Íàâèãàöèÿ
The United States of America
8.12. The United States of America
The USA represent an unique phenomenon in the world’s history. In fact, they have turned from a colony to the leading world’s state for 300 years. This fact testifies the specificity of development of the national epochal cycle. The country has come to the flourishing with a rapid rate of movement along the history. The other leading European countries «spent» millenniums to go through this process.
The revolutionary phase of the first epochal cycle is connected with establishment of the British colonies by the most «passionary» migrants from Great Britain (1607). The transportation of the social experience of emigrants from the Old World to the American soil created a generally favorable ground for the dynamic development of a new complex nation. The involutionary period of its formation covered the latter half of the 17th century. The urban culture developed here faster than in Europe. Both the urban and country cultures were free from pre-capitalistic anachronisms. On the other side, the inner tendencies of the involutionary period actively stimulated the development of the extensive slave-owning forms of the economic development of the Southern states of the country, creating pre-conditions to the following conflict between the slave-owning agrarian South and industrially growing North.
The co-evolutionary stage is identified with events of the War for Independence (1776-1783). A regular consequence of the transient moment in the development became the Declaration of Independence (1776). One could speak about the stable evolutionary-democratic development of the USA since 1783. The most outstanding historic personalities were as follows: George Washington (1732-1799) – one of the parents-founders and the first President of the USA; Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826), who strengthened the constitutional order in the USA; Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) – the ideologist of the American pragmatism. The positions of the USA in the Southern America were consolidated by the Monroe Doctrine (1823) that gave an indirect support to the fight for national independence of Latin-American states against the European colonial powers. The foundation of the leading political parties of the USA, Democratic (1828) and Republican (1854) ones, and the political activity of the Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865) may also be referred to this period.
The revolutionary stage of the second epochal cycle is identified with the peripetias of the War between the States (1861-1865) which led to the abolishment of slavery by giving an additional impulse to development of the national market and accelerated the organic process of country’s industrialization.
The strengthening of the involutionary tendencies provided for the economic growth of the USA to the end of the 19th century and expanded the US possibilities in the sphere of external policy. After the war between America and Spain (1898), the expansion of the USA to Latin America is enlarging, which led to the establishment of political control over the majority of states of this continent. The following content of the evolutionary period became the participation of the USA in the First World War. However, the victory of isolationists over the line of President Woodraw Wilson (1919) weakened country’s external political positions in the League of Nations for some time.
Events of the Great Depression (1929-1933) became a turning (co-evolutionary) point in the history of the USA. The country entered the evolutionary period of the second epochal cycle since the times of the «New Deal» of President Franklin Delano Roosevelt (1933-1945). After the Second World War (1939-1945), the country turns into a superpower. This process was favored by the creation of A-bomb (1942-1945), creation of the NATO (1949), and realization of the Marshall plan (1947-1953) provided for a significant growth of the West-European economies.
The war of the US in Vietnam (1964-1973), youth protests (1968-1975), the deepening of racial problems, the Watergate process that ended in the resignation of President Richard Nixon (1974), the victory in the cold war, the beginning of the transformational processes in Central and Eastern Europe and the disintegration of the USSR (1989-1991), the presidency of Bill Clinton (1992-2000) which led the USA to the maximally possible status of the «last world’s state»[64] – all this gives serious grounds to assume that the USA are standing on the threshold of revolutionary events of the third epochal cycle, their probability growing since the beginning of the 21st century.
The overall prognosis of development of the situation in the above-mentioned countries of our research sampling may be presented as the following table.
| # | Country | Number of completed epochal cycles | Developing Epochal Cycle | Period (Phase of the Developing Epochal Cycle) | Probability of Actualization of the Prospective Transient Period (Revolution/Co-evolution) with the beginning of |
| 1. | Vatican | 6 | 7 | Evol. | High (Revol.) |
| 2. | Italy | 4 | 5 | Evol. | High (Revol.) |
| 3. | Germany | 3 | 4 | Evol. | High (Revol.) |
| 4. | Great Britain | 3 | 4 | Evol. | High (Revol.) |
| 5. | France | 2 | 3 | Evol. | It is difficult to define |
| 6. | Ukraine | 2 | 3 | Co-evol. | Actual (Ñî-evol.) |
| 7. | Russia | 1 | 2 | Co-evol. | Actual (Ñî-evol.) |
| 8. | Belarus | 1 | 2 | Revol. | Actual (Revol.) |
| 9. | China | 3 | 4 | Evol. | Actual (Ñî-evol.) |
| 10. | India | 2 | 3 | Evol. | Low |
| 11. | Japan | 2 | 3 | Co-evol. | High (Ñî-evol.) |
| 12. | USA | 1 | 2 | Evol. | High (Revol.) |
The analysis of the social development with use of the methodics of universal epochal cycle in the research of a situation at the level of specific national state formations gives certain grounds to assume that, with the beginning of the new millennium, there is a growing probability that Western countries (the countries of the European historical-cultural area, in particular, Italy, Germany, Great Britain, and the USA) «enter» the period of crisis – new social revolutions which will open new horizons of social development to the world. The establishment of a new-type policy, devoid of the former «party-class» heredity will be the semantic content of the naissant situation in this region. At the same time, the situation in the Asian region (taking into account the other characteristics of development and those over the whole world) will be defined by the growing tendencies, characteristic of the evolutionary period of the social development. According to the former Secretary of State of the USA James Baker, they will be as follows: «the liberalization of economies» and «the emergence of a truly world economy», «the weakening of the spirit of collectivism (communism)» and «expanding possibilities for less amplitudinous conflicts», «the development of democracy as not only the form of state governance, but as a common set of norms and cultural values», and, in general – expansion of the conflict between «the nascent global democratic culture and the new movements»[65].
Thus, the hypothetical schemes of changes of the epochal cycles of the world’s history, built on the global, regional, and partially national levels, are to be empirically verified. This work assumes the development of a system of empirical indices and the conduction of necessary measurements, including the measurement of the corresponding societal indices. However, even in such a condition, the work performed confirms, in our opinion, the rightfulness of the offered conception of historical development. This conception can become a theoretical ground for the development of new methodological approaches in the system of social sciences.
CHAPTER 9
Glossary of main notions
and social theories
Anomy – state of a social system, which is characterized by the absence of commonly accepted values and norms as universal regulators of social behaviour of people. The phenomenon of anomy is inherent in social crises. The category if anomy is one of the key notions in the sociological conception of Durkheim. Under conditions of a global anomy, we observe the post-soviet society. A deepening of demoralization generates the normative reactions to the anomy: the traditionally archaic (requirement to return the old system of values) and authoritaristic (to bring a strong personality to power, which will establish «a hard order») ones. There exist two types of nonnormed reactions to the anomy: social cynicism (ignoration of norms) and extremism (orientation to destructive means of achievement of political purposes)[66].
Asymmetry (asymmetria in Greek) – lacking or breaking of a symmetry as high equilibrium; a natural property inherent in all social structural formations including societal qualities, which reflect the corresponding binary indices (scales); it lies in the basis of the formation of epochal and vital historical cycles of the social development. A degree of asymmetry, e.g., of the distribution of two components of the binary indices of societal qualities of the society is historically variable and can reveal the state of evolutionary development of the society[67].
Berdyaev Nikolai Aleksandrovich (1874-1948) – Russian philosopher. Berdyaev’s social theories are closely connected with his religious philosophy. He asserted that the historical process consists in a struggle of good against irrational freedom. When irrational freedom reaches a supremacy, reality begins to decay and return to the initial chaos. In the social life, a revolution is an extreme form of the return to chaos. Creation begins only in the period after the revolution, when new forms of life arise. But people never achieve the purposes they set before themselves even in creative epochs of the history. Historical failures pass the earthly time onto the eternal one in the divine life. The historical time can be symbolized with a line expanding forwards, but there is no difference between the past and the future in the existentialistic time (God’s realm), between the beginning and end. Therefore, the life at God’s realm is not a part of the history but is metahistorical. The metahistory is permanently present as a background of the history. All perversions of the personality, which are observed in the world, are overcome by means of a long-term process of development of reincarnations in many projections different from the projection of the objective world of phenomena[68].
Binary (binarius in Latin) – main characteristic of all natural processes since they consist of two opposite phases or sides. Under consideration of a social structure, duality represents a binary system basing on mutually balanced forces of opposite poles[69].
«Call» – «Reply» – notion introduced by A. Toynbee for designation of one of the defining characteristics of the rhythm of existence of civilizations. In Toynbee’s opinion, the passage of main stages of the life cycle by a civilization (birth, growth, fracture, degradation, and decay) is regulated by the law «call-reply»: every stage of development of a civilization is an adequate reply to a call of the environment. The last is natural for the first parent civilizations and natural-social for subsequent ones.
Calls can be stimulated by severe conditions of life, unexpected blow of enemy, or unfavorable social status. A call is created, as a rule, by the action of several factors. The absence of any call stimulates regress. A call should not be neither very weak since it stimulates no active reply nor too severe, which can stop the birth of a civilization or terminate its existence at a certain stage.
The basis of an adequate reply is created by the activity of the creative minority inventing new constructive ideas of historical transformations corresponding to a call. The development of a civilization continues until the minority is able to reproduce replies adequate to a call. Having lost this ability, the dominating minority degrades. On the opposite pole, the majority is represented by the «internal proletariat» – marginals. On the external boundaries, one can observe the concentration of the «external proletariat» – younger peoples to be backwards as compared with the fractured civilization by their level of development. However, a decline of civilizations can be postponed due to a rational policy of the governing class[70].
Civilization – level of social development, material and spiritual culture[71].
1) form of existence of living creatures endowed by intellect, 2) synonym of culture, totality of spiritual and material achievements of the society, 3) process of establishment of a public society, 4) comparatively self-supporting integral social-historical formation localized in space and time, which can have hierarchical levels. The term was introduced by Mirabeau (1757) and used by A. Fergusson and later by L. Morgan and F. Engels for designation of the highest epoch as compared with wildness and barbarism. Spengler considered the civilization as a concluding stage of the existence of culture, and Toynbee as a unit of the historical process. The civilizational approach to study of the history is concentrated at the mosaic of cultural-historical forms classified in the proper manner. Every civilization enriched the mankind with its experience[72]. The American politologist S. Huntington believes that since differences between civilizations formed during centuries, they are fundamental and more stable than ideological and class differences, moreover, modern conflicts will move from political borders to the lines of contact of civilizations, especially to countries whose population is represented by different civilizational groups.
Co-evolution – phase transition opposite to a revolution (in the direction from the state of involution to the state of evolution). Co-evolution is realized under conditions of one epochal cycle and, therefore, changes only the polarity of system properties of the society or vectors of social development[73].
