Навигация
Australia
7.4. Australia
Australia has a specific history. The large territory, inhabited on the boundary of Anno Domini by Aborigines practically did not have any state formations till the discovery of the continent by the Europeans (1606 – the Dutchman Willem Jantz). In fact, the revolutionary stage of the first Australian epochal cycle begins in the middle of the 18th century (1768-1779 – James Cook). The involutionary stage is identified with the war of the European immigrants against the Aborigines in the 19th – the first part of the 20th century. The co-evolutionary stage began in the latter half of the 20th century with the creation of a civilization that has an European identity.
7.5. Antarctica
Antarctica is the sixth continent of the Earth with the area of 50 million square kilometers, being twice more than the area of Australia. It is discovered in 1820 by Bellingshausen and Lazarev, the great Russian navigators. Prior to this moment, the history of the continent remained under the ice cover. The international-legal status of Antarctica is defined by the corresponding treaty of the 1st of December, 1959, which foresees the exploitation of the territory of Antarctica for peaceful purposes only, prohibits declaring the territorial claims in Antarctica, and ensures the freedom of scientific researches under the condition that natural resources be conserved and preserved[59].
CHAPTER 8
National-state (micro) level of analysis
of the history
Having viewed the main points of the scheme of development of epochal cycles at the global (macro) and regional (medi) levels, we focus our attention at the research of historical cycles at the national-state (micro) level, which corresponds to the scale of our research in general.
The criteria for construction of a similar sampling may be the following: various states should be represented, first, countries of all continents, second, countries belonging to various world religions, and, third, countries with the population of at least 8 million persons as of the end of the 1990’s.
According to the criteria given above, the required sampling may be the following:
| ## | Country | Population (millions) | Religion | The beginning of development |
| EUROPE | ||||
| 1. | Austria | 8.039 | Catholicism | ХIII century |
| 2. | Belgium | 10.190 | Catholicism | 1830 AD |
| 3. | Bulgaria | 8.628 | Orthodox | 680 AD |
| 4. | Vatican | 1 thousand | Center | 750 AD |
| 5. | Great Britain | 58.550 | Anglicanism | VI century |
| 6. | Greece | 10.560 | Orthodox | VIII century BC |
| 7. | Spain | 39.220 | Catholicism | VII century AD |
| 8. | Italy | 57.520 | Catholicism | VIII century BC |
| 9. | Netherlands | 15.615 | Protestantism | ХIV century |
Continued
| ## | Country | Population (millions) | Religion | The beginning of development |
| 10. | Germany | 83.870 | Catholicism, Protestantism. | 843 AD |
| 11. | Poland | 38.915 | Catholicism | 960 AD |
| 12. | Portugal | 10.800 | Catholicism | 1143 AD |
| 13. | Russia | 150.50 | Orthodox | 1147 AD |
| 14. | Belorussia | 10.204 | Orthodox, Uniate. | ХII century |
| 15. | Hungary | 9.963 | Catholicism | 1000 AD |
| 16. | Romania | 22.260 | Orthodox | 1859 |
| 17. | Ukraine | 50.500 | Orthodox | 988 AD |
| 18. | France | 58.160 | Catholicism | 843 AD |
| 19. | Czech Republic | 10.320 | Catholicism, Protestantism | Х century |
| 20. | Sweden | 8.928 | Protestantism | IХ century |
| 21. | Yugoslavia (Serbia) | 10.635 | Orthodox, Catholicism, Islam | IХ century |
| ASIA | ||||
| 22. | Afghanistan | 23.230 | Islam | ХVIII century |
| 23. | Bangladesh | 124.17 | Islam | 1947 |
| 24. | Vietnam | 74.570 | Buddhism | VI century AD |
| 25. | Israel | 5.575 | Judaism | ХI century BC |
| 26. | India | 961.69 | Buddhism, Islam, Hinduism | IV century BC |
| 27. | Indonesia | 208.06 | Islam, Catholicism. | VI century AD |
Continued
| ## | Country | Population (millions) | Religion | The beginning of development |
| 28. | Iraq | 21.810 | Islam | VI century BC |
| 29. | Iran | 66.820 | Islam | VI century BC |
| 30. | China | 1232.310 | Confucianism, Taoism, Buddhism, Islam, Catholicism. | ХIV century BC |
| 31. | Korea | 45.710 + 24.550 | Buddhism | VI century AD |
| 32. | Malaysia | 20.770 | Islam | ХIII century AD |
| 33. | Pakistan | 133.572 | Islam | ХII century AD |
| 34. | Saudi Arabia | 18.835 | Islam | VI century BC |
| 35. | Turkey | 63.050 | Islam | 1071 |
| 36. | Japan | 125.580 | Buddhism, Shintoism | VI century BC |
| AFRICA | ||||
| 37. | Algeria | 29.505 | Islam | 1711 |
| 38. | Ethiopia | 57.970 | Monophysite Christianity | V century AD |
| 39. | Ghana | 17.895 | Catholicism | III century AD |
| 40. | Kenya | 29.460 | Islam | ХIV century AD |
| 41. | Nigeria | 105.470 | Islam | ХIV century AD |
| 42. | Republic of South Africa | 42.120 | Catholicism, Islam | 1820 |
| AMERICA | ||||
| 43. | Canada | 28.975 | Catholicism | 1608 AD |
Continued
| ## | Country | Population (millions) | Religion | The beginning of development |
| 44. | Mexico | 96.630 | Catholicism | VI century AD |
| 45. | USA | 266.890 | Catholicism, Protestantism, Islam | 1607 AD |
| 46. | Argentina | 34.845 | Catholicism | ХVI century AD |
| 47. | Brazil | 163.640 | Catholicism | 1500 AD |
| 48. | Chile | 14.420 | Catholicism | Х century AD |
| 49. | Peru | 23.565 | Catholicism | VI century BC |
| AUSTRALIA | ||||
| 50. | Australia | 18.350 | Catholicism | ХVII century |
First of all, we would like to emphasize the existence of the most characteristic peculiarities of the microlevel of development of cycles. Firstly, ethnic differences are becoming more clear, secondly, the chronology is changing since various nations created their political organizations in different times, thirdly, the differences in the number of epochal cycles are defined more clear, which is the consequence, on the one hand, of the historical age of a nation, and, on the other hand, of the intensity of its history.
