Навигация
3.2 Games
While the tide of this chapter is “How to put words to work”, it would be wrong to suggest that vocabulary learning has to be all work and no play. Language play, including word games, has a long history. Children of all cultures seem to enjoy games of the “I spy ...” or “Hangman” type, and there is a long tradition of adult word games, a number of which have been adapted for television. Most first-language word games transfer comfortably to the second-language classroom.
Word clap: Students stand or sit in a circle, and, following the teacher's lead, maintain a four-beat rhythm, clapping their hands on their thighs three times (one-two-three ...) and then both hands together (four!). The game should start slowly, but the pace of the clapping can gradually increase. The idea is to take turns, clockwise, to shout out a different word from a pre-selected lexical set (for example, fruit and vegetables) on every fourth beat. Players who either repeat a word already used, or break the rhythm – or say nothing – are “out” and the game resumes without them, until only one player is left. The teacher can change the lexical set by shouting out the name of a new set at strategic points: Furniture! Nationalities! Jobs! etc.
Categories: Learners work in pairs or small groups. On a piece of paper, they draw up a number of columns, according to a model on the board, each column labelled with the name of a lexical set: e.g. fruit, transport, clothes, animals, sports. The teacher calls out a letter of the alphabet (e.g. B!), and to a time limit (e.g. three minutes), students write down as many words as they can beginning with that letter in the separate columns {banana, berry; bus; bikini, blouse; bear, bat; baseball, basketball...). The group with the most (correct) words wins.
Noughts and crosses: Draw two noughts and crosses grids on the board:
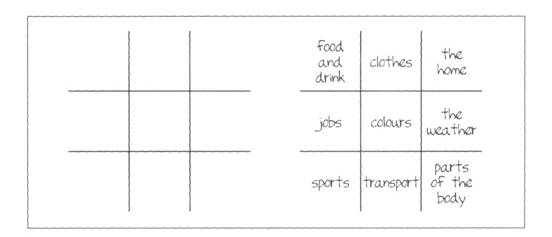
One is blank. In the other each square is labelled with a category, or with nine different phrasal verb particles {up, on, off, in, back, etc), or nine different affixes {un-, non-, -less, -tion, etc). Prepare a number of questions relating to each category. For example (if the class is monolingual): How do you say “tamburo” in English? Or, What is the opposite of “shy”? Divide the class into two teams: noughts and crosses. The object is to take turns choosing a category and answering a question in this category correctly so as to earn the right to place their team's symbol in the corresponding position in the blank grid. The winning team is the first to create a line of three (noughts or crosses), either vertically, horizontally, or diagonally.
Coffeepot: This is a guessing game. One learner answers yes/no questions from the rest of the class (or group) about a verb that she has thought of, or that the teacher has whispered to her. In the questions the word coffeepot is used in place of the mystery verb. So, for example, students might ask Do you coffeepot indoors or outdoors? Is coffee potting easy or difficult? Can you coffeepot with your hands? etc. If the verb that the student has selected is yawn the answers would be: Both indoors and outdoors; It's easy; No, you can't, but you might use your hands ... To make the game easier a list of, say, twenty verbs can be put on the board and the person who is 'it' chooses one of them. This can also be played in pairs.
Back to board: This is another guessing game, but this time the student who is 'it' has to guess a word by asking the rest of the class questions. The student sits facing the class, back to the board; the teacher writes a recently studied word or phrase or idiom on the board, out of sight of the student. The student asks different students yes/no or either/or questions in order to guess the word. For example: Helga, is it a verb or a noun? (A verb.) Dittmer, is it an action? (No.) Karl-Heinz, is it something you do with your mind? (Yes.) ... etc. To make the game easier, the words chosen can be limited in some way – e.g. all phrasal verbs; all character adjectives, and so on.
Chapter IV. Teaching word parts word chunks
4.1 Teaching word formation and word combination
We looked at some of the principles of word formation in English. We noted that words can be formed by the addition of prefixes and suffixes – a process called affixation. (The word affixation is itself an example of the result of adding affixes to the root fix.) We also saw how, by compounding, two or more words can join up to make one. Thus: black + board = blackboard. Or, new words can be created by a process called conversion, when a word that in one context is one part of speech (such as a noun), in another context can be enlisted to serve a different function (such as a verb). Hence, you may have heard the relatively recent term to board as in The teacher boarded the new words and the students wrote them down.