Cycle [from kyklos (in Greek) – circle] – totality of mutually connected phenomena and processes, which reflects a completed circle of development during a certain temporal period. All the natural processes are cyclic including both the process of development of a civilization or a single society in space and time and change of forms or conditions of their existence irrespective of whether the question is cycles concerning specific spheres of social life (policy, economy, and culture) or the evolution of social signs laying in the basis of these phenomena[74]. Cycle is a totality of processes, works, and phenomena, which are interrelated and form a certain system or a completed circle of development[75].
Depression (depressio in Latin) – 1) dispirited blue psychic state; 2) stagnation of the economy after a crisis of overproduction, which is characterized by a stoppage of a further fall of production, trade, etc. and, at the same time, a slight demand for goods, mass unemployment[76].
Development of personality – process of formation of a personality as the social quality of an individual as a result of his socialization and education. By possessing natural anatomic-physiological preconditions to formation of the personality, a child begins to interact with the surrounding world in the process of socialization by mastering the achievements of the mankind. Aptitudes and functions of the personality, which are created during this process, reproduce historically formed human features. The child masters the reality during his activity with the assistance of adults. The process of education is a leading one for development of the personality, and the type of development of the personality is defined by a type of the group, in which the child is integrated.
East-West – geographical differentiation of the world-wide historical process attaching the civilizational and regional peculiarities to it. Objective-cultural adoptions as a consequence of peaceful contacts («Great silk way») or war conflicts (Greek-Persian wars, campaigns of Alexander the Great; crusades, great geographical discoveries; colonial captures) more often promote the acceleration of the historical development of «West» at the expense of subjection of «East». Approximately till the XV century when peculiarities of the historical development of West as a result of Reformation, Renaissance, and later Enlightenment were formed, the sociocultural values of East were universal, and those of West were unique. From the second half of the XX century, west values, conversely, are declared as universal. For example, Japan became «West» on East, and Turkey is «East» on West.
El’konin Daniil Borisovich (1904-1984) – soviet psychologist. By developing a position of the cultural-historical theory for solution of a wide circle of problems of the child psychology, he advanced the conception of periodization of the psychical development of children, based on the notion of «leading activity»[77].
Epoch – period of time (usually long) in the historical development of the nature, society, science, etc., which is distinct by characteristic peculiarities and significant events, processes, and phenomena.
Epochal historical cycle in the context of the proposed conception is a hypothetical model of the scheme of a cyclic historical development from the revolutionary stage (radical qualitative overturn of the whole social structure of the society leading the development in the direction of progress or regress, which generalizes results of development of the society during the whole epochal cycle and brings it to a new stage of development, to the involution, which is the period of the mastering of new qualitative changes acquired by the society during the revolution, and further to the co-evolutionary stage. The last is a phase transition from the state of involution to the state of evolution, which conducts a epochal historical cycle to the state with maximum utilization of results of the previous stages of development, whereas evolution is preparing a new revolution opening the next epochal cycle. The approximate scheme of universal epochal historical cycle can be as follows: revolution – involution – co-evolution – evolution.
Era – 1) moment, from which one conducts the chronology, e.g., Christmas in Christians (our Era); 2) large historical period, epoch[78].
Erikson Eric (1902-1994) – American psychologist, the representative of ego-psychology. Contrary to the thesis of psychoanalysis on the antagonism of a personality and the society, he emphasized the biosocial nature and adaptive character of behaviour of a personality, whose central integral quality is the psychosocial identity. Being subjectively experienced as the feeling of continuous self-identity, the psychosocial identity is based on the acceptance by the personality of the own integral image in the unity with diverse social connections. A change in social-cultural conditions of the existence of the personality leads to the loss of the previous identity and the necessity of formation of a new one. Personal difficulties arising in this way can cause a hard neurosis («loss of himself»). On this basis, Erikson made conclusion about the conditionality of mass neuroses by deep shocks in the life of the society on turns of the history[79].
Evolution – one of the forms of development in the nature and society – continuous quantitative change, as distinct from revolution, being a radical qualitative change; evolution prepares revolution and creates the corresponding soil for it, whereas revolution completes evolution, promotes a further development, and opens quantitatively new possibilities for evolution[80].
Formal group – consolidation of people for implementation of a socially prescribed activity under condition of their direct communication and interaction[81].
Gender – one of the principal notions of the contemporary sociology meaning a collection of expected samples of behaviour (norms) for men and women. As distinct from the notion of sex, gender is referred, first of all, to socially formed features of «womanhood» and «manhood» (executiveness/intentionality). The term «gender» was proposed by the American psychoanalyst R. Stoller in 1968[82].
Gender roles depend on culture. In nomadic cultures (of nomads and gatherers), education of boys and girls is practically the same since men and women perform almost the same work. In agricultural societies, roles are more differentiated; in industrial societies, gender roles are extremely diverse. Among administration, women constitute 20% in the South Korea, 17% in the USA, and 45% in Switzerland. Gender roles also depend on epoch. From 1960 till 1995, the share of American women in labour power has grown from one third to almost three fifths[83].
Gumilev Lev Nikolaevich (1912-1994) advanced a conception of development of the ethnic history. Ethnos is considered as a collective of people, which was naturally composed on the basis of an original stereotype and exists as an energetic system opposing itself to other similar collectives. Nonhomogeneity of the distribution of biochemical energy of the vital substance of the biosphere for a long-term historical time influences the behaviour of ethnic collectives in various epochs and in various regions. Gumilev called the effect performed by variations of this energy, as a specific property of the character of people, by passionarity. Passionarity is the irreversible internal aspiration to activity directed to the implementation of some goal. A passionary person can consider this goal to be more valuable than even life. Ethnogenesis is regarded as a process of development of the ethnos from the moment of its origin till disappearance or the transition to the state of homeostasis. Gumilev distinguished the phase of stationary push (search for a success with risk for life), acmic phase (aspiration to the ideal of victory, sacrifice), fracture (aspiration to well-being without any risk for life), inertial phase or obscuration (quiet inhabitants adapted to the biocenosis of an areal). An approximate scheme of the phases of ethnogenesis, composed by Gumilev, has the following form: a growth – «Be by whom you must be»; the acmic phase (passionary overheating) – «Be by himself; the passage to the phase of fracture – «We are tired of the great persons»; the phase of fracture – «Permit us to live!»; fracture – «Only not so as it was»; the transition to the inertial phase – «Be such as I»; obscuration – «Be such as we»; the transition to homeostasis – «But when will it finish?»; homeostasis – «Be satisfied by himself»; the transition to the memorial phase – «Not all is perished!»; the memorial phase – «Remember how it was nice»; and the degeneration – «We wish nothing».
Harmonization – process of achievement of the state of harmony or the dialectic «removal» of contradictions in the process of origin of the state of a self-organizing system, which is characterized by stability with respect to various destabilizing factors.
Harmony (harmonia in Greek) – 1) combination of music tones in a simultaneous sounding, consonance; 2) coordination, fine combination, commensurability of various properties, objects, phenomena, parts of the whole[84].
Hegel Georg W. F. (1770-1830) – German philosopher. In his works, he stated the comprehension of history as a development of spirit in time. By Hegel, the goal of the history is a development of the freedom of a citizen in the civil society. Since the realization of freedom necessarily includes the fact that the «world spirit» realizes itself as free, the history is also a progress in realization of freedom. In Hegel’s opinion, the principle of historical development is the reflection of a state of the society. When the spirit of an epoch will realize itself, the form will be historically completed. Realization means the overcoming of the previously existing form of spirit and, by virtue of this, the starting point of a new spirit of the epoch. This constitutes the essential difference between Hegel’s conception of history and Marx’s conception. The last emphasizes a conditionality of the historical development by more dynamical production forces and less movable social relations. The development of the world spirit occurs not automatically. It cannot avoid the participation of people. By pursuing their private interests, people make more than they intend. Without comprehension of this fact, they realize regularities of the history by pushing its course forwards.
Historical sociology – trend of the sociological science studying social regularities of development of the society, its systems, institutions, phenomena of social life in the process of their historical evolution. In the comparison of historical phenomena and processes, one determines the common and the partial in them, changes, tendencies, stages of development. A subject of investigations of the historical sociology is the social history of a society since, according to the idea of F. de Coulange, «the history is not a collection of facts occurred in the past. It is a science of the human society». It is worth to note the tendency to synthesis of the history and the theory of sociology[85].
Historical time – process of equalization of energy potentials between elements of the ethnosphere disturbed by passionary pushes[86].
Involution (envolutio in Latin) – reverse development, diminution, simplification, and reduction, which are related with a loss of some function. Involution in a social development is the period of mastering the new qualitative changes acquired by the society in the course of the revolution. Involution conditionally reminds the period of socialization of the man, first of all, the period of his adaptation in the case of a change in profession[87].
Jung Carl-Gustav (1875-1961) –Swiss psychiatrist, psychologist, founder of analytic psychology. He advanced the assertion that, besides the individual unconscious, there also exists the collective unconscious. The foundation of spiritual life includes the inherited experience of the previous generations, which is formed by the totality of archetypes. Archetype is a means of connection of images passing from one generation to another. According to Jung, the archetype presents structural elements of human psychics, which are hided in the collective unconscious. The last is common for all the mankind. They are inherited like the construction of body. The collection of archetypes is bounded; they lie in the basis of creation, assist to the internal unity of human culture, and make the interrelation of various epochs of development and mutual understanding of persons[88].
Karma – one of the cardinal positions of the Indian philosophical thought. Its essence is that a sum of good and evil actions of every man (its karma) defines the form of a subsequent reincarnation. The law of karma regulates the infinite process of circulation of vital bodies. The buddhist interpretation of the law of karma recognizes the possibility of improvement of karma under conditions of the current existence for the sake of achievement of nirvana in prospect. The highest justice of the karmic law consists in the requital to everyone by its merits.
From the historical view point, the notion of karma is associated with the process of overcoming the certain stages of development, with «reincarnation» of civilizations during a change of epochal cycles. For example, the West Roman Empire – Empire of Carolus Magnus – Holy Roman Empire. This notion is also related to the conception of Spengler on «maternal» and «daughter» civilizations[89].
Marx Karl (1818-1883) – German philosopher, the founder of scientific communism. He inferred that if every single process is a process of development, then the position of materialistic dialectics is all-embracing. Development is not a direct manifestation but the essence of processes occurring in the nature and society. The universality of development supposes the infinite variety of mutually conditioned interacting phenomena and transformation of some forms of motion of the matter to other ones. For this reason, the universal process of development is composed from a set of particular processes including those which by themselves are not processes of development. In that the development differs from a simple translation, reversible processes, and a recurrence, the universality of development does not limited. On the contrary, it can be interpreted as a contradictory unity of diversity, the unity of oppositions. The termination of development is a transition from one of its forms to the other. The ideal state would be such one, in which the free development of everyone is the condition of free development of all. A key role in social development is played by class struggle.
Mentality – structure, composition of the soul of men, ethnos, and socium, relation of their elements and states[90].