It is worth to note that the construction of schemes of the development of epochal cycles for all countries of the presented sampling is the subject of a special research. That is why, we only demonstrate the work of our conception by the example of 11 countries, included into the representative research sampling of 50 countries.
Now let us directly examine the scheme of epochal cycles of Vatican, Italy, Germany, Great Britain, France, Ukraine, Russia, Belorussia, China, India, Japan, and the USA, representing the historical advance-guard of Europe, Asia, and America in the sampling presented above.
Похожие работы
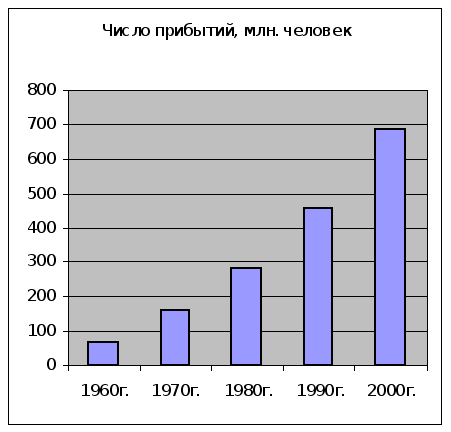
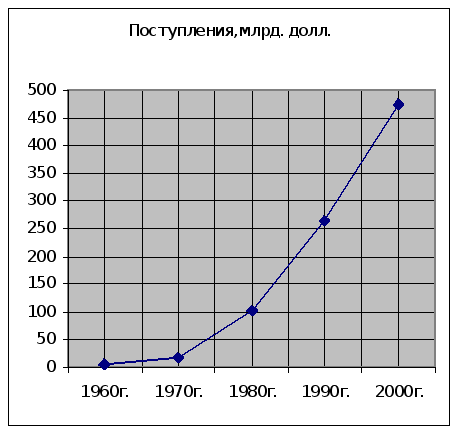
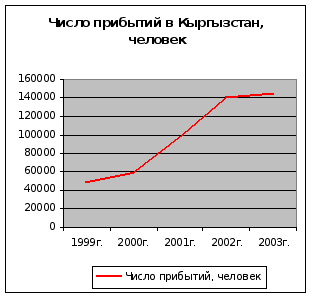
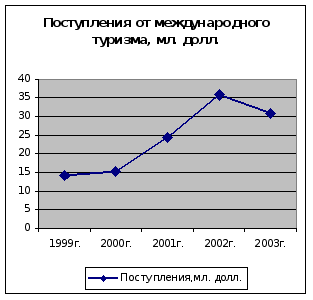
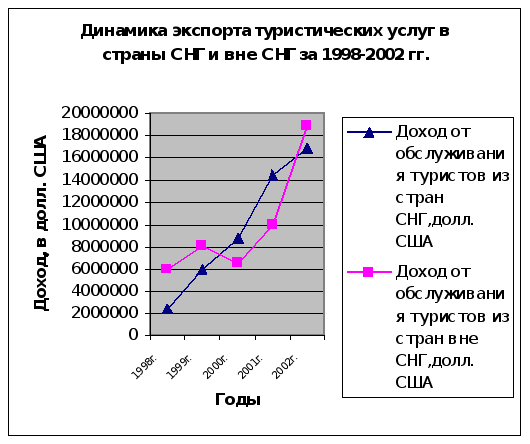
... , приносящие доходы стране и новые рабочие места, в том числе и в смежных с туризмом отраслях экономики. Роль международного туризма в экономике Кыргызской Республики определяется степенью достижения этой цели. Реализация Концепции развития туризма в Кыргызской Республике до 2010 года, разработанная в рамках Комплексной основы развития Кыргызской Республики (КОР) и Национальной стратегии ...
... говорить сегодня о КСО? Мне кажется, всегда актуально говорить о корпоративной социальной ответственности, потому что это неотъемлемая часть корпорации. Как и корпоративная культура, социальная ответственностью необходима в современных условиях для нормальной жизнедеятельности компании. Елена Витальевна, если в целом говорить о российских компаниях, на каком уровне развития, по Вашему мнению, ...
... новую песню?) Yes, I will (да, приду, да, буду, да сделаю). Не то чтобы will сдавал позиции. Просто come и gonna отвоевывают позиции под лучами англоязычного солнца. Конечно, об активном разговорном American English — языке общаг, кухонь, "Макдональдсов", спортивных площадок, колледжей и казарм — можно говорить еще и еще, но, как выражаются американцы: next time — как-нибудь в следующий раз. ...
... т.к. английскому языку не свойственна палатализация согласных (rouble, steppe). Наблюдается перенос ударения, отпадание конечного гласного и т.п. Если проследить звуковые изменения, которым подвергаются русские заимствования в английском языке. то мы увидим, что они действительно преобразуются в своем звуковом облике по внутренним законам английского языка. Однако это касается главным образом тех ...

0 комментариев