovert and introvert pupils together. The information about sensory preferences is important in planning the techniques to accomplish a task. If the number of visual learners prevails pre-service teachers should prepare some visual support to their oral instructions.
Later, during post observation session, student teachers are recommended to reflect whether learning activities and instructions that they have observed coincide to learners’ preferences. At the same time student teachers should consider the objectives of the lesson whether they were achieved successfully with or without catering for learners’ preferences. More advanced task for student teachers is to think about the learning activities which suit student’s natural learning styles and develop other skills through proper instructions.
Похожие работы
... learners. Chapter 2 describes importance of using pair work and group work at project lessons. Chapter 3 shows how to use project work for developing all language skills. Chapter 4 analyses the results of the questionnaire and implementation of the project work “My Body” in form 4. 1. Aspects of Intellectual Development in Middle Childhood Changes in mental abilities – such as learning, memory, ...
... CLT: "Beyond grammatical discourse elements in communication, we are probing the nature of social, cultural, and pragmatic features of language. We are exploring pedagogical means for 'real-life' communication in the classroom. We are trying to get our learners to develop linguistic fluency, not just the accuracy that has so consumed our historical journey. We are equipping our students with ...
... finding excuses for leaving the classroom, or bothering the teacher with questions. The committed student, on the other hand, devours more and more knowledge. Basic to the success of independent work is a student's commitment to it. When a student recognizes his or her own ignorance and sees work as the way to overcome it, commitment grows. If the teacher tests often and tests widely, the teacher ...
of promoting a morpheme is its repetition. Both root and affixational morphemes can be emphasized through repetition. Especially vividly it is observed in the repetition of affixational morphemes which normally carry the main weight of the structural and not of the denotational significance. When repeated, they come into the focus of attention and stress either their logical meaning (e.g. that of ...
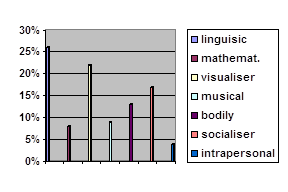
0 комментариев