Methodology of history [from Metodos (in Greek) – way of cognition and logos (in Greek) – word, doctrine] – system of principles, methods, and procedures of formation and use of the methods of historical cognition and the doctrine about this system. In the course of development of the methodology of history, one can distinguish three stages: classical one – clear contraposition of a subject and an object of historical cognition and action, comprehension of the historical reality as, on the whole, «transparent» for the subject of cognition by rational means; nonclassical one – opposition to the scientific-centrist study of the history (personalism, phenomenology, hermeneutics, existentialism); contemporary post-nonclassical methodology of history, which is characterized by the synergetic paradigm, polyvariance, efficiency of scenarios, its pluralism, nonlinearity. Historical reality is considered not as objective and independent of the will and consciousness of a subject of the global natural-historical process but, on the contrary, the individual existence of the man is perceived as a unit authentic form of the historical being[91].
Model – abstract representation of a theory, its operationalization which can be empirically verified. In this case, not every measurement can be implemented directly. Therefore, in the creation of models, one uses constructs and concepts. Constructs mean the representations which can be substantially defined and measured by using a certain number of indicators. Concepts are the most general notions which can be measured by using constructs. Social modelling is a scientific method of cognition of social processes and phenomena with the help of reproducing their characteristics on other objects. The need in social modelling is conditioned by the necessity of improvement of the technology of management of the social sphere, overcoming of difficulties in the sphere of social design and prognostication, prevention of negative consequences of certain administrative decisions. Successfulness of social modelling depends on the availability of a proper theory describing the phenomenon subject to modelling and on the degree of formalization of the basis of this theory. Specificity of the laws of development of a society makes the question of the adequacy of social modelling to be more complicated than in natural sciences[92].
Models of social action – means of action, which are typical of large social communities, are regulated by values and norms, and are characterized by social-economic resources as well as the level of adaptation of these communities to the institutional environment[93].
Modern (moderne in French) – trend in architecture and fine arts late in the XIX – early in the XX century, which aspired to creation of a new style free of historical adoptions and to use of new technical possibilities.
Modernization – totality of various economic, political, governmental-legal, psychological, and culturological changes in a specific society in the direction of bringing it up to date and a permanent improvement; making the social and political systems and their fragments to be close to the maximally possible level of development[94].
New economic policy (NEP) was carried on in the USSR in 1921-1929 as a mean to overcome the crisis generated by the policy of «war communism». NEP was a symbiosis of the restricted freedom for private initiative and regulated «state communism» under the political control of the Communist Party. The similar model is acting in China from the beginning of reforms introduced by Den Xiao Ping in 1978.
Ontogenesis [from ontos (in Greek) – existing and genesis (in Greek) – origin, development] – individual development of an organism from the moment of origin to the termination of life. The development of a personality is comprehended as a perspectively directed natural-historical process of formation of a subject with a definite form of vital activity, in which the psychical development of the man is interconditioned by a real development of the personality. A human individual reproduces achievements of the history of human culture during his intravital development. The development of activity is a condition and means of development of the personality. The historical origin of leading kinds of activity allows one to rationally explain analogies between the psychical development of an individual and historical development of the mankind. Every historical epoch and every society generate the own periodization of the psychical development of childhood, whose limits and contents are defined by a specific-historical situation, accumulating requirements of a definite society to childhood and its limits, of development of a child[95].
Period –chronological interval, from the historical viewpoint, between definite important events which substantially influence the rhythm of change in stages of the social-historical development, for example, the periods of crusades, great geographical discoveries, Great French Revolution, etc.
Periodicity –periodic order of the derivative of mediated existence of a definite number of elements composing a continuous series. Periodicity consists of differences in the limits of a unit entity and is a variety of that is relatively distinct. Therefore, one should distinguish the following in any period: limits or poles of the period, b) bounded number of elements included in the period due to their properties to be between those two poles, c) internal sequence existing between two or more elements. This sequence reflects a relation between quantity and quality (i.e., the possibility of a transition of one to another). A representation of the period in the temporal dimensionality is equivalent to the definition of process. This process will be evolutionary if it exhausted and regressive (involutionary) if it ascending (or repeating)[96].
Personality – 1) system of self-regulation of the social activity of the man. Its establishment makes him by a subject of this activity and social relations, into which the man enters, 2) system of psychological mechanisms of the social subjectivity of the man, which are formed only through the interaction with other persons on the basis of that culture, whose carriers they are. The human personality in its occupational manifestations reveals for other persons as a certain totality of socially significant features of the personality. The formation of personality begins with the first contacts of a newborn child with the social world and occurs in the process of socialization of the individual due to, first of all, the intercourse with other persons. The personality is a complex polystructural polyfunctional system. Common functional subsystems are: 1) mechanisms of internal regulation of the orientation of a human activity, regulation of what he makes, 2) mechanisms of internal regulation of the means of his activity, regulation of how he makes. Social properties of the personality, which are historically determined, simultaneously define a further development of the society[97].
Phase [from phasis (in Greek) – appearance] – 1) definite moment, stage in development, in the change of a form or state of something or somebody; definite period in development of the historical process; 2) separate component of some inhomogeneous physico-chemical system[98].
Plan of social development – scientifically substantiated system of indices of improvement of conditions of work and way of life, which is supported by corresponding calculations and forecasts of material-technical security.
Policy (politika in Greek –state social affairs) – sphere of activity related to relations between social classes, nations, and other social groups, whose kernel is the problem of conquest, retention, and use of the state power. Policy is a historical phenomenon arising with differentiation of a society. The contents of policy is defined by social relations. External policy is a continuation of the internal one with other means. Policy is a concentrated representation of the economy. However, since it is impossible to retain the economic supremacy without political power, policy has a superiority above economy[99]. Policy (politike in Greek –state activity) – sphere of vital activity of the society, system of definite social relations, interaction of classes, nations, other social groups, states. It is a totality of actions, measures, and institutions, which put into agreement the interests of individual classes of a separated society, realize the preferential satisfaction of interests of the economically ruling strata by means of the representation of their interests as total ones. Policy is the art of the possible, a factor of conservation of the conditionality of a differentiated society[100].
Post-modernism – interdisciplinary intellectual movement, a new aspect of view and a collection of conceptual approaches to the sociocultural reality rather than a new theoretical paradigm. It involves: 1) a new tendency in self-consciousness of developed west societies, which was characterized by Lyotard as a distrust to metatheories, a refusal from «great tasks» of the mankind, which are oriented to future – ideas of progress, a sequential development of freedom, universality of knowledge, industrial-technical development, liberation of people from a burden of every-day work, 2) global state of the civilization during three last decades of the XX century.
A schematic-semantic contraposition of modernism and post-modernism was developed by the American literary critic Ikhab Hasan by the method of binary oppositions as follows:
| Discourse of modernism | Modernization | Discourse of post-modernism | Post-modernization |
| Story | Universalization of history | Anti-story | Localization of history |
| Metatheories | Dogma | Antitheories | Discourse |
| Paradigm | Linearity | Syntagma | Nonlinearity |
| Monism | Standardization, mass-making | Pluralism | Polyvariance, individuality |
| Integrity | Homogeneity of time | Mottling | Heterogeneity of time |
| Purpose | Dehumanization | Play | Humanization |
| Hierarchy | Bureaucratization | Anarchy | Democratization |
As distinct from positivism theoretically providing the process of modernization and aspiring to ground the system unity of the social world, post-modernism takes the diversity and mottling as a foundation of the contemporary world. As a distinctive feature of the corresponding conceptual approach, we consider eclecticism, equality of rights of various styles of thinking, pluralism of esthetic standards, negation of division into «high» and «lower» cultures, break with the cultural tradition of modernist enlightenment. One denies the expediency of creation of a unit theory but one recognizes the necessity to use all the theoretical heritage for implementation of a new synthesis[101].
Prognosis – precognition or foreseeing based on definite data. If a prognosis is made at a certain moment and is not revised as circumstances, affecting separate elements of the prognosis, change, there are few chances for coincidence of the prognosis and reality[102]. Scientific prognostication of the future is a very complicated applied task of humanitarian sciences. Since it is impossible to foresee neither a final result nor the moment of termination of historical processes (moreover, the single lesson being given by history consists in that just those do not learn on its lessons who do not wish to learn), any possibility for a futurological utilization of history seems illusory. However, the new paradigm of the sociology of history allows one to develop a methodics of scientific prognostication at the level of hypothesis, in particular, by using the principles of social engineering.
Progress (progressus in Latin) – development of the new and advanced; movement to a higher level of development, to a more modern state; change to the best[103].
Progress and regress – referential notions meaning the development of a society or its subsystems in the line of ascent from a less perfect state to a more modern one (progress) and the return to old obsolete forms of development, which testifies to the social stagnation and degradation (regress). Problematic is the definition of the scale of values of the criteria for the perfect state of a society. For example, marxism considers the development of a mode of production as a criterion of social progress. As for the definition of a degree of humanization of a society, one should use some other approach. All indices, fixing the movement of a society forwards and having no relation to regress (decline, degradation, and stagnation), can be empiric evidences for social progress[104].
Project (projectus in Latin) – 1) developed plan of a building, a scheme of a technological process, etc., 2) preliminary text of a document, 3) plan, intention[105].
Purposes of social development are defined depending on a specific historical situation, according to the reached level of development of social structures and institutions. The interpretation (not always rational one) of short- and long-term problems of social development fills in the social life by sense and allows one to define valuable orienting points in the context of the notions «aim» and «means».
Regress (regressus in Latin) – return, reverse motion, transition from higher forms of development to lower ones, change to the worse, opposition to progress[106].
Reincarnation – possibility to transform a died ancestor to its totem and backwards; potential possibility to a revival in various forms. For example, the revival of the ancient cultural tradition during Renaissance[107].
Results of social development – they can be different depending on achievement of the corresponding aims. The simplification of a social structure, regress under conditions of the transient periods of social-historical development can be a reason for negative results. On the other hand, the «price» of progress, e.g. in the case of a forcible modernization (industrialization in the USSR), can be too high, destroying the potential of social capital, i.e., the total possibility to implement the perspective of social development.
Rubinshtein Sergei Leonidovich (1889-1960) – soviet psychologist and philosopher, the founder of the occupational approach in psychology. He stated that the man and his psychics are formed and revealed in a primordially practical activity and, therefore, must be studied in their manifestations in main kinds of their activity. As the principal peculiarity of activity, Rubinshtein considered its sociality: activity is carried out only by a subject; activity as the interaction of a subject with an object is substantial and objective rather than pure symbolic and fictitious; activity is always creative and self-supporting. Activity is mediately defined by its object through its internal specific regularities (through purposes, motives, etc.) rather than directly[108].