Then again words can cluster (but not join up) to form multi-word units – loosely called chunks – that behave as if they were single words. For example, alongside black, the Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English lists: black and white, black and blue, black sheep, in the black and to black out. (This last is an example of a phrasal verb.) Many chunks have an idiomatic meaning – that is to say the meaning of the chunk as a whole is not directly inferrable from the individual words: He's the black sheep of the family; you've introduced a red herring, etc.
The way bits of words combine, and the way words themselves can be combined, is a constant source of difficulty for learners. Errors of the following types are common:
Affixation errors
There are uncountless ways to bring happiness to my life thanks to the internet.
After finishing the paragraph and reading it again, I felt unsatisfy. I think that my real and only knowledgements are in the vocabulary.
Compounding errors
In London I took a two floor bus and of course crossed the city in the highest floor.
I saw my dog died in a box's shoes.
Errors of multi-word units
We have also a buses network.
Sometimes dog isn't the best man's friend.
Collocation errors
I don't like when I do mistakes.
Some teachers are strict they put us a lot of homework and exams.
Phrasal verb errors
She used to go to school with her maid, and a maid was picking up her from school.
There are some days that the better it's stay in bed and don't get up you.
Idiom errors
I have no more money. So most of time I just watch shops' window.
I don't like to blow my own horn, but my grammar knowledge and my vocabulary are quite good.
In responding to these kinds of problems, there are two possible approaches.
You can either
- teach rules, or
- expose learners to lots of correct examples
A rule-based approach starts by isolating and highlighting any relevant patterns or regularities. Take word formation, for example. In a rule-based approach, words can be grouped and presented according to the manner of formation (affixation, compounding, conversion, etc). Within these categories finer distinctions can be made. So, of the words formed by affixation we can select those formed by the addition of prefixes, and this group can be narrowed down further to those that have a negative meaning. The way these words are formed can then be described in general terms in the form of a rule – or 'rule of thumb'. Here is an example of such an explicit rule statement (from Gude K and Duckworth M, Proficiency Masterclass, OUP):
| B Negative prefixes. The prefixes mis-, dis-, ig-, and un- can all be used to give a word a rather negative meaning. The prefix may help you to guess the meaning of the word. mis- = 'wrongly, badly' or 'not done' (mismanage) dis- = 'away from, the opposite of, lack of' (distaste) ig- = 'not, lacking in' (ignorant) un- = 'not, lack of, the opposite, reversal or removal of' (undo) Here is some advice to help you choose the correct prefix. dis- can be used to form verbs, eg dissatisfy, adjectives, eg dishonest; and nouns, eg disability. The prefix ig- appears only before the letter n. |
Here, on the other hand, is a table which suggests – but doesn't explicitly state – a rule about noun and verb endings:
| 1 Now you can strengthen the thin green line. Strengthen is a verb which is formed from the adjective strong. Work in pairs and complete this table. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
from Naunton J, Think First Certificate, Longman
A similar approach is used with word collocations, wherever a general tendency can be identified. Here, for example, is a coursebook extract that focuses on the difference between make and do combinations:
VOCABULARY
Make or do?
Похожие работы
... materials based on electric devices manuals are studied. In the next chapter lexical and grammatical peculiarities have been reviewed. 2. Lexical and grammatical peculiarities of scientific-technical texts In any scientific and technical text, irrespective of its contents and character, can be completely precisely translated from one language to other, even if in an artwork such branch of ...
... . 6. The Scandinavian element in the English vocabulary. 7. The Norman-French element in the English vocabulary. 8. Various other elements in the vocabulary of the English and Ukrainian languages. 9. False etymology. 10.Types of borrowings. 1. The Native Element and Borrowed Words The most characteristic feature of English is usually said to be its mixed character. Many linguists ...
... Smirnitsky 2). He added to Skeat's classification one more criterion: grammatical meaning. He subdivided the group of perfect homonyms in Skeat's classification into two types of homonyms: perfect which are identical in their spelling, pronunciation and their grammar form, such as «spring» in the meanings: the season of the year, a leap, a source, and homo-forms which coincide in their spelling ...
... clear and lucid language. There are some problems which are debated up to now, for example, «the reality of the perfective progressive». 1.3 The analysis of the stylistic potential of tense-aspect verbal forms in modern English by home linguists N.N. Rayevska [3; 30] is a well-known Ukrainian (Kiev) scholar who specialized in the study of English language and wrote two monographs: 1. The ...
0 комментариев