Навигация
Educational institution
Summary
Subject: Lithium
He performed the: .
Checked: .
City: 20 г.
Content
1 Introduction
2 Characteristics
2.1 Physical
2.2 Chemical
2.3 Lithium compounds
2.4 Isotopes
3 History and etymology
4 Occurrence
5 Production
6 Applications
6.1 Medical use
6.2 Other uses
7 Precautions
7.1 Regulation
8 Conclusion
9 References
1. Introduction
Lithium (pronounced /ˈlɪθiəm/, LITH-ee-əm) is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number three. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive, corroding quickly in moist air to form a black tarnish. For this reason, lithium metal is typically stored under the cover of petroleum. When cut open, lithium exhibits a metallic luster, but contact with oxygen quickly turns it back to a dull silvery gray color. Lithium in its elemental state is highly flammable.
According to theory, lithium was one of the few elements synthesized in the Big Bang. Since its current estimated abundance in the universe is vastly less than that predicted by physical theories, the processes by which new lithium is created and destroyed, and the true value of its abundance,[1] continue to be active matters of study in astronomy.[2][3][4] The nuclei of lithium are relatively fragile: the two stable lithium isotopes found in nature have lower binding energies per nucleon than any other stable compound nuclides, save deuterium, and helium-3 (3He).[5] Though very light in atomic weight, lithium is less common in the solar system than 25 of the first 32 chemical elements.[6]
Due to its high reactivity it only appears naturally in the form of compounds. Lithium occurs in a number of pegmatitic minerals, but is also commonly obtained from brines and clays. On a commercial scale, lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride.
Trace amounts of lithium are present in the oceans and in some organisms, though the element serves no apparent vital biological function in humans, though the lithium ion Li+ administered as any of several lithium salts has proved to be useful as a mood stabilizing drug due to neurological effects of the ion in the human body.[7] Lithium and its compounds have several industrial applications, including heat-resistant glass and ceramics, high strength-to-weight alloys used in aircraft, and lithium batteries. Lithium also has important links to nuclear physics. The transmutation of lithium atoms to tritium was the first man-made form of a nuclear fusion reaction, and lithium deuteride serves as a fusion fuel in staged thermonuclear weapons.

Figure. 0. Silvery white (seen here in oil)
2. Characteristics
2.1 Physical
Like the other alkali metals, lithium has a single valence electron that is easily given up to form a cation.[8] Because of this, it is a good conductor of both heat and electricity and highly reactive, though it is the least reactive of the alkali metals due to the proximity of its valence electron to its nucleus.[8]
Lithium is soft enough to be cut with a knife, and it is the lightest of the metals of the periodic table. When cut, it possesses a silvery-white color that quickly changes to gray due to oxidation.[8] It also has a low density (approximately 0.534 g/cm3) and thus will float on water, with which it reacts easily. This reaction is energetic, forming hydrogen gas and lithium hydroxide in aqueous solution.[8] Due to its reactivity with water, lithium is usually stored in mineral oil or kerosene.[8]
Lithium possesses a low coefficient of thermal expansion and the highest specific heat capacity of any solid element. Lithium is superconductive below 400 μK at standard pressure[9] and at higher temperatures (more than 9 kelvin) at very high pressures (over 200,000 atmospheres)[10] At cryogenic temperatures, lithium, like sodium, undergoes diffusionless phase change transformations. At 4.2K it has a rhombohedral crystal system (with a nine-layer repeat spacing)[11]; at higher temperatures it transforms to face-centered cubic and then body-centered cubic. At liquid-helium temperatures (4 K) the rhombohedral structure is the most prevalent.