Sense of social development – one of the most abstract and simultaneously valuable categories. In the book of Frankel «Man seeking sense», it is noted that the finding of the category of sense allows one to overcome the existentialistic emptiness and to fill in life with a holistic content. This can be said about social development. This category, besides a vulgar content like the notion «American dream» or Russian expression «from dirt on throne», has a deep historic-sophistic sense, especially clearly comprehended in the periods of social cataclysms, when the vector of social-historical development is radically changed. The loss of the sense of social development testifies to the profound valuable crisis, e.g., the time of the downfall of West Roman Empire, disintegration of the USSR, etc.
Small group – social group, whose members directly interact with one another. A quantitative composition of a small group does not exceeds several tens of persons. A totality of small groups functioning in various spheres of vital activity of the society defines the social microenvironment immediately influencing the formation and development of a personality.
Social-economic policy as a conscious purposeful action is carried on along with rationalization of the state apparatus (M. Weber) and is aimed at the organic development. The need in an efficient social-economic policy as a regulative mechanism of the market element arises in crisis periods, e.g., the time of the «Great Depression» (1929-1933) and «New Deal» of President of the USA F. D. Roosevelt.
Social development – type of changes in the society which is characterized by a transition of all social relations to a qualitatively new state. Social development is a result of the interaction of the totality of social processes, whose base is a purposeful activity of persons – subjects of these processes. The mechanism of social development is functioning via both the arising of new needs in the process of activity of various social subjects and search for possibilities of their satisfaction. Social evolution as gradual quantitative changes in the social system prepares and completes the social revolution as qualitative changes in all social structures, which change due to a radical reconstruction of social relations and social institutions. A characteristic of social development is a social time, in which the direction of development reveals. The important role in the provision of stability of social development is played by social reforms and social planning[109].
Social efficiency. In the science-wide meaning, the notion of «efficiency» goes back to the notion «effect», which appeared in natural sciences and primarily denoted «phenomenon» accompanied by some results. With expansion of the sphere of scientific cognition, the term «effect» became a close synonym for terms «useful result» and «useful action leading to the desired result». Efficiency characterizes the relation between levels of some activity by the degree of approach to the final or prescribed goal. From this viewpoint, efficiency plays the role of the measure of activity and presents a certain property of the system object. By applying this notion, we qualitatively and quantitatively define how some theoretical possibility of approaching the purpose with respect to the very purpose is realized. By comparing this possibility with the very purpose, it is necessary to perform measurements and then to compare by some accepted criterion. As one of the possible scientific criteria of cognition of the existing systems, efficiency eventually has the valuable nature. The estimation of relations of means to an aim separates the valuable aspect of cognition of the reality from other gnostic reasonings.
Social engineering – notion introduced into the scientific turnover by K. Popper in the 40s of the XX century. It means a totality of systemized methods, means, ways of transformation of social sciences, first of all sociological knowledge, into social programs and projects. On the other hand, social engineering is a specific branch of sociology studying the methodological and theoretical foundations of social invention, and construction of new or improvement of existing social realities. In the first case, social engineering presents itself as a practical-applied activity, and, in the second, as the science on this activity, peculiarities, and tendencies of its functioning and development. K. Popper considered social engineering as a purposeful interference of the man with social processes by «the method of trials and errors». An analogous position was occupied by F. A. Hayek who considered that the order in a society is reached with the help of rationalized spontaneity rather than through a realization of programs. Main functions of social engineering are as follows: aim-forming (creation of a new reality produces new needs); constructive-prognostic (prevention of unfavorable phenomena); expert, control, design-constructive ones. Note that social construction and innovations are the most complex forms of social-engineering activity[110].
Social genesis [from societas (in Latin) – society and genesis (in Greek) – origin] – process of origin, establishment, and further development of a society as the highest form of natural organization[111].
Social hierarchy – structural organization of a society or separate groups by the sign of levels with subsequent submission of lower levels to higher ones. Whereas the notion of stratification accents differences and makes every stratum (estate) autonomic, the notion of social hierarchy passes ahead the subsequent interrelation and co-submission between different levels. Social hierarchy is characterized by: functional-purposeful unity of levels composing it; dominant of subjective organizational-administrative bases of its formation and existence; predominantly vertical connections and the pyramidal model of the structure of a socium; centralization of functions and structural components with their simultaneous polycentralism, which is an indicator of stability and vital ability of hierarchic formations[112].
Social law – category for designation of forms of manifestation of the social causality and universal dependence of objective, necessary, stable, and repeating ties between processes and phenomena in the society.
The social law is a law of functioning and development of the social reality. It is a law of the society not directly but only through the social reality. The social law reveals only through the activity of people since any ties between social processes and phenomena arise only due to the activity of people. Social laws are characterized by such notions and terms as type, contents and structure, mechanism, character, sphere, and direction of its action, forms of governance, functions, requirements of the law. The clarification of social laws is a necessary condition of control over social processes and prognostication of their development. The category «social law» is commonly accepted neither by the classical nor contemporary sociology[113].
Social mechanism – totality of actions and deeds inalienable from their subjects-carriers, due to which various social phenomena occur and the social process is realized. A structure-forming element of the social mechanism is the interaction of social subjects, motivation of behaviour, legal and moral norms, political belief, social status and social position, institutional means. Social processes and phenomena can be a social mechanism of processes and phenomena in the wider context. The attachment of a conscious-controllable character to the social mechanism is realized through social technologies which help to attain the optimum variant of such an action. A social mechanism involves spontaneous factors complicating the prognostication of specific consequences of an action. The functioning of a social mechanism is an object of scientific investigation, and the social technology is designed with regard for the goal of a transformation, which is an object of the socioengineering activity[114].
Social process –subsequent change of a state or movement of elements of a social system and its subsystems, or any social object; it occurs under influence of internal or external conditions, has a stable order of the interaction of its components, temporal duration, and orientation to one or another state of the social object. The mentioned processes are often conjugate and have symmetric structural mechanisms differing by the sign of orientation: integration and disintegration of a social system, stability (static character), mobility (dynamism) of a social structure[115].
Social programs – presentation of principal positions of activity of social structures, political parties, and organizations in a definite perspective. Programs-maximum define the final aim, general problems, and give the theoretical foundation of principles and methods of their solutions. Programs-minimum define the nearest problems and specific plans of activity for achievement of the final aim. Subjects of social programming are bodies of state administration of various levels. The purposeful social programming can be an important directive planning document including the resource, executive, and temporal provision of the complex of social-economic, scientific-research, and organizational-administrative measures ensuring the most efficient and well-timed solution of the state-wide social problems[116].
Social psychics – historical-cultural and psychological readiness of the socium to reproduction of definite behavioral models of reaction to a problematic situation and the necessity to solve new problems advanced by social life. The psychics of a community, i.e., a certain nonaccidental human formation (society, nation, ethnos, family, social organization) is also called by mentality, spirit of people. The societal psychics is a peculiar psychoculture realized in material phenomena (articles of culture and household, architecture, music, literature, painting, rituals, traditions), energy (rhythms of the socium reflecting in behaviour, facial expressions, rate of reactions), information («noosphere», social and natural metabolism). The societal psychics includes a group of properties, states, and processes, which are studied by using the structural-functional model due to their complexity and multidimensionality[117]. The societal psychics is a collective dictionary of historical-cultural heredity of the society[118].
Social relations – relations between groups of persons, which occupy various positions in the society, take different participation in its economic, political, and spiritual life, differ in the life style, levels, and sources of profit, structure of consumption. Subjects of social relations are various communities of persons which actively interact on the basis of a certain means of social activity[119].
Social revolution – radical qualitative changes of the social life guaranteeing a translational progressive development. One distinguishes social revolution as a social-political overturn covering the whole society and revolution as qualitative changes in separate branches of social life. Social revolution is preceded by a revolutionary situation – complex of social-economic and political preconditions for radical revolutionary changes. The intensification of political activity stimulates the appearance of revolutionary movements joining leading social-political forces at a certain stage of development of the society. Political forces of a revolution aspire to power as a means of realization of own interests. The basic sense of a social revolution consists in the redistribution of power and property. Pareto believed that the sense of a social revolution consists in a replacement of the personal composition of a ruling elite.
In the context of the proposed conception of universal epochal cycle, revolution is a phase transition, opposite to co-evolution, from one normative state (evolution) to other normative state (involution). Revolution is a final stage of development of the epochal cycle, in which the previous results are «generalized». At the same time, by changing the vector of social development and by presenting fundamentally new historical possibilities to the society, revolution «open» a new epochal cycle. In this phase, there occur radical changes of societal (system-wide) characteristics of the society, which implies the break of continuity of the epochal cycle and the appearance of the social system at a new level and a new trajectory of development[120].
Social synergetics investigates the general regularities of social self-organization, i.e., interrelations of social order and social chaos. Order is a set of elements of any nature, between which there exist stable («regular») relations repeating themselves in space and time. Chaos is a set of elements, between which there are no stable (repeating themselves) relations. Since the self-organization is a qualitative structural change of some objective reality, synergetics is a theory of development. The traditional theory (dialectic conception of G. Hegel and K. Marx) considered a development as a process of transition from one order to another one. It is characteristic of synergetics that chaos is considered as the same regular stage of development as order. Synergetics looks at the process of development as a regular and, moreover, multiple alternation of order and chaos. The essence of development of the social reality reduces neither to a one-sided increase in order (O. Comte) nor to a one-sided increase in a degree of freedom (chaos) (H. Spencer). Development is a growth of the degree of synthesis of order and chaos conditioned by the aspiration to the maximum stability. The global process acquires a nonlinear and asymptotic character[121].
Social time – fundamental form of social-historical existence of people and the condition for their activity. Large and small scales of the social life are connected with metric characteristics of time: duration, sequence, recurrence, one-momentariness, multi-momentariness, and rhythm. The time of existence of social subjects involves diachronic and synchronic components. The coexistence of various generations characterizes the historical sense of social reality, which makes the social time to be inhomogeneous. The social time dialectically characterizes the activity and intercourse. The social time in the modus of future can be an object of planning, prognostication, and social modelling. The relation to the historical past and future organically enters the ethnic (national) self-consciousness of individuals. The vector of social time is directed from the past through the present to the future[122].
Social transformation – conversion, transition, modification. The notion of social transformation is connected with the process of co-evolution, i.e., development opposite to revolution when the polarity of social properties of the society is changed.
In the soviet ideological system, the notion «transformation» was connected with criticism of the conceptions «post-industrial society» and «state of common prosperity» related to the theoretical substantiation of the evolution of capitalism under the influence of the scientific-technical revolution, change in the forms of production management, which excludes the necessity of revolutionary struggle of the working class. After the «perestroika» (middle of the 80s of the XX century), the notion «transformation» became to be related with democratic reconstructions and economic reforms dismantling the model of «barracklike socialism».
Societal [from societas (in Greek) – common] – term proposed in 1903 by sociologist A. Keller for description of the organizational aspects of the life of a society; it is used in the interpretation of social relations inherent in historically formed communities – nation, ethnos, class, social group, society on the whole – rather than artificially created ones. The synonym of the term «societal» is the notion «system-wide»[123].
Societal index – qualitative and quantitative characteristic of societal properties, states, and processes. The corresponding indices are a result of an empiric sociological study and perform the instrumental-methodological function with the purpose of verification of a hypothesis.
Societal process – sequential regular change of societal properties and states in the course of the historical development of nations, regions, civilizations. `The varieties of societal processes are identification, investment, marginalization, deviation, individuation[124].
Societal properties – system of qualitative and quantitative characteristics of societal psychics. Having been expressed through the scales of binary oppositions, this system is formed by six couples of properties. The first – extroversion/introversion. Extroversion – the society is open for a dialog, is less traditional, intends to well look before others, is dynamic, is capable to assimilate large territories. Introversion – closed society, most comfortably feels itself on the own territory, alters itself but not a situation. The second pair of properties (rationality/irrationality) predestines behavioral priorities of the society – intellect or intuition. The third pair of properties (emotionality/pragmatism) characterizes the specificity of forms of a reaction – by basing on emotional-perceptible processes or on intellectual (cognitive) ones. The fourth pair (sensority/intuitivism) characterizes the aspiration to «earthly values» or to «abstract ideals». The fifth pair (externality/internality) characterizes potentialities from the viewpoint of self-definition. Eventually, the sixth pair of properties: intentionality/executivity. Intentionality is a quality characterizing the external activity of a subject. The signs of intentionality: will, self-sufficiency, organizational exactness. Executivity – property characterizing the dependence of a subject on external circumstances. Signs: slowness of actions, reflectivity of thinking. Societal indices can be represented in the form of the corresponding binary scales-oppositions, each of which is asymmetrically balanced in a stably functioning society with a prevalence of one of the parts of a binary opposition. In a transient state of the society, these parts of the index can briefly (situationally) acquire the form of symmetry and take the values of half-and-half, which is the sign of an extremely unstable (nonequilibrium) state of the society. Ukraine encountered similar states during the so-called «constitutional crisis» (II quarter of 1995), at the final stage of adoption of the Constitution (II quarter of 1996), and during elections of the Verkhovna Rada of the 13th convocation (I quarter of 1998), which outwardly manifested in the form of crisis sharpening.
Societal states – three mutually transient states of a social object in the process of development: conventional state – the reply to a call is «yes», correcting one – «no», and chaotic one – «other».
Society – complex multidimensional formation which is qualitatively different from the nature, internally divided, and simultaneously organically integral. It exists as a totality of historically formed means and forms of interaction and consolidation of individuals and their groups, in which one observes an all-round multilevel interrelation of persons. In the narrow sense: a) diachronically or synchronically fixed social organism, b) relatively self-supporting, stable, and integral part of such an organism, c) common basis, «field» of intersection and stratification of individual actions of persons (A. Toynbee), d) correlate of a state (civil society), e) correlate of a community. From positions of the abstract philosophy, society is characterized as an all-embracing system limited by conditions of sociality and semantic communication and moving in the spatial dimensionality to a world-wide planetary formation. Sociology is studying a society through the prism of of social reality as a social system with a definite organization of its elements and structures[125].
Socionics –science arising at the joint of sociology, psychology, and informatics, which considers the personality, group, and nation as carriers of a certain type of informational metabolism (exchange). They interact with each other on the basis of objective laws related to the mental sphere of the man. Jung grounded the existence of 8 psychological types and introduced the notion of «psychical function» into science. Developed conscious functions of some types of personality «charm» the same functions of other types, just those which are not developed and hided into the subconsciousness. Psychical function is an ability of the man with particular skill to investigate one of the aspects of the informational flow.
Types of informational metabolism[126].
| Irrational | Intuitive | Logical | Extrovert Introvert | Don Quixote Balzac |
| Ethical | Extrovert Introvert | Huxley Esenin | ||
| Sensorial | Logical | Extrovert Introvert | Alexander Great J. Gaben | |
| Ethical | Extrovert Introvert | Caesar Dumas | ||
| Rational | Logical | Intuitive | Extrovert Introvert | J. London Descartes |
| Sensorial | Extrovert Introvert | Holmes Gorky | ||
| Ethical | Intuitive | Extrovert Introvert | Hamlet Dr. Watson | |
| Sensorial | Extrovert Introvert | Hugo Dreiser |
Socium [from socium (in Latin) – common] – type of sociality existing as a stable community of persons, which is characterized by the unity of natural, social-productive, mental, etc. conditions of vital activity, genetic connection of generations, stability of a social organization, a certain level of culture. It reveals itself in the form of a society, large and small social groups. As a social reality, socium is an integral, self-organizing, vital, open system functioning due to the exchange of activity and information between individuals and communities. Production of material and mental goods is a means of existence of the socium rather than its goal. The historically appeared means of social organization is a form of solution of contradictions between individual and social bases[127].
Solov’ev Vladimir Sergeevich (1853-1900) – Russian philosopher, a creator of the orthodox Christian philosophy, being anthropocentric by its character. The doctrine of God-mankind as a source of the revival of the world is used by Solov’ev for interpretation of the history of the mankind and problems of social life. In its development, the world passes the following stages: first (prior to the man) – evolution of the nature, second (human activity) – history. Since the lower level does not disappear but joins with the more perfect activity, evolution is the process of gathering the Universe but not only a process of development and improvement[128].
Spengler O. (1880-1936) – German philosopher and historian, who conceptually connected ideas of development of culture and civilization. Culture is originated at the moment when the great soul awakes from the protospiritual state of the eternally infantile mankind, some face appears from the abyss of the featureless, something limited and coming from the infinity arises. Culture is flourishing on the soil of a strictly bounded landscape, to which it remains to be vegetatively bound. Culture dies when this soul realizes the full sum of its potentialities in the form of peoples, languages, dogmas, arts, states, sciences and, thus, again returns to the protospiritual element. If the purpose is reached and the idea along with all the completeness of internal possibilities is completed and realized outside, culture suddenly stiffens and die out, its blood coagulates, strengths are overtaxed – it become a civilization. In the materialistic comprehension, one believes that the laws of causal nature govern and the world history is filled by ideals of usefulness like enlightenment, humanity, peace over the world, which are denoted as aims of the history attainable with the help of progress. History is an eternal establishment and, hence, an eternal future; the nature is the appeared and. hence, the eternal past.
Stage – separate moment, interval of time in development of some movement, process, etc.[129]
Sztompka Piotr – contemporary Polish sociologist. He systematized main conceptions of development, which are briefly presented in his book «Sociology of social changes. – Moscow, 1996». There, he gave the principal categories such as progress, social time, historical tradition and the most influental conceptions of historical development: classical evolutionism – idealistic conception of evolution of O. Comte; naturalistic conception of evolution of H. Spencer and materialistic conception of evolution of L. Morgan; sociological conception of evolution of E. Durkheim; co-evolutionism in the cultural anthropology and sociology. There are presented the theories of modernization and historical cycles as specific conceptions of development along with the criticism of conceptions of development, in particular, a disproof of «historicism» of K. Popper.
P. Szompka presents the own conception of historical development in the context of ideas as a historical force, activity of prominent persons as agents of changes, social movements as factors of social changes and revolutions as the peak of social changes. With the conception of A. Toffler, he grounds the refusal from the idea of progress with infinite number of the stages of growth, which was the basis for almost all theories of development in sociology in the XIX–XX centuries. Infinite industrial growth cannot be an actual purpose of the mankind. If to describe the historical development in terms of continuous wave motion, then the first and second waves are agrarian and industrial epochs, and the third is an attempt to create a new civilization with nonindustrial values based on the organic coalescence of nature and technique, which corresponds to direct needs of a single person.
The idea of progress as a purpose of development of the society is connected with development of the human psychics as a regular change of psychical processes in time, which is expressed in their quantitative, qualitative, and structural transformations. The development of psychics is characterized the irreversible character of changes, orientation (i.e., ability to accumulation of changes, «building on» of new changes over previous ones) and their regular character. The development of psychics is realized in the form of phylogenesis (establishment of the structures of psychics in the course of biological evolution of a species or the sociocultural history of the mankind on the whole and its separate ethnic, social, and cultural groups) and in the form of ontogenesis (formation of psychical structures during the life of a single organism).
To modernize – to change something in accordance with contemporary requirements and tastes, to renew[130].
Toynbee A. J. (1889-1975) – English historian and sociologist. He advanced the conception of civilizational development, which has two degrees of continuity. One should distinguish continuity between sequential periods and phases in the history of the society and that as a connection of the very societies in time. Chapters of history of any single society remind sequential stages of the human experience. For example, the connection between one society and the other reminds relations between the parents and child. Civilizations develop due to a gust which leads them from a call through the reply to a further call: from differentiation through integration to a new differentiation. This process has no spatial coordinates because progress named growth presents a cumulative translational movement as mastering the external world and as the internal self-determination and self-organization. Growing civilizations differ from primitive societies by translational movement at the expense of the creative minority. Toynbee denied Spengler’s idea on that the development of a civilization can be compared with the development of an organism passing the phases of childhood, youth, maturity, and senility. To dogmatically assert that some term of existence is predestined to every society is the same that to demand that every play consist of the same amount of acts. The growth of a society is interrupted by a fracture as a consequence of the internal burst which implies the loss of the property of self-determination by the society. The governing minority creates a universal state, internal proletariat – ecumenical church, and external proletariat – groups of armed barbarians. In the history of decline of any civilization, one can find a rhythm of decay. The formation of an universal state is a symptom of social decay, and a next fracture will stimulate a final decay.
Transformation – mutually stimulating changes of the models of social action, on the one hand, and functioning the social institutions related to a intentional purposeful effect of nominal establishments (formal norms, procedures, or rules), on the other hand.
Vector of social development. Vector is the segment of a straight line of definite length and direction, which represents some magnitude characterizing not only by a numerical value but also by a direction (e.g., force, speed, etc.)[131]. In the context of the conception under study, it defines a direction of the social-historical development at nodal and cuspidal points. A nodal point is a synonym of the notion of attractor – limiting state such that, having reached it, the system cannot return to none of its previous states. A cuspidal point – synonym of the notion of bifurcation – corresponds to a branching of some old quality into a finite set of quite definite potentially new qualities. A vector can be conditionally «positive» directed to the side of progress or «negative», which characterizes a «regressive» development. The definition of the vector of social-historical development is one of the methodological tools used in creation of a working hypothesis for development of epochal cycles[132].
Vygotsky Leonid Semenovich (1896-1934) – soviet psychologist. He advanced a doctrine about development of psychic functions in the process of the mastering, mediated by intercourse, of cultural values by an individual. Cultural signs (first of all, signs of language) serve a kind of tools. By operating them, the subject can affect others and forms the own internal world, whose basic units are meanings (generalizations, cognitive components of consciousness) and senses (affective-motivational components). Psychic functions given by nature («natural») are transformed into functions of the highest level of development («cultural»). By originating in direct contacts of a child with adults, the highest functions then root themselves in his/her consciousness. On the basis of this idea, there appears a representation about «the zone of nearest development» concerning the difference in the level of difficulty of problems solved by a child without assistance (actual level of development) and that under guidance of adults. Only that education is efficient which «runs ahead» the development[133].