Figure. 1. Lithium pellets (covered in white lithium hydroxide)
2.2 Chemical
In moist air, lithium metal rapidly tarnishes to form a black coating of lithium hydroxide (LiOH and LiOH·H2O), lithium nitride (Li3N) and lithium carbonate (Li2CO3, the result of a secondary reaction between LiOH and CO2).[12]
When placed over a flame, lithium gives off a striking crimson color, but when it burns strongly the flame becomes a brilliant white. Lithium will ignite and burn in oxygen when exposed to water or water vapours.[13]
Lithium metal is flammable, and it is potentially explosive when exposed to air and especially to water, though less so than the other alkali metals. The lithium-water reaction at normal temperatures is brisk but not violent, though the hydrogen produced can ignite. As with all alkali metals, lithium fires are difficult to extinguish, requiring dry powder fire extinguishers, specifically Class D type (see Types of extinguishing agents).
Похожие работы
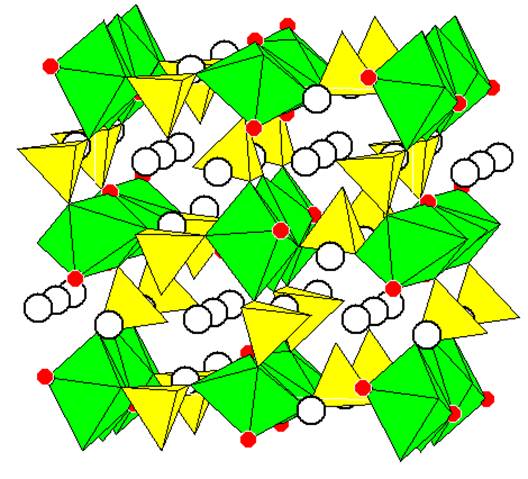
... 780 °C и выдерживали 18 часов на воздухе [6]. LiFePO4 получен аналогично, но в инертной атмосфере [10]. 1.3. Смешанные фторидофосфаты щелочных и переходных металлов Просмотр реферативных журналов, баз данных PDF-2 и ICSD обнаружил только три фазы формульного типа A+2MPO4F, из них с литием только одна: Li2NiPO4F [11]. Известны также Na2MnPO4F [12], Na2MgPO4F [13], Na4,6FeP2O8,6F0,4 [14, 15, ...
... веществом, как уже было сказано выше, являются только частые лекарственного патогенеза. Для большинства патогенезов лекарственных химических средств гомеопатия широко пользуется данными профессиональной токсикологии. II. Гомеопатические разведения (потенции) и способ их приготовления Лекарство, даваемое в ничтожно малом количестве, ...
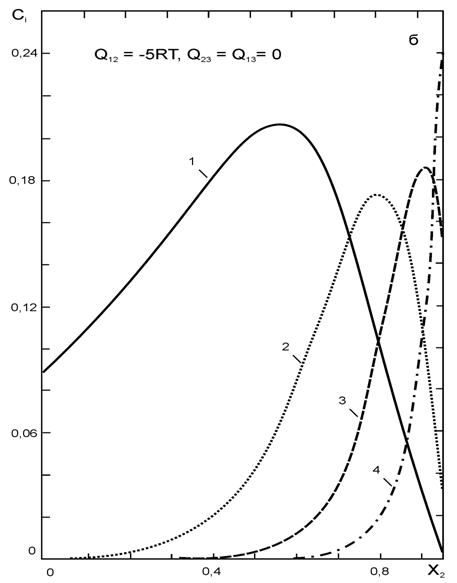
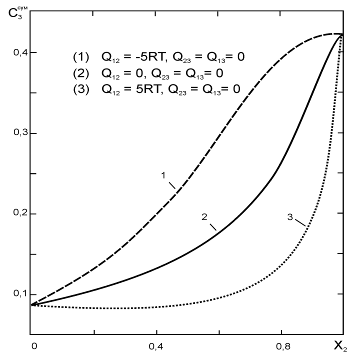
... впервые получены следующие результаты: · Разработана обобщенная координационно-кластерная модель для описания взаимодействий и расчета термодинамических характеристик раствора неметалла в расплаве из трех металлических компонентов. · Установлена связь между термодинамическими свойствами (коэффициентами термодинамической активности и параметрами взаимодействия компонентов первого порядка) и ...
... слушает только THE RAINCOATS,а по большому счету "забил "на всю эту шумиху вокруг его творчества.На 12-ой церемонии вручения британских наград,проходившей 16 февраля в лондонском Alexandra Palase ,НИРВАНА получила титул "лучшей новой группы" в международной категории.Воспользовавшись паузой между студийными сейшенами,Крис Новоселич принял участие в аакции War Child в поддержку детей,пострадавших ...



0 комментариев