Instead of conclusion
The applied meaning of the presented conception is defined by the possibility of implementation of a social-historical prognosis. The problem of scientifically grounded prognostication, on the one hand, is very complex methodologically and, on the other hand, is also important both in political and social-economic contexts. A. Toynbee said: «The impossibility to define a final purpose of development implies the impossibility to exactly define a character of the very development»[134]. As a methodological foundation of short-, middle-, and long-term prognoses, one can take the idea of formation of a universal epochal cycle. The use of this conception for futurological studies of the social-historical development at the global, regional, and national levels has certain peculiarities. However, first of all, we consider general regularities following from the proposed conception. It should be recognized that the largest methodological problem is created by a peculiar «migration» of the size of a subject under study. For example, assume that the influence of the subject «we» attains a maximum in the transient (co-evolutionary) phase of the epochal cycle as result of norms of «collectivistic moral» dominated in the previous involutionary period. Then, in the revolutionary phase of the cycle, the subject individualizes and the cohort of « revolutionaries» becomes so mass that it exceeds the demand of the society for «shakers» of bases.
In the involutionary period, the economy develops, as a rule, extensively at the expense of attraction of new irreplaceable resources. The evolutionary period of the cycle is defined by the tendency of intensive liberal development of the economy. The type of demographic reproduction also undergoes certain changes. For the involutionary period, it is characteristic the model defined by rather high rates of birth and mortality, and the traditional family occupies dominant social positions. But in the evolutionary period of the cycle, inversely, we observe that the tendency to a decrease in the levels of birth and mortality becomes defining. As a consequence, the society encounters the effect of «ageing» of the population. Egalitarian intrafamilial relations become stronger.
Of course, the proposed hypothetical scheme-prognosis can be only an illustration rather than the definition of all possibilities of the method. For example, in the political sphere, we can only say about the main tendencies of the future. Beginning from the boundary of our era (the epoch of Christ), the leading contradiction of social development is that between «the forms of religious and scientific consciousness». In this case, for countries of the West-European cultural area (modern advance-guard of the world-wide historical process), the dialectic overcoming of the mentioned contradiction occurred in the chronological frameworks of the epoch of Enlightenment. As for a new dialectic contradiction («moral – right»), it was overcome in these countries during the epochs of Modern and Post-Modern. Completing this historical period, the countries of the West Europe and North America meet a new epoch, whose content will be the contradiction between political and ordinary consciousness. Somewhat «shifted» (from the viewpoint of the global analysis, by 100-150 years) becomes the situation for the countries of the Central and East Europe and Asia, for which the contents of the epoch of Post-Modern will be still actual in the first half of the XXI century.
The change of tendencies laid in the basis of the prognosis will require the introduction of proper corrections in time. On the whole, the depth and detailed elaboration of a prognosis depend on the degree of progress in social sciences.
We have already noted that, on the global level, one can identify the completion of the involutionary stage of the eighth (the fourth one from the Christmas) epochal cycle, which sums up, on the whole, the development of the industrial civilization and «leads» the world to active vital activity according to the tendencies of the evolutionary period of the epochal cycle. Moreover, if this situation is characteristic, to a full extent, of the countries of the Asian-Eurasian megaregion, then the main tendencies of development of countries belonging now to the advance-guard of the world-wide historical process consist in their approaching to conditions of the formation of a post-industrial (informational) civilization. By using mechanisms of the newest technologies, they stimulate the creation of a global economic system. At the same time, at the threshold of the XXI century, we have observed an increase in the global inequality between countries of the core and periphery of the new system[135].
Radical geopolitical changes in the 90s of the XX century transformed the system of international relations. After the disintegration of the USSR, the USA remained a single «universal» superstate and will conserve the dominant position approximately up to the middle of the XXI century. At the same time, by virtue of the development of new centers of force, a new anti-American block headed by Russia and China will be objectively formed. The international system, based on competition of many centers of force, stimulates numerous wars and generates nonstability.
The perspective of an open conflict between forces of globalization (West-European enclave) and agents of localization – presented by the European nationalism in the XX century and Islamic fundamentalism in the XXI century – can cast the world civilization into the condition of «new barbarism». This, probably, «corresponds» to the content of the transient (co-evolutionary) phase of the mankind and its final transition to the conclusive evolutionary period of the eighth (fourth) epochal cycle at the global level.
We expect different futurological fates for separate regions. For Eurasia, the tendency of completion of the formation of the «Great Europe from French Brest to Belorussian Brest becomes clear, though we do not exclude breakdowns in the process of European integration, in particular, those related to the problems of establishment of the common, external, and defensive policy of the European Community, to the fate of the common monetary unit «euro», and to the redistribution of the economic power in the frameworks of the trans-Atlantic community. Of great importance is the fate of Russia for the future of Eurasia.
The strengthening of federative unity stabilizes a situation in the region. Asia is overcoming the consequence of the financial crisis in 1997. At the same time, the competition between China, new nuclear states of Pakistan and India, and Japan, which makes its geopolitical possibilities to be stronger by the military-political alliance with the USA, will become sharper. Simultaneously, the absence of the Asian system of safety increases the nonstability generated by long-term conflicts such as the interstate India-Pakistan conflict or ethno-religious contradictions destroying Indonesia. Political contradictions can stop the tendency to the Asian economic integration, which will affect the plans of creation of the Asian-Pacific free trade zone till 2025.
Being in the gloom of poverty and local regional conflicts, Africa has hypothetical chances in the system of the global economy. Dangerous becomes the tendency of ethno-political conflicts breaking Somali and Zaire and destabilizing the situation in the region of Great Lakes. A further growth of the population can turn into a regional demographic catastrophe.
By developing integrational structures of the North-American free trade zone (NAFTA), North America gradually realizes the economic expansion into South America with the purpose to create the zone of free trade from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego. Democratization of the power in the countries of Latin America creates a common political field of both Americas. It is a further approaching of North and South America that will become a tendency of the next stage of the regional epochal cycle.
We note that the tendencies of social-historical development at the global and regional levels properly affect the national level of development. Moreover, the lower the hierarchical level of an «element» of the unit social system of the mankind, the stronger becomes the desynchronization of development, defined by own peculiarities.
After a withdrawal from the transformational crisis (2000-2012), Ukraine is fated, on the whole, to repeat the historical experience of West European countries and countries of North America of the post-war period but with own sociocultural peculiarities. It is expected that Ukraine will «arrive at» the revolutionary phase of the new epochal cycle in the second half of the XXI century.
From the time of disintegration of the USSR, Russia as well as Ukraine is in the stage of the transformational crisis (co-evolutionary phase of the epochal cycle). In this case, the probability of conservation of the historical «inertia» to the unification of Russia, Ukraine, and Belorussia by type of the European Union remains high. The conservation of uncertainty concerning the reformation of the federal structure (the fate of Russia-Belorussia union, definition of the status of Chechnya and other regions) of Russia stimulates the regional stress breaking the orthodox-moslem consensus.
Contrary to Ukraine and Russia, Belorussia is, in essence, in the revolutionary phase opening a new epochal cycle of development. In the behavior of the contemporary administration of Belorussia, we see rather expressive «revolutionary» features. In our opinion, one can say that processes and phases of development, which are opposite in orientation, occur in Belorussia, on the one hand, and in Russia and Ukraine, on the other hand. By using the symbolic language of N. Rerikh we may assume that Belorussia will become, probably, a peculiar «connective tissue» between three east-Slavonic peoples.
As for the leading states of the European Community, we note that France is completing the evolutionary stage of the cycle beginning from student disturbances in 1968. The identification of the national interests with imperatives dictated by the European Community remains problematic for this country. The main tendencies of the further social-historical development of France will be defined by the elections of President and Parliament in 2002. With the accession to power of the red-green coalition and after the national unification, stimulating the process of Integration of Europe, Germany approaches, in fact, to the revolutionary phase of a new epochal cycle. The first symptoms are a possible restructurization of the political system of the country which is related to the scandal concerning the financing of parties. We clearly observe the tendency of gradual disappearance of traditional political parties of the industrial epoch and the objective formation of parties of a «new type» as a consequence of new post-industrial values of the time of «Internet». In Great Britain, the victory of the Labour Party in elections in 1997 marked the beginning of the final phase of the evolutionary stage of a new epochal cycle. This phase of development will be brought nearer by growing tendencies to the transfer of powers from the center to places (restoration of assemblies in Scotland, Welsh, and North Ireland). In this case, of importance is the geographical and economic closeness to Europe (launch of the tunnel under the Channel, intention to carry out the referendum on joining the European Monetary Union, etc.). Italy is also on the threshold of the revolutionary stage of development. One may expect the sharpening of contradictions between the rich North and poor South, which finds itself at the center of ways of illegal migration to Europe. The threat comes from the geographical proximity of Italy to conflict zones in Balkan Peninsula, Near-East, and North Africa. Vatican finds itself in front of the choice between the weakening of positions of the Catholic Church and attempts to join all existing orthodox confessions under the roof of the universal church, which will be one of the signs of approaching «the end of times» according to the system of esoteric knowledge.
Being characterized by the Confucian tradition and peculiarities of longer epochal cycles on the boundary of the XXI century, China is «flowing» in transformational processes (1978-?) of the co-evolutionary transient period and, without any doubt, will become one of the world «centers of force» (by Brzezinski). With the appearance of the Celestial Empire on these positions, there appears a possibility to solve the problem of Taiwan on new principles of the unification of countries with coinciding vectors of social development.
India along with China (with some delay) goes on the way of the co-evolutionary stage of development of the epochal cycle. This phase of development comprises the search for an agreement between moslems and hinduists with the purpose to conserve the unity of the country. The solution of this problem allows India following China to become one of the regional leaders, pretending to the influence both in South Asia and in the whole world, in the subsequent evolutionary period.
The situation in Japan approaches to the co-evolutionary stage of the epochal cycle by actualizing the synthesis of traditional and post-modernist values. It is seen that its content will be a transformation of the society, which is still industrial in its essence though comparatively more developed than in other industrial states. Possessing shorter cycles of development as compared with China and India, Japan is «doomed», respectively, on a more radical manifestation of transformational processes. As for the last, we note the high probability of nonpredictability of events and noncontrollability of the transient situation in many respects.
The USA are on the threshold of the revolutionary phase of a new epochal cycle. A mechanism of these historical changes can be «launched» in the nearest period of 2000-2002 (the period of maximum solar activity). It is obvious that, in the first quarter of the XXI century like in the time of the «Great Depression», the USA are in prospect to be the leader of a new epoch and to open a new experience of the policy, eventually having «finished» with the traditional practice of a party-class paradigm, for the whole world.
In fact, already in the midst of the second half of the XX century with the active participation of the USA, the preconditions for such a policy were developed, the UNO being a possible precursor of the new world government. These preconditions strengthen the current tendencies to globalization of the economic development of the world.
A probable economic decline in the period of a revolutionary crisis will be compensated to a great extent due to prosperity of the economy in the 90s of the XX century and the contemporary level of the world financial control from the side of the USA. In this case, whereas nothing threatens the leadership of the country in the technological sphere, the probability of a decrease of its political influence is rather high. Indeed, the nation has already no wish to pay by lives of its soldiers for victories in local wars. At the expense of a growth of the amount of Afro-Americans, Spanish-Americans (immigrants from countries of South America), and Asian-Americans, the ethnic structure of the population of the USA will radically change in the first half of the XXI century. The situation will promote a growth of racist extremism and failures in the operation of the ethnocultural «melting crucible». In this case, it is rather probable that the «two-party» political mechanism will be broken. This can be stimulated by a possible splitting in the financial oligarchy, whose fractions can be oriented either to the conservation of workplaces in the USA or to the export of capital, which is formalized in the external strategical policy of isolation or expansion. The basis of the arising situation in the country will be formed by the new global contradiction of social development, the contradiction between the political and ordinary consciousnesses.
The verification of the working hypothesis with empiric data will allow one to refine the foreseen tendencies.
Appendices
Appendix 1
THEME OF THE PUBLIC LECTURE
PRESENTED BY DOCTOR OF SOCIOLOGICAL SCIENCES E. A. AFONIN
AT V. I. VERNADSKY NATIONAL LIBRARY
ON OCTOBER 22, 1998
THEME OF THE LECTURE: «SOCIAL RELATIVISM OR
SOCIOLOGY OF THE TRANSIENT TIME OF SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT»
1. CYCLICITY OF NATURE AND NATURAL PROCESSES
1.1. Cycles «cosmic», «biological», «social» (by the terminology
of P. Sorokin).
1.2. Cycles of development of a personality in ontogenesis (by
the generalization of D. Feldshtein)
1.3. Experimental confirmation of the hypothesis of
evolutionary changes of «sociopsychotype» (on materials of
the complex of sociological and social-psychological
studies performed at the system of bodies of the State
Safety of the USSR in the second half of the 80s and during
elections in 1994 and 1998 in Ukraine).
1.4. Epochal social-historical cycle (author’s conception).
2. PROBLEM OF MACRO (INTEGRAL) INDICES IN SOCIOLOGY
2.1. Principle of L. Pasteur – P. Curie.
2.2. Societal processes, states, features. Societal indices
(by O. Donchenko).
2.3. Statistical effects of «demographical transition».
2.4. Methods of mathematical statistics and their use in social
studies during the transient time of social development.
3. SPECIFIC SOCIOLOGICAL (MONITORING) STUDIES IN UKRAINE: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS (UKRAINE, RUSSIA, AND BELORUSSIA)
4. FACTOR OF SOLAR ACTIVITY AND ITS INFLUENCE ON SOCIAL-HISTORICAL PROCESSES. IS A SOCIAL BURST PROBABLE
IN UKRAINE ?
5. APPLIED ASPECTS OF THE NEW APPROACH.
Appendix 2
TEXT OF THE INFORMATION EXTENDED DURING THE WORK
OF THE 65TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE OF THE INTERNATIONAL
FEDERATION OF LIBRARIAN ASSOCIATIONS
(IFLA 99, BANGKOK, THAILAND)
AND THE ANNUAL CONFERENCE OF
CORRESPONDENTS OF THE EUROPEAN CENTER OF PARLIAMENT
STUDIES AND DOCUMENTATION
(ECPRD-CORRESPONDENTS
CONFERENCE, BERN, SWITZERLAND)
Dear colleagues !
The group of scientists, representatives of nongovernmental nonprofit organizations such as the Ukrainian Social Innovation Society, Atlantic Council of Ukraine, and Librarian Department of the Ukrainian Parliament, has begun the initiative study in the context of the sociology of history, which covers the period of two millennia (AD).
PROJECT IS CONDITIONED BY:
* globalization of transformational processes;
* objectivity, irreversibility and cardinal character of current
social changes;
* noncorrespondence of the existing ideas to new conditions
of social development;
* growth of danders which acquire extreme forms during the
the transient period;
* decrease in efficiency of the activity of global, regional,
political, economic, and other international and national
institutions.
Now once again, we are faced with the urgent need to basically reinterpret the historical development, to introduce corrections to the existing ideas as for a periodization of the history, and to create efficient prognostic models of social development. Motives to the realization of these urgent needs become, in fact, the basis of our research initiative.
MAIN AIM of the basic stage of the research project is the development of an applied model of «universal epochal cycle» as a means of social analysis and prognostication. A further work on the project will be open and interdisciplinary due to the wide participation of experts in the fields of political science, economy, right, psychology, ethnology, studies of religion. language, arts, etc.
RESEARCH PLANS will be carried out on a wide historical material, which represents 50 countries of the world community chosen by geographical, cultural-religious, and demographical signs. The sampling includes 20 countries of Europe, 15 of Asia, 3 of North America, 4 of Latin America, and Australia.
The research plan foresees the use of modern methodologies, methods, and technologies. In particular, the use of Internet will be aimed at:
* telecommunication of participants;
* publication of running results of the study;
* diagnostics, etc.
GUARANTEES OF SUCCESSFULNESS OF THE PROJECT are ensured by the available methodological and methodical tools mastered by our group, which allow one to obtain a number of weighty applied results including those concerning the optimization of national budget social expenditures, international cooperation, and collective safety.
***
Dear colleagues, I hope for the constructive dialog and support of our research project.
Sincerely,
Doctor of Sociol. Sci. Eduard Afonin
Supervisor of the project,
Head of Information and Library Department
of Secretariat of Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine,
President of Ukrainian Social Innovation Society
Address:
Eduard Afonin
Head of Information and Library Department
of Secretariat of Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine,
3, Sadova Str., Kyiv-8, 01008
tel/fax: (380 44) 226-2145
e-mail: afonin@rada.gov.ua
Appendix 3
RECORD OF THE MEETING OF THE WORKING GROUP OF THE
PROJECT, DEVOTED TO DISCUSSION OF THE BASIC HISTORICAL-
SOCIOLOGICAL CONCEPTION «SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT AD».
RECORD NO. 1
OF THE MEETING OF THE WORKING GROUP OF THE PROJECT
«SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT AD»
KYIV SEPTEMBER 10, 1999
THERE WERE PRESENT: Afonin E. A., Dr. Soc. Sci., President of the Ukrainian Social Innovation Society (USIS); Bandurka O. M., Dr. Jur. Sci., Rector of the University of Internal Affairs (Kharkiv); Kokoshyns’kyi O. A., Vice-President of the Atlantic Council of Ukraine; Malyshko M. I., Cand. Jur. Sci., Prof., Head of Chair of the Kyiv National University of Culture and Arts; Martynov A.Yu., Cand. Hist. Sci., researcher of the Institute of History of the NAS of Ukraine; Ryabiko V. V., Ass. Prof., Vice-President of USIS; Salamatov V. O., Cand. Psych. Sci., Head of Depart. of the Academy of State Management at President of Ukraine; Chechnev B. O., Cand. Phil. Sci., Resp. Secr. of the All-Ukrainian weekly magazine «Zakon i Biznes» (Law and Business).
AGENDA
1. Introductory word about the idea and organization of the interdisciplinary project (IP) «Social development AD»
Speaker – Afonin E. A.
2. On the conception of IP «Social development AD as an object of the sociology of history (sociology of social changes)».
Speaker – Martynov A. Yu.
HEARD:
1. Introductory word «About the idea and organization of IP «Social development AD».
Afonin E. A. presented main positions of the proposed IP «Social development A.D.». In particular, he noted that the idea of IP was maturing during the last decade, which was marked by radical and mostly unpredictable changes such as, e.g.: «downfall of the Berlin wall», «disintegration of the USSR» and economic decline of countries-republics of the former USSR, economic jump of South-Asian «tigers», etc.
The first conceptual presentation of the project idea was given by the author in the final (applied) part of the scientific report «Social relativism or sociology of the transient time of social development» made at V. I. Vernadsky National Library of the NAS of Ukraine on October 22, 1998.
The main idea of the project is such that, on the basis of ideas on cyclicity of the social development, there appears a reliable instrumental possibility to reconstruct the objective logic of principal historical changes associated with such events as «revolutions», «transformatons», state overturns, various manifestations of the element of social protest, numerous civil conflicts, local and global wars, etc. The last fall in the so-called transient conditions of the social development and can fully serve as peculiar indicators of epochal changes.
The author believes that the study of a connection between the historical process or social-historical activity of the mankind and a level of Sun’s activity, which was performed by A. Chizhevsky at the beginning of the XX century, is methodologically necessary for the analysis of epochal changes. Having established the direct connection, the researcher found no exception beginning from 500 BC. We only remark that, according to Chizhevsky, not every «maximum» of the solar activity induces a peculiar «maximum» of the historical activity. To realize the last, it is necessary the presence of appropriate internal (in author’s opinion, social-economic, political, and, we add, spiritual) preconditions.
Of important are ideas on the cyclic character of psychical development of a man since it is one of the main elements of the social structure. In particular, it is worth to note the theoretical-practical generalizations by D. Feldshein. Basing on the occupational approach (S. Rubinshtein, O. Leont’ev, A. Brushlinsky, et al.) and age periodization of psychical development of a personality in ontogenesis (D. El’konin) which were develop in the framework of psychology, This researcher proved the cyclic (periodic) character of changes in the psychical structure of a personality and, respectively, in the psychological structure of activity, where its communicative and objective plans are alternatively actualized.
I am sure that, by generalizing this idea on the theoretical basis mentioned above in the spirit of the anthroposociogenetic approach, it is quite rightfully to consider radical social changes in the context of societal processes, conditions, and features, which are realized within the limits of a unit epochal historical cycle. Indeed, the social history is composed from sequentially realized epochal historical cycles.
The above-presented and other aspects of the proposed basic conception are published in the article «Development of Ukraine: macrosocial approach [in Ukrainian] // Viche. – 1996. – No. 1. – P. 39-49. A. Yu. Martynov will report about all this in more details.
As for the general scheme of organization of the IP, we start from the necessity to distinguish two aspects of the work. One of them is related to development of the basic sociological conception, which is elaborated now by A. Yu. Martynov. B. O. Chechnev and I will also take part in development of the methodological foundation of the project. We also hope for a running participation of each of the members of the working group as experts in elaboration of the methodological basis of the IP. To the end to ensure the principle of openness of the IP, the authors plan a special stage of approbation and expansion of the information about the basic conception by means of its publication as a separate edition (in Ukrainian, Russian, and English), as articles in the domestic sociological journal of the Institute of Sociology of the NAS of Ukraine and others, in Russian and Polish social-political journals, and on the special site (devoted to the project) in the Internet. We hope that such measures allow us to optimize the content of the basic conception and stimulate wide interdisciplinary (in the field of social and humanitarian sciences) practical investigations.
Openness of the project and a «free» access to the work on its tasks do not remove the possibility to deepen into special applied studies. Thus, we foresee the organizational promotion to various theoretical and practical works in the field of disciplines of the social and humanitarian trends. In particular, we expect that every member of the working group on development of the IP will prepare some applied variant of the basic conception and will carry out the proper investigation. The last can be performed by the very member of the working group directly and with attraction of other participants, persons working for doctor’s degree and post-graduates, students and lecturers, representatives of policy, economy, science, culture, and education. In the course of the basic conception of cyclic social development, as an object of special studies, one can take the development of separate social (including state ones) institutions. It is quite possible to study the cycles of development of policy, economy, science (natural or humanitarian one), education, literature, arts, sport, etc. The working group of the project takes in hands the obligation to coordinate such investigations and to promote a wide clarification of the results obtained within the frameworks of the project.
The working group is planning:
1. To carry out a wide discussion of the basic conception of the IP «Social development AD as an object of the sociology of history (sociology of social changes)».
2. To solve the problem of organization of the special web-site in the Internet, concerning the IP.
3. To prepare for publication the basic conception of the IP «Social development A.D. as an object of the sociology of history (sociology of social changes)».
QUESTIONS:
Salamatov V. – How can we take into account the contents of specific notions ? For example, in the cross cultural studies by the west-European criteria, Ukraine is a quite collectivist country. But here (in Ukraine), all say about the individualism of Ukraine’s society.
Afonin E. – By societal (macrosocial or system-wide) criteria and ideas of cyclicity which consist the base of our project, Ukraine of the soviet period was characterized by such a societal quality as «executiveness, which define its behavior on the whole as «collectivist», indeed. The corresponding social normative reveals itself at all aspects of life of the population of the soviet Ukraine, stimulating the people to sacrifice. «First, think about the Motherland and then about yourselves» – we repeated by choosing a profession or an example to imitate and by estimating himself or surrounding persons. By basing on the results of the comparative analysis, one can even state that collectivism was manifested in Ukraine even more than in Russia. A good proof of this assertion is related to the widespread opinion known at that time that Ukraine was the first among the other republics of the USSR (first of all, in comparison with Russia and Belorussia) in developing the all-people initiative upon the fulfillment of recurrent decisions of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of the USSR.
Now, the post-totalitarian Ukraine is attracted to the other social dimensionality, to the other social quality. The question is the «intentionality», whose manifestations are perceived by the ordinary consciousness, in fact, as individualism. These social normative are adequate to the formula specularly opposite to that presented above: «State is strong with strong citizens». New societal qualities are established by means of nonlinear social changes, creating the so-called transient condition of th society which is characterized, for a certain time, by a fluctuation – oscillations between two normative states defined above.
Thus, it is quite justified that a west observer finds Ukraine as a «collectivist» country, and a domestic one as an «individualist» one.
Salamatov V. – I say about a different thing. The semantics of the same notions changes from one culture to another, therefore, we may meet a double and even triple context in the context of a study. Hence, it would be methodologically expedient to start from traditions of the Moscow school of logic and to consider specific notions only in the context. As known, we cannot establish societal characteristics of, e.g., the Trypillya culture.
Afonin E. – First, the approach accepted in this study allows, in principle, one to retrospectively define societal characteristics of any culture including the Trypillya one. I do not say that it is a simple task. To make this, we need a representative objective evidence, so to say, «traces» of the proper culture.
Second, the definition of societal characteristics of a modern social object is based, in our approach, on the universal, integral standardized, symbolic model, in which the mechanism of autocorrection is inherent, i.e., the ability to correct the used symbolic model with regard for natural geographical peculiarities of a specific cultural environment irrespectively of the desire of an experimenter. In other words, the apparatus complex, which is developed by us and will be utilized in the study, immanently involves the requirements of the Moscow school of logic.
In our opinion, the more serious difficulty for our investigation is its financial neediness. In fact, already at the first stage of study, we must perform the very important specific measurements of societal characteristics on the representative sampling (about 50 countries), defined in the project. These data and appropriate chronological tables allow us to reconstruct historical cycles of the countries of the sampling, region, and civilization on the whole. A total cost of derivation of the basic empiric material, by the estimates of the «Gellap-International» company, equals about 0.4 mln USD. But we hope to leave this situation with the help of an alternative procedure of measurement by using the Internet.
Salamatov V. – The comparative analysis should be performed with minimum of ideological (political) loads.
Afonin E. – The object of our analysis leaves the frameworks of political analysis since the societal level is an integral level of analysis of a holistic object, in which the political aspect emerges as a component.
HEARD:
Ïîõîæèå ðàáîòû
... , ïðèíîñÿùèå äîõîäû ñòðàíå è íîâûå ðàáî÷èå ìåñòà, â òîì ÷èñëå è â ñìåæíûõ ñ òóðèçìîì îòðàñëÿõ ýêîíîìèêè. Ðîëü ìåæäóíàðîäíîãî òóðèçìà â ýêîíîìèêå Êûðãûçñêîé Ðåñïóáëèêè îïðåäåëÿåòñÿ ñòåïåíüþ äîñòèæåíèÿ ýòîé öåëè. Ðåàëèçàöèÿ Êîíöåïöèè ðàçâèòèÿ òóðèçìà â Êûðãûçñêîé Ðåñïóáëèêå äî 2010 ãîäà, ðàçðàáîòàííàÿ â ðàìêàõ Êîìïëåêñíîé îñíîâû ðàçâèòèÿ Êûðãûçñêîé Ðåñïóáëèêè (ÊÎÐ) è Íàöèîíàëüíîé ñòðàòåãèè ...
... ãîâîðèòü ñåãîäíÿ î ÊÑÎ? Ìíå êàæåòñÿ, âñåãäà àêòóàëüíî ãîâîðèòü î êîðïîðàòèâíîé ñîöèàëüíîé îòâåòñòâåííîñòè, ïîòîìó ÷òî ýòî íåîòúåìëåìàÿ ÷àñòü êîðïîðàöèè. Êàê è êîðïîðàòèâíàÿ êóëüòóðà, ñîöèàëüíàÿ îòâåòñòâåííîñòüþ íåîáõîäèìà â ñîâðåìåííûõ óñëîâèÿõ äëÿ íîðìàëüíîé æèçíåäåÿòåëüíîñòè êîìïàíèè. Åëåíà Âèòàëüåâíà, åñëè â öåëîì ãîâîðèòü î ðîññèéñêèõ êîìïàíèÿõ, íà êàêîì óðîâíå ðàçâèòèÿ, ïî Âàøåìó ìíåíèþ, ...
... íîâóþ ïåñíþ?) Yes, I will (äà, ïðèäó, äà, áóäó, äà ñäåëàþ). Íå òî ÷òîáû will ñäàâàë ïîçèöèè. Ïðîñòî come è gonna îòâîåâûâàþò ïîçèöèè ïîä ëó÷àìè àíãëîÿçû÷íîãî ñîëíöà. Êîíå÷íî, îá àêòèâíîì ðàçãîâîðíîì American English — ÿçûêå îáùàã, êóõîíü, "Ìàêäîíàëüäñîâ", ñïîðòèâíûõ ïëîùàäîê, êîëëåäæåé è êàçàðì — ìîæíî ãîâîðèòü åùå è åùå, íî, êàê âûðàæàþòñÿ àìåðèêàíöû: next time — êàê-íèáóäü â ñëåäóþùèé ðàç. ...
... ò.ê. àíãëèéñêîìó ÿçûêó íå ñâîéñòâåííà ïàëàòàëèçàöèÿ ñîãëàñíûõ (rouble, steppe). Íàáëþäàåòñÿ ïåðåíîñ óäàðåíèÿ, îòïàäàíèå êîíå÷íîãî ãëàñíîãî è ò.ï. Åñëè ïðîñëåäèòü çâóêîâûå èçìåíåíèÿ, êîòîðûì ïîäâåðãàþòñÿ ðóññêèå çàèìñòâîâàíèÿ â àíãëèéñêîì ÿçûêå. òî ìû óâèäèì, ÷òî îíè äåéñòâèòåëüíî ïðåîáðàçóþòñÿ â ñâîåì çâóêîâîì îáëèêå ïî âíóòðåííèì çàêîíàì àíãëèéñêîãî ÿçûêà. Îäíàêî ýòî êàñàåòñÿ ãëàâíûì îáðàçîì òåõ ...
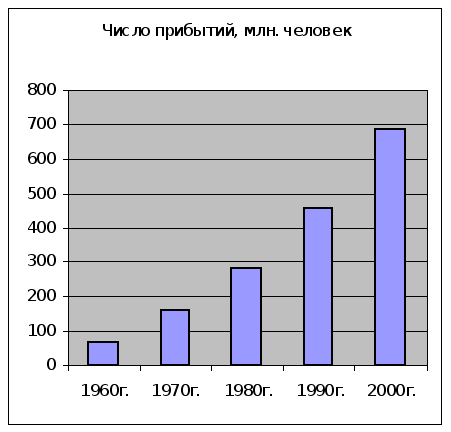
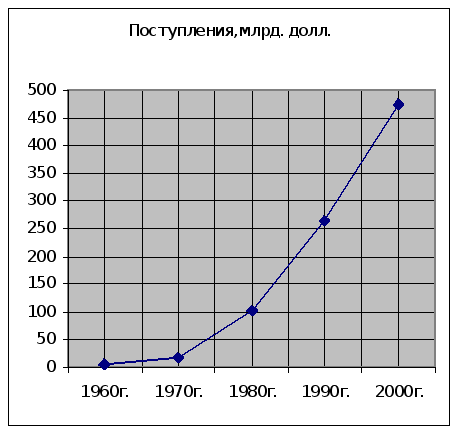
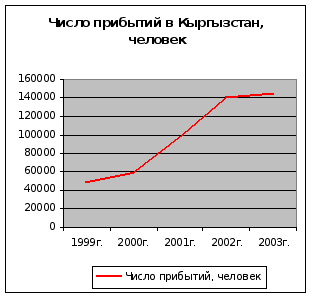
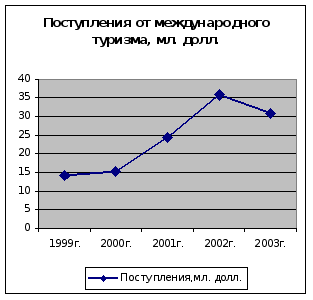

0 êîììåíòàðèåâ